"Do cochlear implants improve speech perception in children with fitted before age 5?" - What type of research question is this?
Descriptive – Seeks to describe a phenomenon.
Comparative – Compares two or more groups or conditions.
Causal (Experimental) – Tests cause-and-effect relationships.
Causal (Experimental) research is designed to test whether one variable directly influences or causes a change in another variable.
This type of research involves manipulating an independent variable while controlling other factors, and measuring its effect on a dependent variable, typically using random assignment and controlled conditions to establish cause-and-effect relationships.
What are the 3 types of neural connectivity?
- Structural
- Functional
- Effective
TRUE or FALSE: Brain "Lesions" and Brain "Tumors" are terms that can be used interchangably.
FALSE. A brain lesion refers to any abnormal change or damage in brain tissue. These lesions can vary in size, location, and severity and may result from various causes, including injury, infection, stroke, tumors, autoimmune diseases, or neurodegenerative conditions.
Define the "threshold of pain"
The threshold of pain in human hearing is typically around 120–140 dB SPL (Sound Pressure Level). At this intensity, sound waves create excessive vibration in the ear, leading to physical discomfort and potential damage to the auditory system.
Let's start with basics:
Define Speech vs. Language
Speech: The physical act of producing spoken words
The neural coordination of speech starts in the ______ of the brain and ends at our speech _______.
The neural coordination of speech starts in the CORTEX/BROCA'S AREA of the brain and ends at our speech MUSCLES (in the respiratory, phonatory, and articulatory systems).
NOT the "outcome measure', but rather the variable that is manipulated by the researcher as part of the experiment.
What variable is this in research?
The independent variable is the factor that a researcher intentionally manipulates to observe its effect on another variable.
Example: In a study testing whether sleep affects memory, the amount of sleep is the independent variable.
Functional Connectivity is highly dynamic. What does this mean?
Unlike structural connectivity, which is based on anatomy, functional connectivity measures synchronization of neural activity, often TASK-BASED conditions.
It is highly dynamic because it WILL change between different tasks.
Match the type of lesion with the possible cause/presentation:
LESIONS:
- Infectious Lesions
- Vascular Lesions
- Neoplastic Lesions
CAUSE/PRESENTATION:
- Sarcomas (connective tissue origin)
- Arteriovenous Malformations
- Brain-Eating Amoeba
- Infectious Lesions --> Brain-Eating Amoeba
- Vascular Lesions --> Arteriovenous Malformations
-Neoplastic Lesions --> Sarcomas (connective tissue origin)
What is "tonotopicity" and where can you find it in the auditory system?
Tonotopicity: the organized spatial arrangement of neurons in the auditory system based on their response to different frequencies of sound
- Basilar Membrane
- Hair Cells
- Auditory Nerves
- Subcortical Structures for Hearing
- Cortical Structures for Hearing
Name the types of aphasia where you'd expect fluent speech, but it may be nonsensical or difficult to find (but not physically speak) the right word.
Wernicke’s (damage to Wernicke’s area—intact production but impaired comprehension)
Transcortical sensory (similar to Wernicke's, but intact repetition skills. May repeat questions instead of answer them)
Conduction (intact production and comprehension, but impairment in their ability to repeat simple phrases; rare)
Anomic (difficult “word finding” or naming; the mildest of aphasias)
How does the Auditory Cortex play a role in feedback/adjustment of motor speech? Think: real-time feedback.
The Auditory Cortex plays a crucial role in the real-time feedback of motor speech by monitoring how speech sounds as it is produced. If it detects an error—such as a mispronounced word or incorrect pitch—it sends signals that help the brain adjust motor commands to correct the speech, ensuring clearer and more accurate communication.
What is a confound, and what type of problems can it cause?
A research confound is an uncontrolled factor in an experiment or study that can influence both the independent and dependent variables, leading to misleading or incorrect conclusions about the relationship between them.
Example?
Name one of 3 major functional networks introduced in this class. What kind of function does it capture?
Remember: Functional connectivity is organized into large-scale brain networks, which are specialized for different cognitive functions.
1. Default Mode Network (DMN) - Active during rest and mind-wandering (self-referential thinking, daydreaming).
2. Dorsal Attention Network (DAN) - Engaged during goal-directed tasks, such as visual attention and decision-making.
3. Salience Network (SN) - Detects important stimuli in the environment and regulates attention shifts.
Neurofibrillary Tangles are deposits of an unwanted protein in the brain that causes cell death and brain atrophy (shrinkage).
What is this protein and what 2 diseases is this seen in?
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE) (localized tau)
Alzheimer’s Disease (widespread tau)
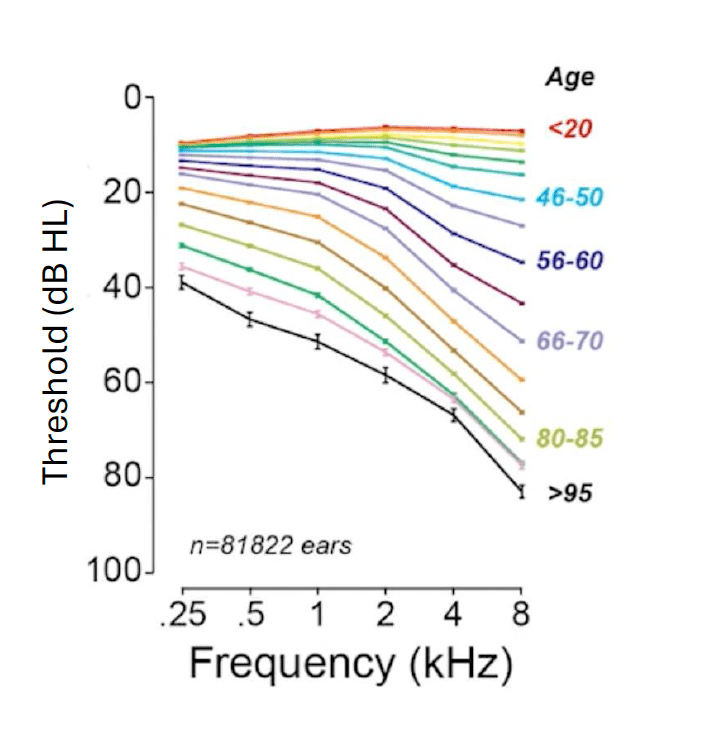
Describe how hearing changes with age. What structures are dying and how does this impact the audiogram?
Stereocillia and OHCs start to die/dysfunction with age, targeting HIGH FREQUENCIES first. The audiogram will be sloping, with elevated thresholds starting at higher frequencies.
Is somebody with Broca's or Wernicke's aphasia more likely to experience acute frustration with their aphasia?
Someone with Broca’s aphasia is more likely to experience acute frustration with their aphasia because they have intact comprehension but struggle to express themselves, making them fully aware of their communication difficulties.
In contrast, individuals with Wernicke’s aphasia often have impaired comprehension and may be less aware of their errors.
The Substantia Nigra produces this neurotransmitter in this area of the brain.
Dopamine in the Basal Ganglia
What are ways to control for confounds?
Randomization – Assigning participants randomly to conditions helps balance out potential confounds.
Matching – Ensuring groups are equivalent on key variables (e.g., matching participants by age in an audiology study).
Statistical Control – Using statistical techniques like ANCOVA or multiple regression to account for potential confounds.
Experimental Controls – Keeping conditions constant except for the independent variable.
Increased local connectivity within cortical regions, particularly in the sensory and association cortices, may, in part, contribute to this disorder.
Autism Spectrum Disorder
What are the two main types of Hematomas (seen in red and blue)?
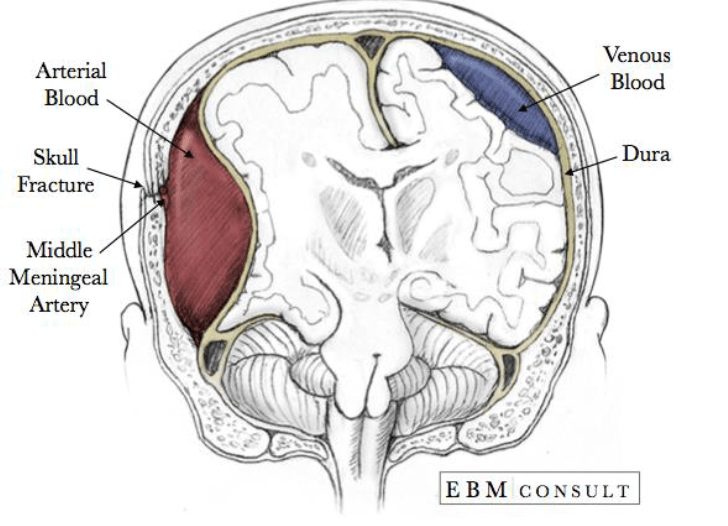
Subdural & Epidural Hematomas
Subdural Hematoma – Bleeding between the dura and arachnoid mater
Epidural Hematoma – Bleeding between the dura mater and skull
A disorder caused by loss of ribbon synapses between IHCs and auditory nerve fibers.
This is difficult to diagnose because the audiogram usually looks normal, but what skill is impaired?
Cochlear Synaptopathy
Outer hair cell function allows for a normal audiogram, but SPEECH IN NOISE will likely be something a patient really struggles with.
(NOTE: I don't have a review question on this, but make sure to study ANSD!)
A patient care team for someone with aphasia may include an SLP, neurologist, occupational therapist, physical therapist, nurse, audiologist, and psychologist or counselor.
Even though aphasia is a language disorder, more than just an SLP is needed because aphasia often results from broader brain injury (e.g., stroke, TBI), which can affect mobility, cognition, hearing, and emotional well-being.
A multidisciplinary team ensures comprehensive care addressing all aspects of the patient’s recovery, not just speech and language.
A patient comes into your SLP practice and is moving like they're drunk, but they're not. Based on these uncoordinated movements and their slurred speech, what motor speech disorder would you guess they have?
Ataxia: a motor speech disorder caused by impaired coordination of speech muscles
Bonus Q: In Friedreich’s Ataxia, the Fraxtaxin gene is over-repeated (mutated) and causes impairments in THIS "power house of the cell".