The protein that assists in protein folding during post-translational processing.
 What are Chaperones?
What are Chaperones?
An increase in this hormone causes sleepiness.
What is melatonin?
These elements have characteristically high electronegativity, ionization energy, and electron affinity. These elements tend to be found on the right side of the Periodic Table and are poor conductors of electricity.
What are Nonmetals?
Within one principle energy level, this subshell has the least energy.
What is subshell s?
A scalar quantity describing the distance traveled by the time required to travel that distance.
What is speed?
The amide bond between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid.
What is a Peptide Bond?
The neurotransmitter assoicated with both schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease.
What is dopamine?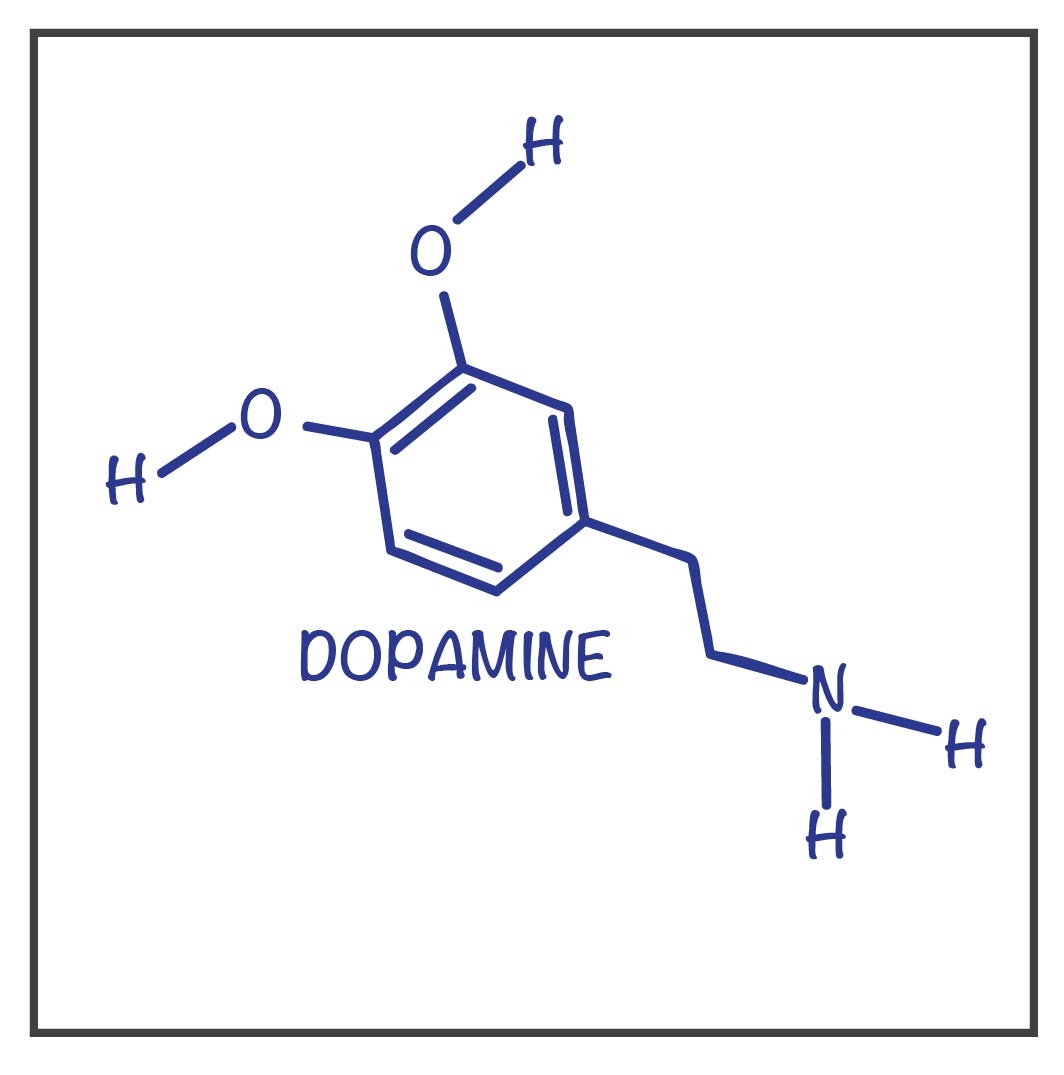
This term is used to describe a measure of an atom’s ability to pull electron density toward itself when involved in a chemical bond. It increases from left to right and bottom to top on the Periodic Table.
What is Electronegativity?
Pi bonds are formed by these orbitals.
What are two p-orbitals?
The equation for Boyle's Law.
What is P1V1 = P2V2?
The transfer of a phosphate group, generally to ATP, which is powered by a gradient formed by oxidation-reduction reactions occurs in the mitochondria.
What is Oxidative Phosphorylation?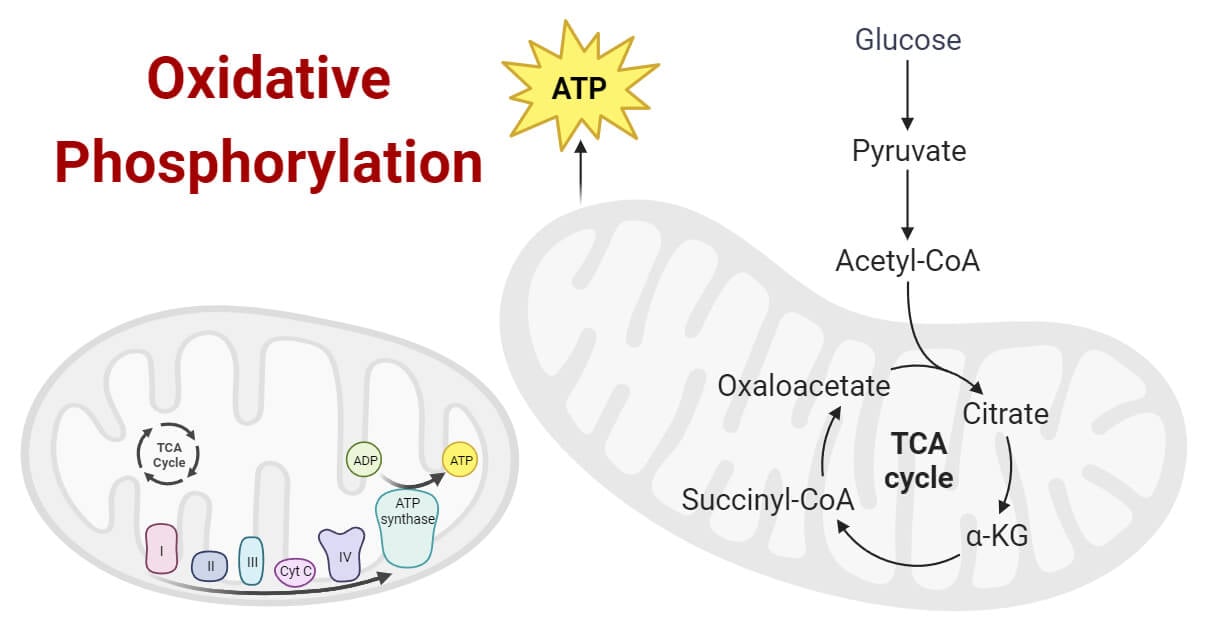
Method encoding that is most conductive to later recall.
What is Semantic?
This term describes the ratio of the concentrations of the products to the concentrations of the reactants at any point during a reaction, where each reactant and product in the expression is raised to the power of its stoichiometric coefficient. Commonly denoted by Q, it is usually compared to the equilibrium constant to determine the direction a reaction will proceed to regain equilibrium.
What is the Reaction Quotient? 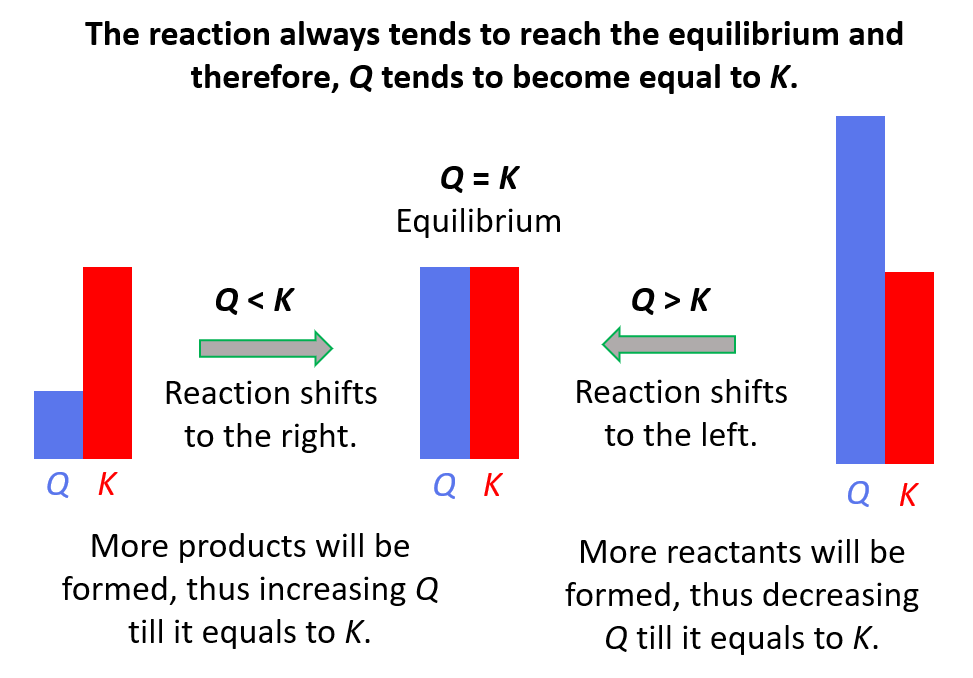
Compounds listed by increasing boiling point of Butanol, Butane, and Butanone.
What are butane<butanone<butanol.
States that the change in internal energy of a system is equal to the heat transferred into the system minus the work done by the system. This LAW is an extension of the law of conservation of energy.
What is the First Law of Thermodynamics?
This molecule contains four linked aromatic rings and provides both fluidity and stability to cell membranes and is the precursor for steroid hormones.
 What is Cholesterol?
What is Cholesterol?
The four lobes of the cerebral cortex.
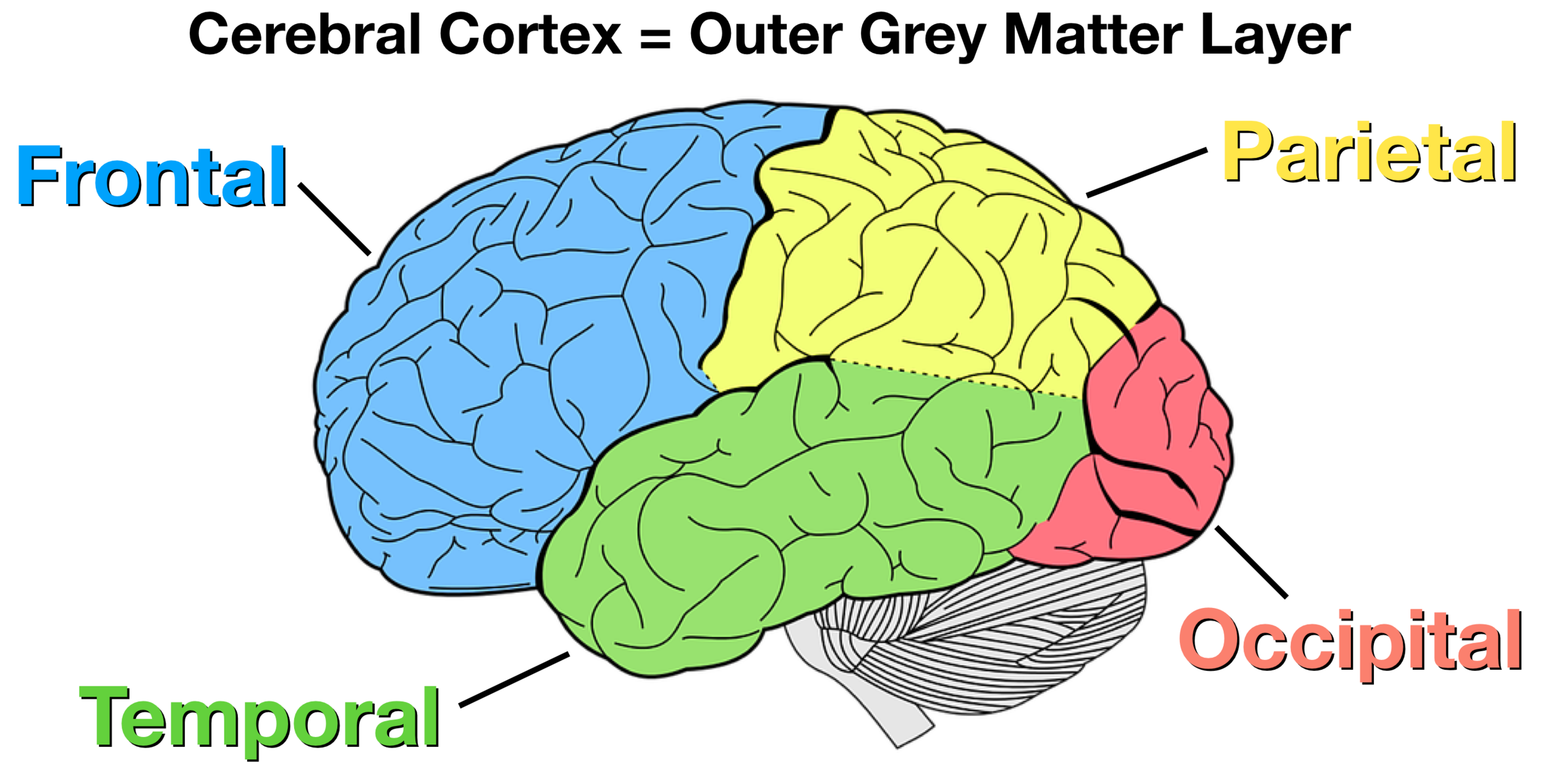 What are the Frontal, Parietal, Occipital, and Temporal lobes?
What are the Frontal, Parietal, Occipital, and Temporal lobes?
This is the name of the group of elements found in Group VIIA (Group 17) of the Periodic Table.
What are Halogens?
Why do carboxylic acids have higher boiling points than their corresponding alcohols?
Hydrogen boiling is much stronger than in alcohols.
The equation for Ideal Gas Law.
What is PV = nRT?
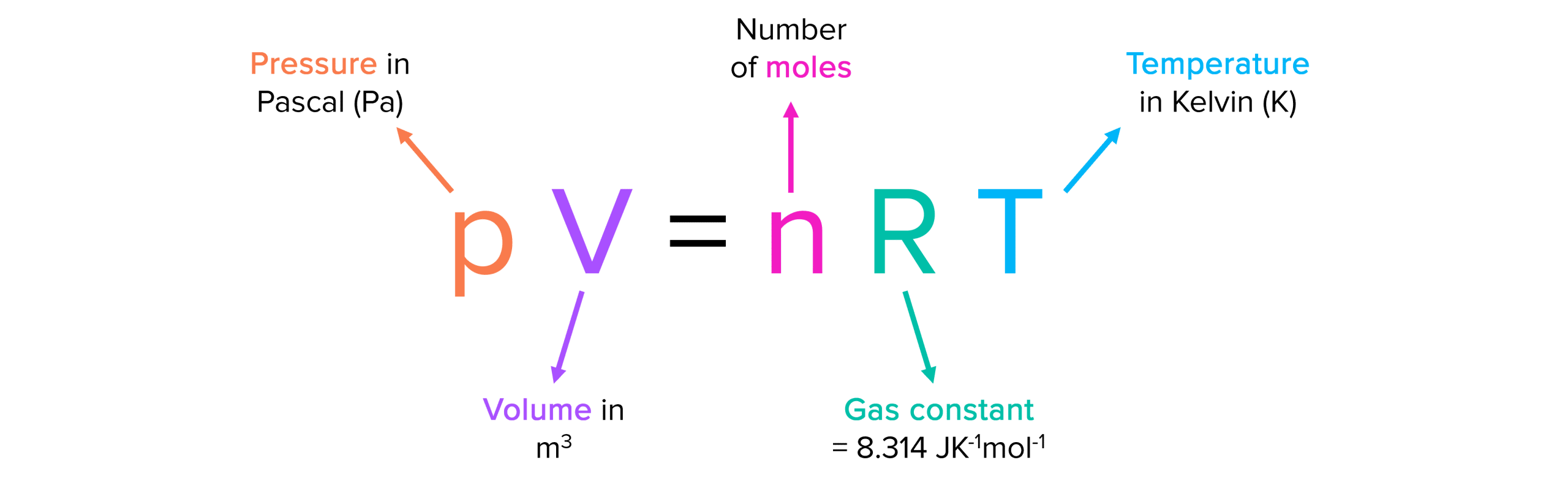

The portion of the nephron not permeable to water. As the filtrate flows through this portion, NaCl is first passively, then actively removed from the filtrate, decreasing filtrate concentration.
 What is the Ascending Limb of the Loop of Henle?
What is the Ascending Limb of the Loop of Henle?
An intended positive effect on a system.
What is a manifest function?
A representation of a displacement reaction showing only the relative species and omitting the spectator ions.
What is a Net Ionic Equation? 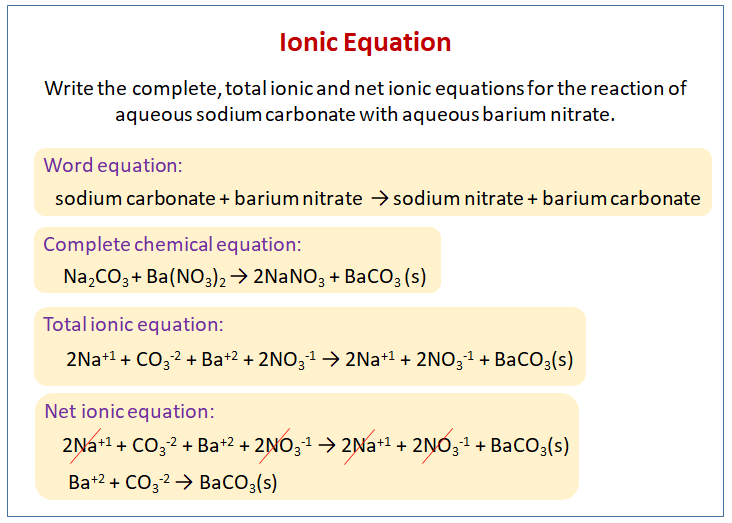
Imines naturally tautomerize to form this.
What are enamines? mines?
mines?
The 1st, 2nd, and 3rd Laws of Motion.
First: States that if no net force acts on an object, its velocity is constant.
Second: States that an object will accelerate in proportion to the net force acting on it. Net force = mass x acceleration.
Third: States that if one object exerts a force on another, the other object exerts a force in the first that is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction.