This style convention is used in Java to show that a variable is a constant
Uppercase letters
ex: private final int RADIUS= 5
This notation is used to check if two values are NOT equal
!=
The notation used to represent the logical OR operator in Java
||
This keyword in Java is used to declare a variable or method that belongs to the class itself, rather than an instance of that class
This means to automatically cast from a smaller type to a larger type
widen
This method returns the value of the first argument raised to the power of the second argument
Math.pow(double a, double b)
This notation is used to compare specific attributes of objects
object1.equals(object2)
A statement that selects a single action from three or more conditional statements based on which Boolean expression is true
Multi-selection statement
A variable that is shared by all instances of a class
Static variable
This method returns the absolute value of the parameter
Math.abs(x)
Casting
If you use the == comparison operator on two objects, this is what is being compared
Their locations in memory
The truth table below represents this logical operator
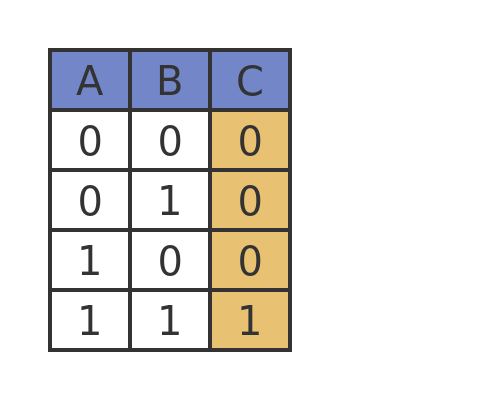
AND
This keyword is often combined with static to ensure an attribute cannot be changed once initialized
final
A method that requires an object of the class to be created before it can be called
The range used to generate a number with Math.random() in Java
0 and 1
A reference variable that points to the same object as another reference variable
Alias
A process in which the evaluation of a logical expression exits when the result is clear, even before the complete evaluation of the expression
Short-circuited evaluation
A method that can be called without creating an object of the class
static method
We must do this to the equals() method to compare objects other than strings
Override the method
The Math class is a part of this Java package
java.lang
(included in all Java programs by default)
This superclass that gives us access to the .equals() method
Object
A set of logical laws used to demonstrate the equivalence of two Boolean expressions
De Morgan's Laws
In a static method, this keyword cannot be used since the method isn't tied to an instance of the class
this
Logical operators follow this order of operations
!, followed by &&, followed by ||