A pt is BEFAST positive if they have had s/s for how long?
what is less than or equal to 4.5 hours
What is this ECG showing?
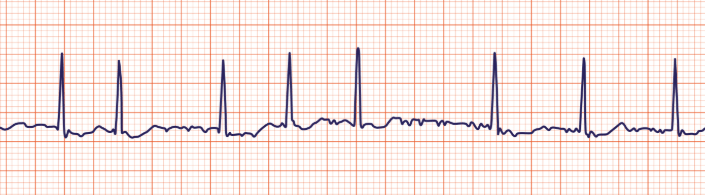
What is atrial fibrilation?
What are the two medications that you can use activated charcoal for without OLMC approval?
Tylenol and Aspirin.
Typically isolated and if ingestionless than 1 hour ago.
What does this ETCO2 waveform indicate?
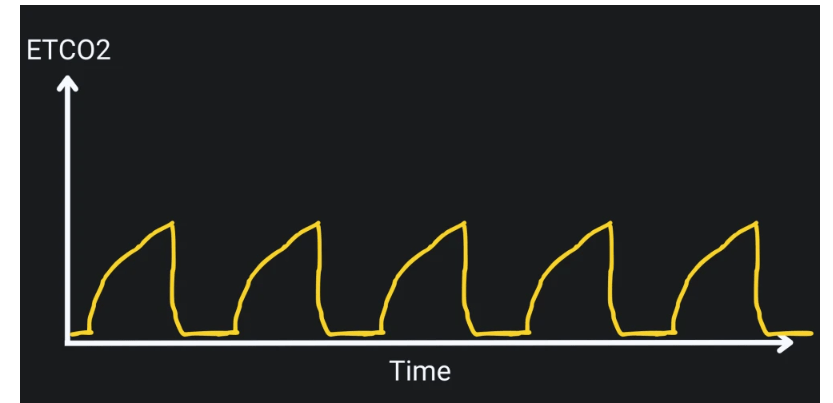
what is bronchoconstriction?
Known as the "shark fin waveform" seen w/ pts w/ asthma, emphysema and COPD
This type of shock results from loss of blood or fluids, leading to inadequate tissue perfusion and is often indicated by tachycardia, hypotension, and cool clammy skin.
What is hypovolemia?
This life threatening electrolyte imbalance is often seen in renal failure and produces ECG changes such as peaked T waves and widened QRS complexes, bradycardia, hypotension, shallow respirations and has potential for cardiac arrest if left untreated.
What is Hyperkalemia?
Our first line defense for hyperkalemia is 10% calcium gluconate 1g IV/IO slowly over 5-10 mins in a proximal port.
What is this ECG showing?
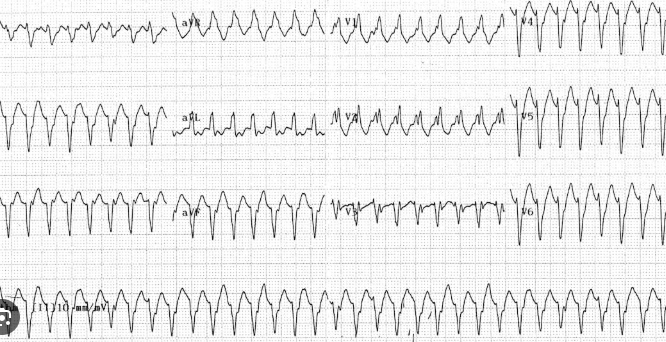
What is V-tach?
Monomorphic ventricular tachycardia
What is the adult dose for atropine w/ bradycardic patients?
0.5mg IV/IO, may repeat q 3-5 mins, max 3mg.
What does this ETCO2 waveform indicate?
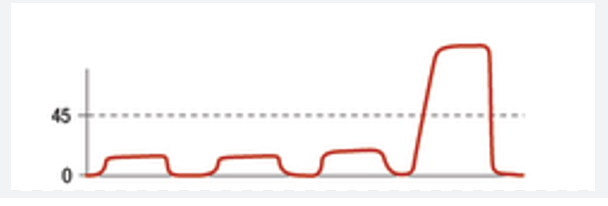
what is ROSC?
A sudden increase in ETCO2 seen during CPR
What would this indicate?
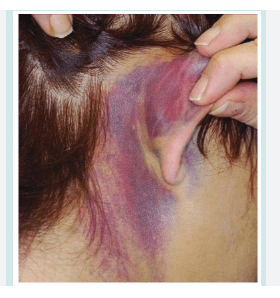
What is a basilar skull fracture?
Battle signs - 4 B's
battle signs, bruises seen, behind the ear, basilar skull fracture
What does qSOFA stand for?
Quick Sequential Organ Failure Assesment.
What is this ECG waveform? *50 bonus points if you know the name of it in english*
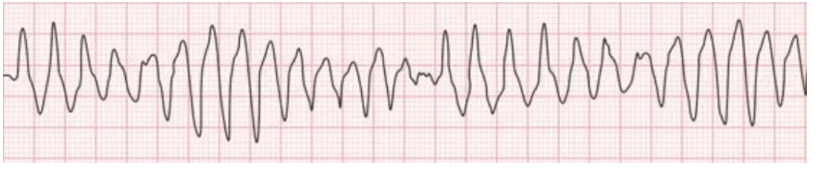
"Torsades de Pointes" - "turning of the points" Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia.
The most common cause of Polymorphic V-Tach is prolonged QT syndrome - abnornmally long repolarization of the heart that turns into a continuous circular electrical route in the ventricles.
This medication is a naturally occuring nucleoside that has the ability to slow conduction through the AV node, it is elminated quickly from circulation and has a half life in the blood of less than 10 seconds.
What is Adenosine?
What does this ETCO2 wavform indicate?
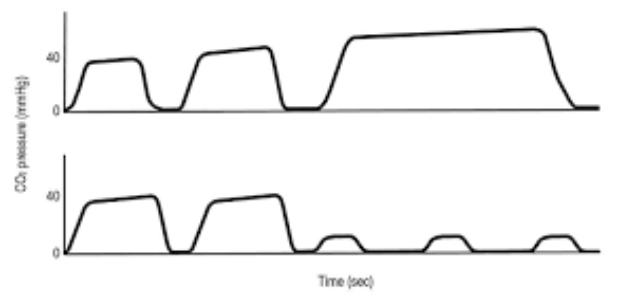
What is hypoventilation?
What is this bruising pattern called?
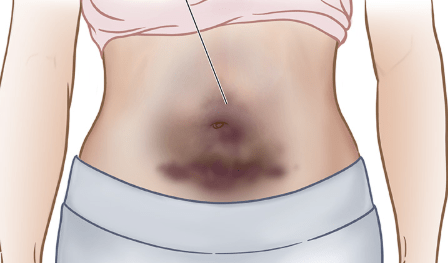
What is "cullen sign"? A.k.a periumbilical ecchymosis.
Intra-abdominal bleeding. May appear 24-48 hours after bleeding starts. Can be from acute pancreatitis, ruptured ectopic pregnancy, aortic rupture, blunt abdominal trauma, spleenic rupture, or even varices.
This condition causes muscles to break down and disintigrate, leading to muscle death and release of toxic compenents. It is common with crush injuries and even w/ ground level falls in elderly individuals w/ prolonged down time.
What is Rhabdomyolysis?
This condition can cause release of potassium, phosphate, myoglobin, creatine kinase and urate. The kidneys are responsible for removing these components from the blood so you can get rid of them in your pee. Large quantities can lead to kidney failure.
What is this rhythm called?
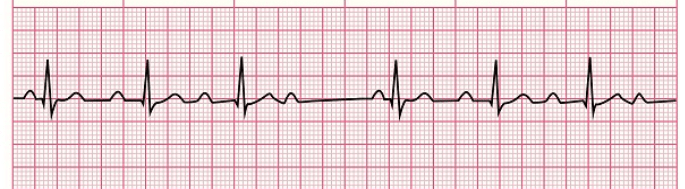
what is a 2nd degree AVB type 1? - aka Wenckebach or Mobitz type 1.
A lengthening PR interval followed by a dropped QRS complex - where a P wave is not partnered w/ a QRS complex. May be caused by enhaced vagal tone, myocardial ischemia or the effects of drugs such as calcium channel blockers (amlodipine, diltiazem, verapamil)
The contraindications for this medication include known pregnancy, non-traumatic chest pain or suspected cardiac chest pain, and pts w/ a hx of schizophrenia or psychosis.
What is Ketamine
What does this ETCO2 waveform indicate?
(hint: the pt is intubated) 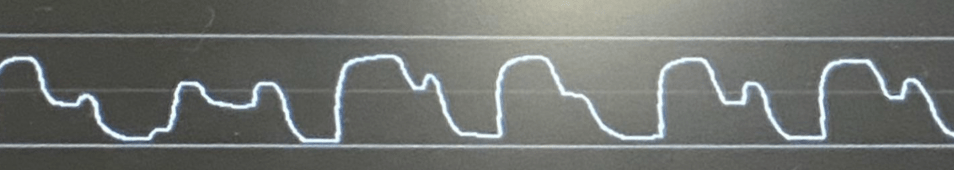
What is breakthrough breathing? aka the "curare cleft"
This waveform indicates that a pt is breathing against the ventialator and or BVM and that they need further sedation.
This deadly triad of hypotension, distended neck veins and muffled heart tones is know as?
What is Beck's triad?
Indicates pericardial tamponade.
This is a tell tale sign of an aortic dissection.
1.) What is chest pain + neuro s/s? (i.e. numbness/tingling, limb paralysis)
An aortic dissection causes what is called a false lumen and depending on how far the dissecton spreads it can cause a myriad of s/s. If the false lumen can go as far as the femoral artery, it can cut off blood flow completely to the leg
What is this ECG rhythm?
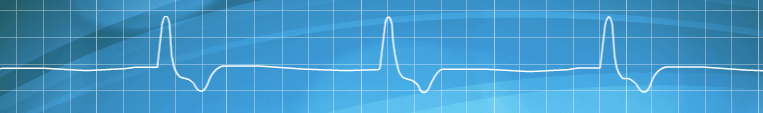
What is idioventricular?
Characterized by a slow, regular, ventricular rhythm (20-40bpm), abscence of P waves, and a prolonged QRS interval.
These medications have what in common?
Rivaroxoban (Xarelto) - Apixaban (Eliquis) -and Edoxaban (Lixiana)
They are XA inhibitiors. Notice they all have XA in the name.
Roman numeral X (10) A inhibitors are used to prevent and treat blood clots such as w/ DVT and PE. They work by inhibiting factor 10A which is an enzyme that plays an important role in the blood clotting process. Interferes w/ the coagulations cascade and prevents blood clots from forming.
What does this ETCO2 waveform indicate?
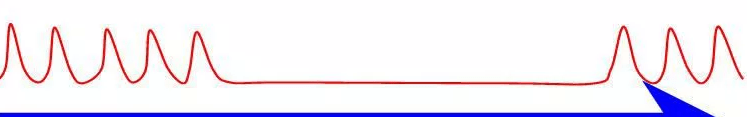
What is increased ICP/brain herniation?
Cheyne Stokes respirations, rapid breathing followed by periods of apnea.
Following blunt abdominal trauma in a T-Bone accident a pt presents w/ referred left shoulder pain, increasing tachycardia, and abdominal rigidity. This specific internal injury should be suspected due to the referred pain.
What is a spleenic rupture?
This is called "Kehr's sign" and is when the interior surface of the diaphragm becomes irritated due to bleeding from a spleenic rupture. They will feel this reffered pain when they are lying flat and their legs are elevated.