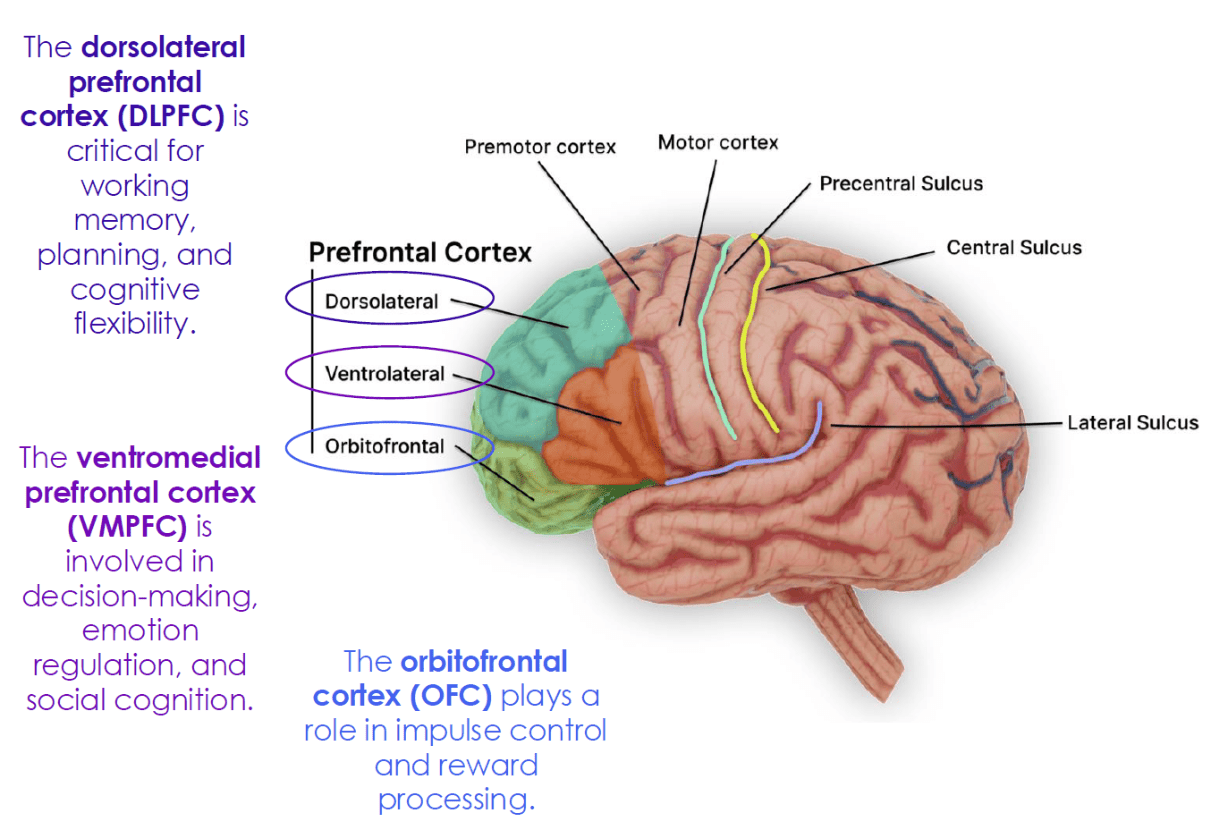
Which prefrontal region is most associated with working memory and planning? (Broadly and Specifically)
Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC)
Which type of attention involves maintaining focus over time?
Sustained Attention
What are the 3 steps of the Information Processing Model?
Encoding, Storage, Retrieval

"The brain’s memory librarian" – organizes and files new long-term memories for storage
Hippocampus
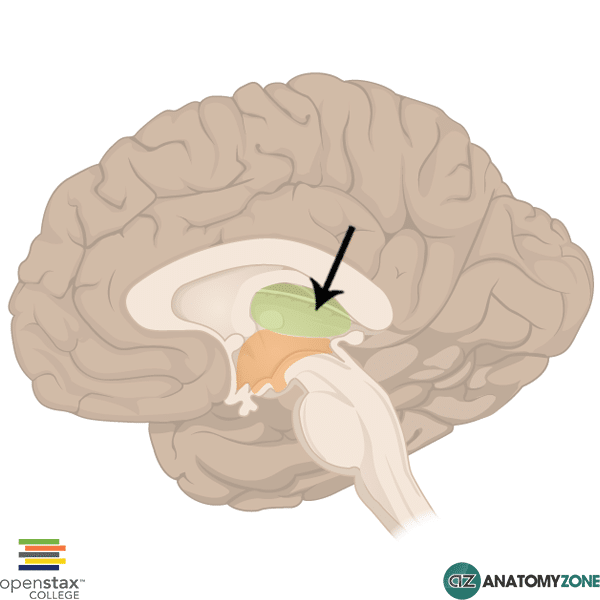
"Sensory relay station" – directs incoming sensory info to the right part of the brain
Thalamus
Describe how you'd set up a response inhibition task using images like this. In that task, what would be a congruent trials vs an incongruent trial?
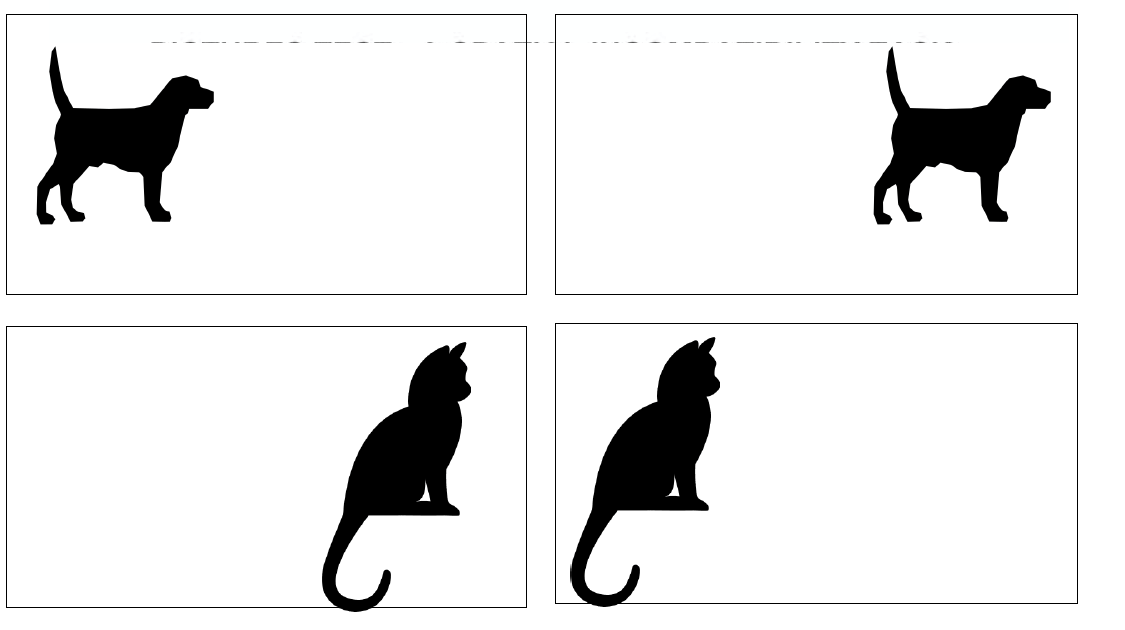
"Press the button on the right when you see a dog, but press the button of the left when you see a cat."
In congruent trials, the stimulus and the required response are spatially aligned.
In incongruent trials, the stimulus and the required response are spatially misaligned
Which brain area is important for shifting attention to different locations or stimuli AND ALSO is most likely to cause hemispatial neglect when damaged (a neurological condition where individuals experience a reduced awareness of stimuli and events on one side of their body)?
Hint:
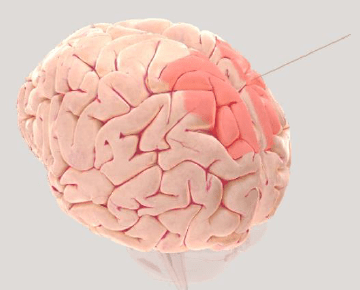
Posterior Parietal Cortex (PPC)
Why do we remember the beginning and end of a list better?
The beginning benefits from rehearsal (primacy), and the end is still active in working memory (recency).

"Speech production HQ" – helps you turn thoughts into spoken words
Broca's Area

"Fear and feelings center" – processes emotions like fear, anger, and pleasure
Amygdala
Describe the relationship between delay of gratification and academic success. What happens when SES is controlled for?
If you can resist an immediate reward in favor of a larger, future reward—you tend to stronger outcomes in areas such as academic achievement, emotional regulation, and long-term goal attainment.
When SES is controlled, much of that predictive power diminishes, indicating that external factors (e.g., family stability, access to resources, enriched environments) play a substantial role in shaping both self-regulation and academic outcomes.
Provide an example of alternating attention in daily life. Be careful not to confuse with divided attention.
Alternating: Cooking dinner while checking homework --> You focus on stirring a pot, then shift your attention to help a child with a math problem, then return to cooking.
Divided: Cooking while listening to a podcast or music with lyrics --> You’re attending to recipe steps, stirring or measuring, while also trying to comprehend what’s being said in the podcast.
Tying your shoelaces evokes long-term memory. What specific subtype?
Procedural Memory
Once you've learned how to tie your shoes, you can usually do it without consciously thinking about the steps involved. You don’t need to recall each movement—your body just knows the loops!
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Corpus-Callosum-58d16cd45f9b581d727aa487.jpg)
"The brain’s bridge" – connects the left and right hemispheres to share information
Corpus Callosum
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/midbrain-pons-gross-anatomy/FZGi6OOL1A2Ph2BJPp5Q_Midbrain_01.png)
"Reflex control center" – handles visual and auditory reflexes and keeps you alert - Top O' the Brainstem
Midbrain
What does the N in the N100 and N400 stand for?
NEGATIVE
The _______includes the caudate nucleus and putamen of the_________
Striatum
Basal Ganglia
Define infantile amnesia.
The inability to recall memories from the first 2–3 years of life, likely due to an underdeveloped hippocampus and reliance on implicit memory.
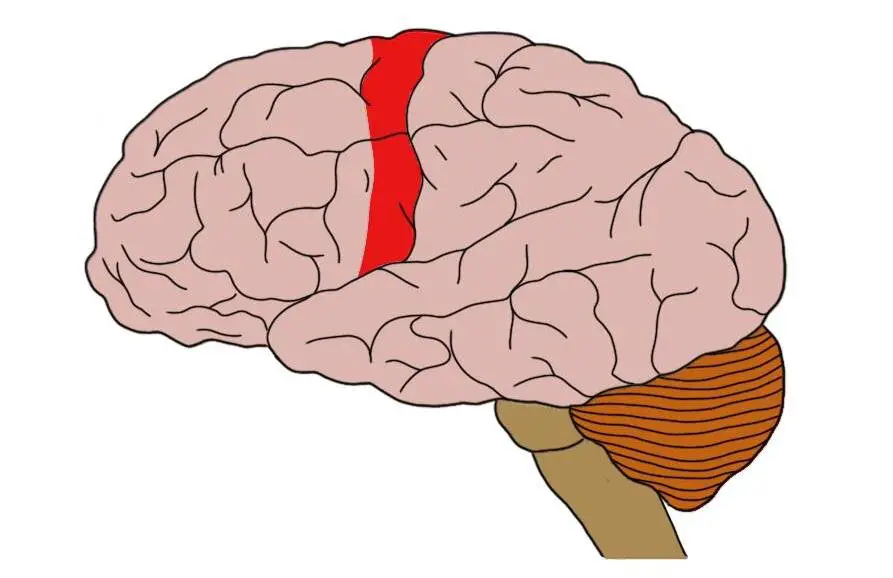
"Movement commander" – sends signals to control voluntary muscles
Primary Motor Cortex
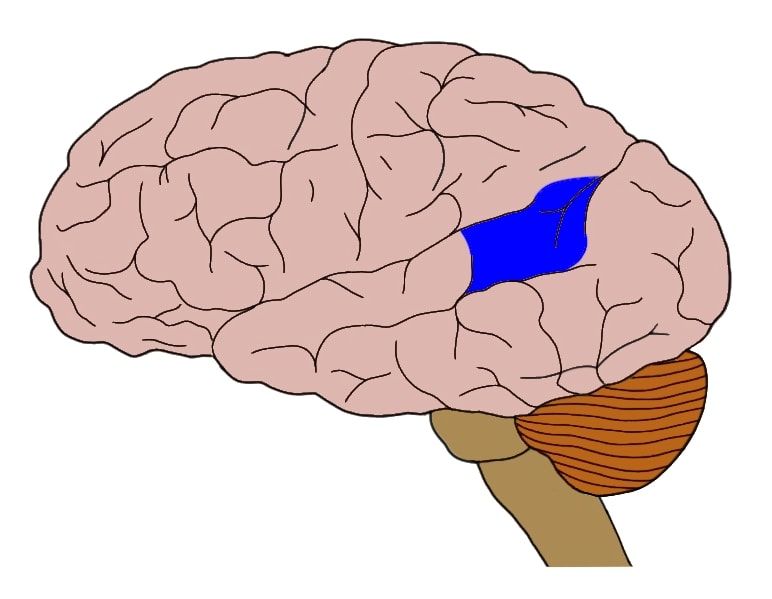
"Language decoder" – helps you understand spoken and written language
Wernicke’s area