The two main divisions of the respiratory system.
What are the upper airway and the lower airway?
The primary muscle of inspiration that increases thoracic volume when it contracts.
What is the diaphragm?
Term used to describe normal, and automatic life breathing
What is tidal breathing?
This assessment tool measures lung volumes and airflow rates.
What is spirometry?
Oral intubation redirects airflow through a tube, bypassing the vocal folds. (Zelenke, Module 2).
What is how oral intubation affects airflow?
These structures form the upper airway.
What are the nasal cavity, oral cavity, pharynx, and larynx?
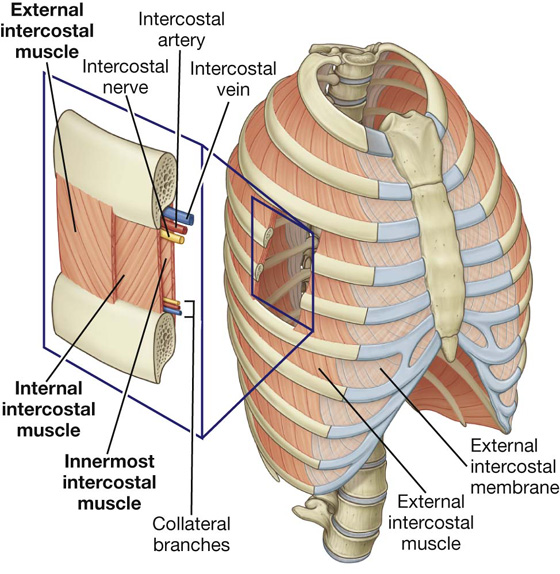
These muscles elevate the ribs during inhalation to assist inspiration.
What are the external intercostal muscles?
In speech breathing, this inhalation to exhalation ratio is used to support spoken communication.
What is 10 percent inhalation and 90 percent exhalation?
This term refers to the amount of air inhaled or exhaled during normal breathing.

What is tidal volume?
Why does oral intubation prevent speech?
The tube prevents vocal fold vibration required for voicing (Zelenke, Module 2).
This structure allows for gas exchange between oxygen and carbon dioxide within the lungs.
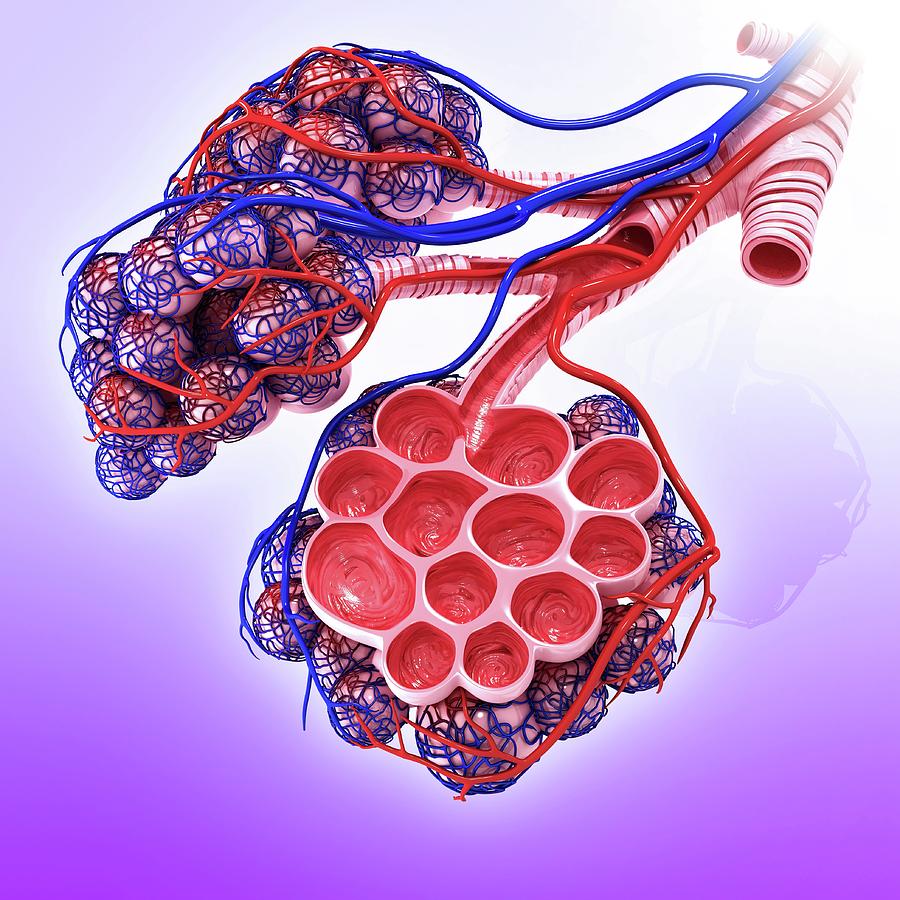
What is the alveoli?
Muscles that actively depress the ribs during forced expiration.
What are the internal intercostal muscles?
This is why speakers rely on prolonged exhalation during speech production.
What is to allow greater control of airflow for speech?
This measure indicates the percentage of hemoglobin in the blood that is carrying oxygen.
What is oxygen saturation?
A tracheostomy is a surgically created opening in the trachea to maintain an airway
(Zelenke, Module 2).
What is a tracheostomy?
These skeletal structures support respiration and protect the thoracic cavity.
What are the rib cage, sternum, vertebral column, and diaphragm?
These nerves innervate the primary respiratory muscles, including the diaphragm and intercostal muscles.
What are the phrenic nerve and thoracic spinal nerves?
This law describes the inverse relationship between pressure and volume that governs airflow during respiration.
What is Boyle’s Law?
This is defined as the maximum amount of air that can be expelled following a maximum inhalation.
What is vital capacity?

How does a tracheostomy impact speech production?
It reduces subglottic pressure needed for phonation (Hoit et al., 2022).
Protects the airway by trapping debris and moving particles away from the lungs to maintain healthy respiration
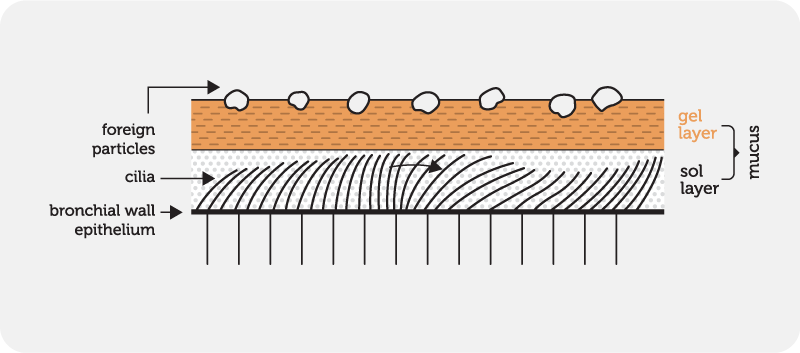
What are cilia-lined airways?
These muscles are essential for speech production because they regulate airflow and subglottal pressure for sustained phonation.
What are the respiratory muscles?
This phrase describes how speech breathing alters an automatic biological process to support communication.
What is modifying automatic respiration to meet the aerodynamic demands of speech?
This is why speech-language pathologists monitor a client’s respiratory rate during assessment and treatment.
What is to evaluate breathing patterns and ensure adequate respiratory support for speech?
What device can restore speech with a tracheostomy?
What is a one-way speaking valve redirects airflow through the vocal folds to allow voicing (Zelenke, Module 2).