This word for something “obvious after the fact” comes from Latin for “after” and “to see.”
What is “hindsight”?
This ancient civilization famously wrote riddles in cuneiform on clay tablets, including one about a house with no doors or windows and a golden treasure inside.
What is “an egg”?
Ancient Egyptians believed this organ was the seat of thought and emotion, and carefully preserved it during mummification — even though we know today it’s not.
What is “the heart”?
A 2003 genetic study revealed that about 0.5% of the world’s male population shares a nearly identical Y-chromosome, likely tracing back to this 13th-century ruler.
Who is “Genghis Khan”?
Ancient Egyptians revered this bird for its association with wisdom and the afterlife — its migration patterns across seasons seemed to them like a journey between worlds.
What is “the ibis”?
Norse mythology describes warriors who died bravely in battle being taken to this legendary hall ruled by Odin.
What is “Valhalla”?
Ancient Rome is famous for building these structures that carried water into cities over vast distances.
What are “aqueducts”?

What is “the mask of Tutankhamun”?
The word “pandemic” is formed from Greek roots meaning these two things: “all” and “____.”
What are "people"?
An ancient Egyptian riddle describes a creature that walks on four legs in the morning, two legs at noon, and three legs in the evening — famously posed to travelers by this mythological figure.
Who is “the Sphinx”?
To prevent illness during the bubonic plague, doctors often carried flowers or aromatic herbs stuffed in scented masks to protect themselves from these unseen dangers thought to spread sickness.
What are “bad/foul smells, miasma”?
In ancient maps, this great sea was often called the “Middle of the Earth,” reflecting its central role in trade and conquest.
What is “the Mediterranean Sea”?
This creature, sometimes called a “living fossil,” has remained virtually unchanged for over 450 million years and has blue blood prized for modern medical testing.
What is the "horseshoe crab"?
Romans wore small charms called bullae around children’s necks to protect them from this supernatural threat.
What is “the evil eye”?
In ancient China, alchemists searching for immortality accidentally created this powerful substance, which later changed the course of warfare.
What is “gunpowder”?
This style of pottery, with red figures set against a black background, was developed in the 6th century BCE and is associated with this ancient city-state’s artisans.
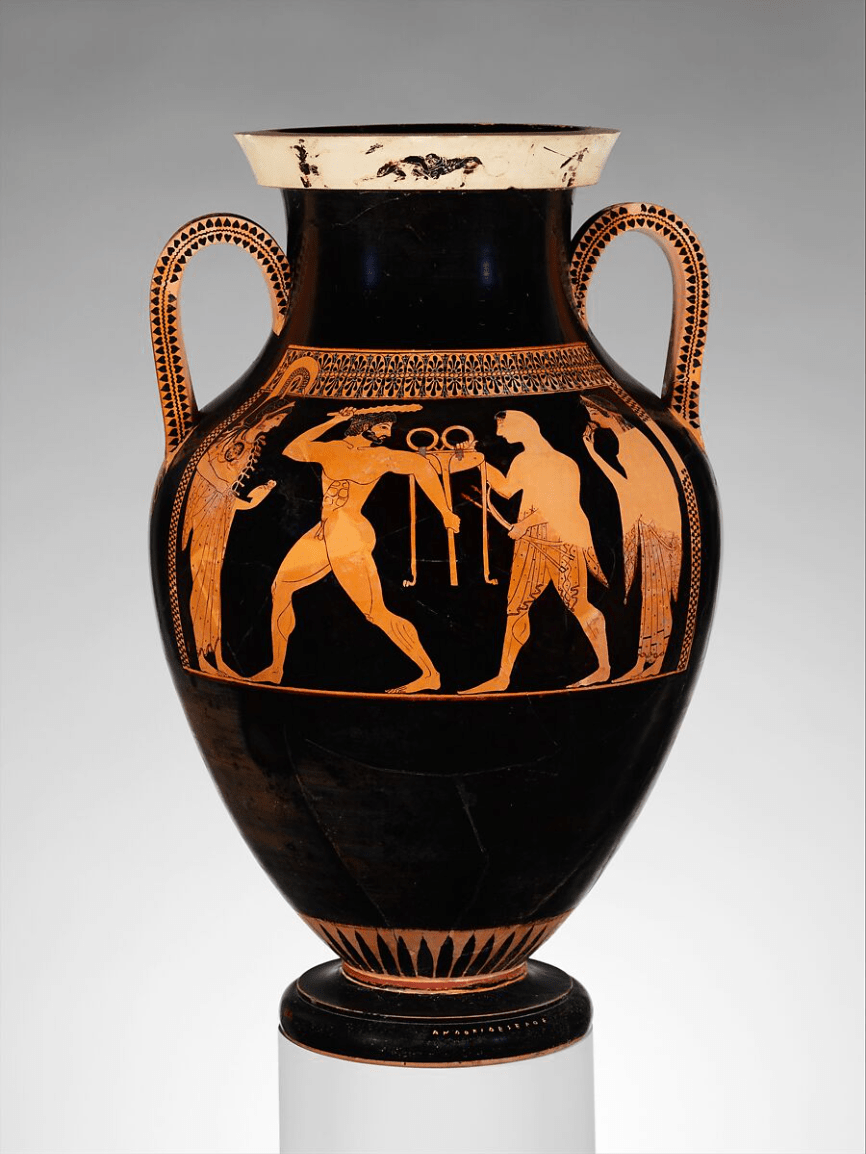

What is “Athens”?
The name of this disease comes from the medieval Italian words for “bad air,” reflecting the ancient belief that breathing night air near swamps caused illness.
What is “malaria”?
In a famous biblical story, this king proposed dividing a baby in two to reveal the true mother, using wisdom and logic rather than violence to solve a dispute.
Who is “King Solomon”?
Ancient Egyptian and Greek texts describe early pregnancy tests based on how a woman’s urine affected the growth of this type of plant.
What is “barley” or “wheat”?
The region between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers — home to the Sumerians, Akkadians, Babylonians, and Assyrians — is often called this “land between rivers.”
What is “Mesopotamia”?
The ancient Greeks believed that barnacle geese grew from trees because they never saw the birds nesting, a mystery later explained by this phenomenon.
What is “bird migration”?
In medieval Europe, it was believed that sleeping under a walnut tree would cause this condition, thought to be sent by witches.
What is “madness” or “insanity”?
This ancient structure in Athens was not just a temple, but also a symbol of mathematical perfection, embodying the golden ratio in its design.
What is “the Parthenon”?
What is this important artifact and why was it important (50 point bonus)

What is “the Rosetta Stone”? Discovered in Egypt in 1799, this artifact helped scholars decode ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs.
This word for a style of sarcasm or mockery is named after an ancient Greek city known for its biting humor.
What is “satire”?
Zeno of Elea created a famous paradox arguing that a runner could never finish a race because he must first reach the halfway point, then half of what remains, and so on infinitely. This paradox is named after which hero of Greek mythology?
Who is “Achilles”?
The Ebers Papyrus from ancient Egypt described using willow bark to treat pain — a natural source of the same compound found in this modern drug.
What is “aspirin” / “salicylic acid”?
As a young prince, Alexander the Great was tutored in philosophy, science, and medicine by this famous Greek thinker.
Who is “Aristotle”?
Some trees, like eucalyptus and sequoias, rely on this destructive natural force not just to survive but to reproduce, as it triggers seed release.
What is “fire”?
Some ancient burial sites show coins placed over the eyes of the dead, intended to pay this figure for safe passage.
Who is “Charon,” the ferryman of Hades?
The first known flushing toilets were developed around 2000 BCE in this ancient civilization on the island of Crete.
What is “the Minoan civilization”?
Worn around the neck, this amulet symbolized the protection of a god for Norse peoples. Name the object or the god it is associated with.
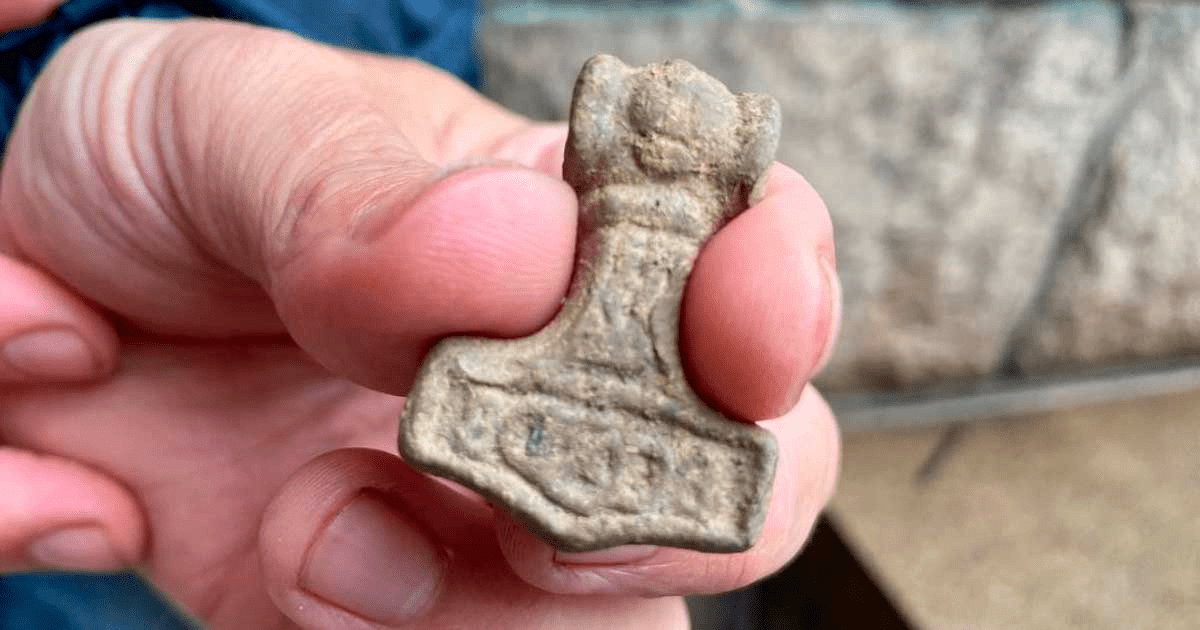

What is “Thor’s hammer” or “Mjölnir”?
This word for a wandering storyteller or singer in medieval Europe shares its root with “walk” or “journey.”
What is a “troubadour”?
This ancient Chinese military thinker is credited with advising that “all warfare is based on deception,” an early articulation of logical misdirection in strategy.
Who is “Sun Tzu”? Hint: The Art of War
Ancient South American civilizations like the Incas practiced this surgical procedure, drilling into the skull — possibly to relieve pressure after head trauma.
What is “trepanation”?
Name any four of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, a list compiled by ancient Greek travelers to celebrate the most awe-inspiring structures they knew.
What are any four of: the Great Pyramid of Giza, the Hanging Gardens of Babylon, the Statue of Zeus at Olympia, the Temple of Artemis at Ephesus, the Mausoleum at Halicarnassus, the Colossus of Rhodes, or the Lighthouse of Alexandria?
Some ancient civilizations interpreted massive fossilized bones they found as evidence for giant humans or gods. Today, many of these “giant” skeletons have been correctly identified as belonging to this type of prehistoric creature.
What are “mammoths” or “mastodons”?
In ancient Scottish Hogmanay celebrations, seeing a blond man as the first visitor after midnight was feared to bring bad luck — a belief rooted in memories of this historical threat.
Who are the “Vikings”?
The earliest known mechanical clock towers in Europe, powered by weights and gears instead of water, began appearing in this century.
What is “the 13th century”?
This stunning set of gold vessels, richly decorated with scenes from mythology, was created by an ancient civilization known for their metalwork and warrior culture. Name the civilization that crafted it, the modern country where it was discovered (Bonus: 50), and the treasure’s name (Bonus: 50).
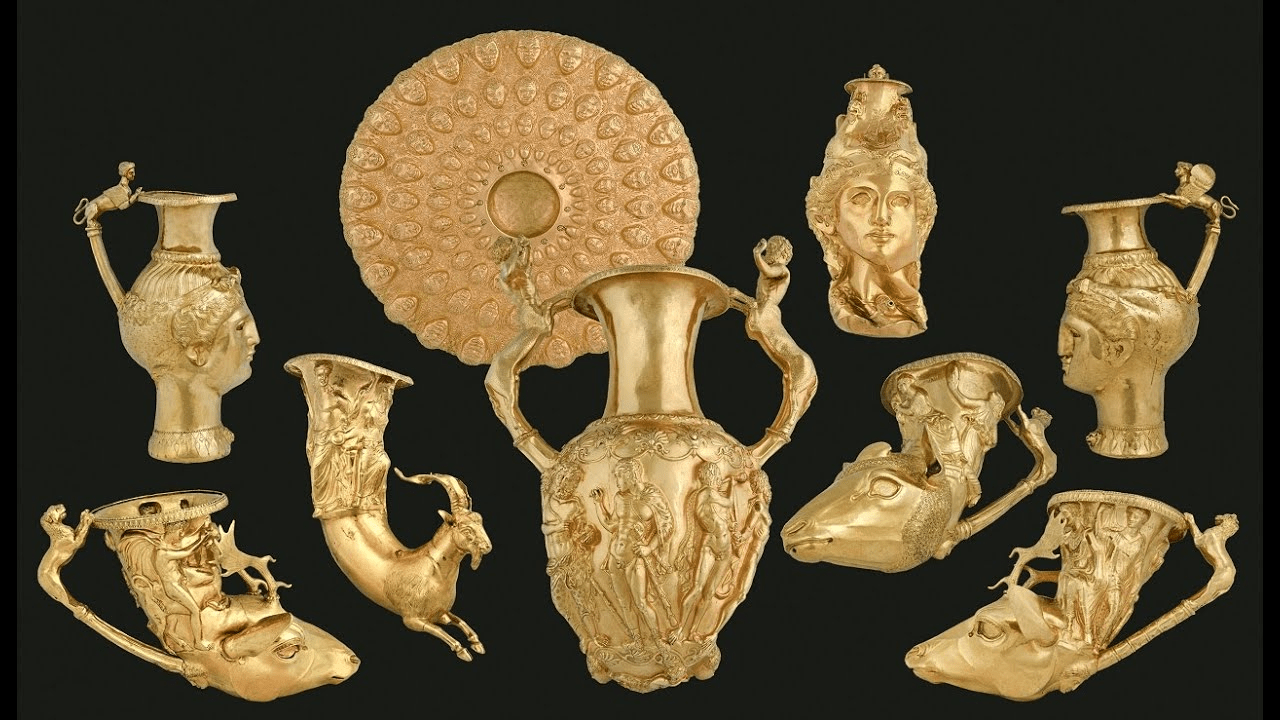
Who are the Thracians, what is Bulgaria, and what is the Panagyurishte Treasure?