The movement of warm and cold air masses, combined with what, explains the basic movement of thermal energy around the earth?
Coriolis Effect
Energy is always in motion
The Sun
The area between the equator and the Tropic of Cancer (in the north) and the Tropic of Capricorn (in the south) is called the:
Tropics
Latitude zone that receives only a small amount of sunlight in the winter:
Polar Region
The condition of the atmosphere at a given time and place:
Weather
Large area of moving air that has a similar temperature throughout.
Air Mass
The Earth's movement on its axis every twenty-four hours is known as what?
Rotation
Hot prevailing winds that blow in the tropics are called the:
Trade Winds
This element of weather is the movement of air caused by the heating and cooling of air masses:
Wind
The 23 1/2 angle on which the earth rotates:
Axis
Any large region where distinct populations of plants and animals are found living together:
Biome
June 21 in the Northern Hemisphere
Summer Solstice
The envelope of gases that surrounds the earth and is held in place by the planet's gravity is called what?
Atmosphere
What are the three basic biomes?
Forests, Wastelands, and Grasslands
Slowest Ocean Currents
Drifts
Sun, Planets, and smaller system bodies are apart of:
The Solar System
The land beyond the mountains that usually remains dry because little water vapor survives the trip over the mountains:
Rain Shadow
Evaporation, Condensation, & preciptation
Hydrologic Cycle
What is composed of the sun, planets, small solar system bodies, and other objects around the sun by the sun's gravity?
Solar System
The point at which the sun reaches its greatest angular distance from the equator is called the:
Solstice
Explain the difference between weather and climate.
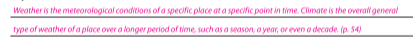
Envelope of gases that surrounds the earth:
Atmosphere
Rain, sleet, or snow resulting from contact with mountains:
Orographic
Water vapor begins condensation
Dew Point
These combine with the Coriolis Effect to help explain the basic movement of thermal energy around the earth.
Wind Belts
The point at which the length of day and night are approximately equal all over the planet for an instant is known as the:
Equinox
The weight of gases in the atmosphere on a surface area is known as:
Atmospheric Pressure
Latitude zone that consistently has very warm temperatures:
Tropics
Line where warm and cold air masses meet:
Front
List and explain the hydrologic cycle
