This probe type is first choice for central line placement.
What is the linear probe?
The antidote for benzodiazepine overdose.
What is Flumazenil?
The location of the endotracheal tube tip.
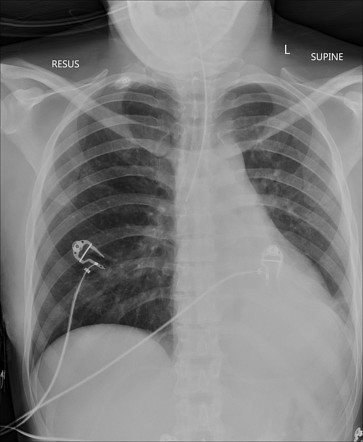
What is the right mainstem bronchus?
This Gram-positive organism is the most common cause of native valve endocarditis.
what is Staphylococcus aureus?
The Berlin definition of this syndrome classifies severity based on the PaO₂/FiO₂ ratio.
What is ARDS?
During arterial line placement, this test should be performed prior to cannulation to ensure adequate collateral circulation.
What is the Allens test?
Sodium bicarbonate is used as a treatment for overdose of this class of medications due to QRS widening.
What are tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs)?
The location of the OGT.
What is the esophagus?
According to current guidelines, this oral antibiotic is the first-line treatment for an initial episode of C. difficile infection.
What is fidoxomicin?
This pressure is measured during an inspiratory hold and reflects alveolar pressure.
What is plateau pressure?
This is the most common complication of lumbar puncture.
What is post-dural puncture headache?
This clinical tool helps guide treatment decisions in alcohol withdrawal by scoring symptoms such as tremor, agitation, nausea, and sweating.
What is the CIWA-Ar (Clinical Institute Withdrawal Assessment for Alcohol, revised)?
The KUB shows this pathology.
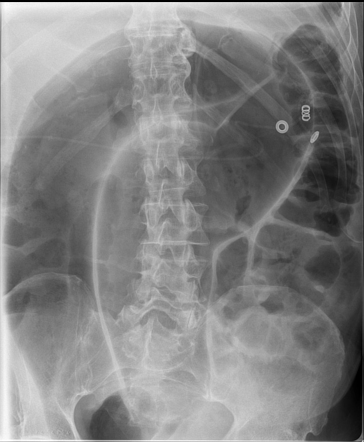
What is a volvulus?
The number of days that are recommended to treat pseudomonas pneumonia.
What is seven?
This ventilator mode delivers a set tidal volume with each breath, regardless of patient effort.
What is volume-controlled ventilation (VCV)?
When performing paracentesis, the most common site of needle insertion is in this quadrant.
What is the left lower quadrant?
This vitamin should always be administered before glucose in patients at risk for alcohol withdrawal.
What is thiamine?
Location of central line tip.
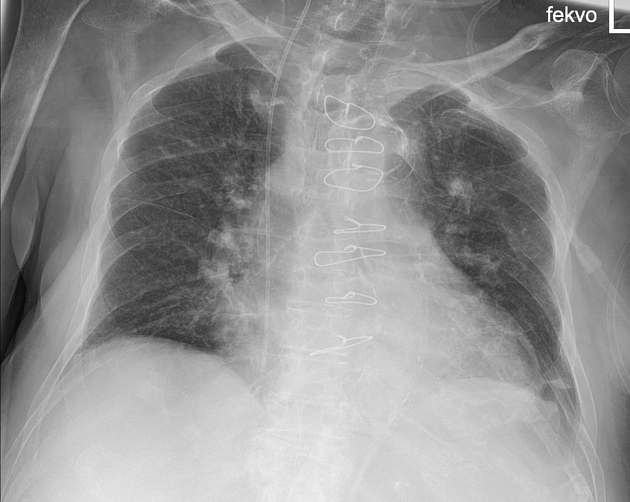
What is the right atrium?
Due to the risk of metastatic endophthalmitis, a dilated ophthalmology exam is recommended for all patients with this type of bloodstream infection.
What is candidemia?
The driving pressure is defined as plateau pressure minus this variable.
What is PEEP?
In thoracentesis, drainage should generally be limited to this volume at one time to reduce the risk of re-expansion pulmonary edema.
What is 1500 cc or 1.5 Liters?
This antidote is first-line therapy for methanol ingestion because it blocks alcohol dehydrogenase and prevents toxic metabolite formation.
What is fomepizole?
Type of hemorrhage.
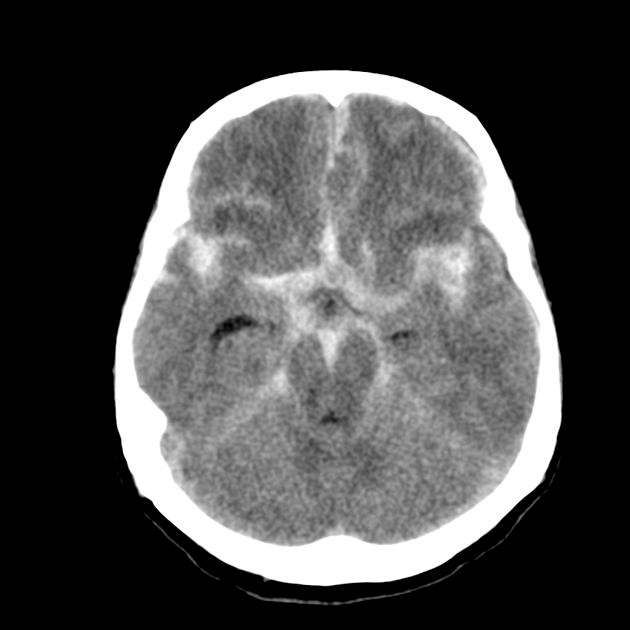
What is a subarachnoid hemorrhage?
This lipopeptide antibiotic is highly effective against MRSA and VRE, but cannot be used for pneumonia because it is inactivated by pulmonary surfactant.
What is Daptomycin?
According to best practice, ventilator liberation protocols should include both daily sedation interruption and this paired process.
What is daily spontaneous breathing trials?