The formula for this hemodynamic value is HR x SV?
What is Cardiac Output
This O2 delivery device should always have the reservoir inflated before applying.....and when in doubt, turn the O2 flow meter all the way up!! Don't hesitate, escalate!
What is a non-rebreather mask (10-15 LPM)
What 3 ions form the basis of cardiac physiology?
What are Ca+, Na+, and K+
When assessing your patient, a change is this is an early indicator that they may be having an increase in ICP?
What is a change in level of consciousness (LOC)
This is a legal requirement that protects the autonomy of patients, including the right to refuse treatment.
What is informed consent?
Which adrenergic receptor is found primarily on vascular smooth muscle and when activated, cause vasoconstriction?
What is alpha-1 adrenergic receptors.
 This is an example of what type of abnormal arterial waveform?
This is an example of what type of abnormal arterial waveform?
What is overdamped - will give you a false LOW blood pressure.
This non-invasive positive pressure delivery device is commonly used for individuals with obstructive sleep apnea?
What is a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) device.
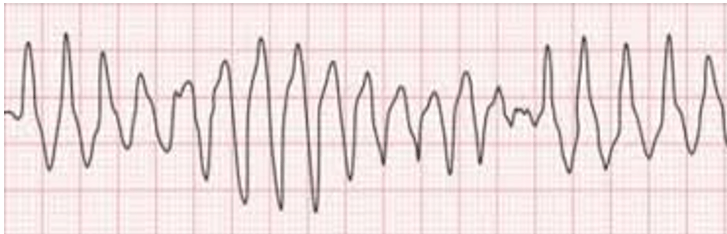 You observe this rhythm on your monitor, what rescue medication to you anticipate giving?
You observe this rhythm on your monitor, what rescue medication to you anticipate giving?
What is Magnesium (1-2G)
This brain drain is used to reduced ICP and remove excess fluid?
What is an external ventricular drain (EVD)
Performing this intervention before a bedside procedure, helps to reduce the risk of preventable errors?
What is a Time-out?
A patient experiencing complete heart block who is bradycardic and symptomatic would benefit from this category of medication that will help increase their HR and force of contraction.
What are inotropic medications (Dopamine, Epi, Dobutamine, Milrinone)
What is central venous pressure (CVP)
Interpret the following ABG:
pH 7.28
CO2 56
HCO3 23
PaO2 98
What is uncompensated Respiratory Acidosis w/o hypoxemia
Bonus! What is the name for similar leads looking at the same areas of the heart?
What is at least 2 leads - contiguous/neighboring leads (looking at the same area of the heart)
This hemodynamic finding is also one of three signs and symptoms of Cushing's Triad?
What is widening pulse pressure?
What is the name of this laryngoscope?

What is a MaC Blade?
This adrenergic receptor is found primarily in the heart and when activated, causes an increase in heartrate and force of contraction
What are beta-1 adrenergic receptors
The resistance or pressure that the heart has to overcome in order to pump blood out of the ventricles.
What is afterload or systemic vascular resistance (SVR)
A patient is wearing a NIPPV device with an IPAP of 12 and EPAP of 8, FiO2 of 50%, with a back up rate of 12. What device are they using?
What is a bilevel positive airway pressure (BiPAP) device.
In this AV heart block rhythm, the PR interval gradually get's longer until there is a complete drop of the QRS complex? Long, long, longer, drop......
What is Second Degree Type 1 AV/Heart Block - also called Mobitz type I or Wenckebach.
The Oculocephalic reflex is also commonly known as this?
What is "Doll's Eyes"?
What is scope of practice/role and responsibilities?
A common adverse reaction to this vasoactive medication if reflex bradycardia due to stimulation of the baroceptor reflex.
What is Phenylephrine (Neosynephrine)
When leveling an arterial line, it is important to level it with this anatomical reference point?
What is phlebostatic axis - 4th intercoastal space, midaxillary
Interpret the following ABG:
pH 7.55
CO2 48
HCO3 32
PaO2 81
What is metabolic alkalosis with partial compensation without hypoxemia (N/V, diuretics, NG suctioning, etc.)
You observe this rhythm on your patient's monitor. When assessing the patient, the patient is unresponsive but you can palpate a carotid pulse. What would you anticipate being your next intervention per ALS? 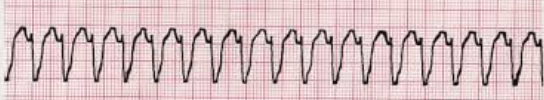
What is synchronized cardioversion @ 100 Joules!
When assessing the unconscious patient, you want to introduce stimuli in what order, increasing only as necessary?
What is auditory, tactile, painful – start with minimal stimulus, increasing as necessary!
This is a structured communication tool shown to enhance communication between members of the healthcare team.
What is SBAR?
Before starting this medication, it is important to make sure that the patient has not taken any phosphodiesterase inhibitors a.k.a erectile dysfunction medications within the past 24-48 hours.
What is Nitroglycerin (Trindil)
This condition occurs when there is an abnormal decrease in SBP and stroke volume greater than 10 mmHg during inhalation?
What is Pulsus Paradoxus
You are emergently intubating your patient - MD gives a verbal order for Etomidate 30 mg and Succinylcholine 200 mg. Which lab value do you want to know before giving Succinylcholine?
What is their recent serum potassium level - succinylcholine causes hyperkalemia.
You observe a nurse instructing a patient to bear down like they are having a bowel movement - they are most likely experiencing this ALS heart rhythm disorder?
What is Supraventricular tachycardia/SVT? Vagal maneuvers (bear down, blow through a syringe-Valsalva maneuver, cold stimulus)
When observing Lundberg waves, which one would be the most concerning? (A,B,C)
What are A waves - transient, periodic severe elevations in ICP (up to 50-100 mm) and often accompanied by clinical deterioration = BAD!
When administering medications through a central venous catheter, it is important to perform this action during the initial and final flush?
What is the push/pause or pulsatile technique? This creates turbulence and keeps the lumen clear and patent.
This common potassium channel blocker medication is often given as a bolus and continuous maintenance drip for tachycardia arrythmias?
What is Amiodarone (Cordarone)