What is the difference between anatomy and physiology?
Anatomy is the study of structure. Physiologiy is the study of function.
What does EOIO stand for?
Extraoral/ Intraoral
What are the 3 dentition periods?
Primary, Mixed, Permanent
Which tooth has a supplemental 5th cusp and what is it called?
Maxillary 1st Molar; Cusp of Carabelli
Hyper
Excessive
What is considered a healthy probing depth?
1-3mm
What is anatomic position?
The body is standing upright, with the feet parallel to each other and flat on the ground. The arms are extended alongside the body with the palms facing forward.
What is this intraoral structure?
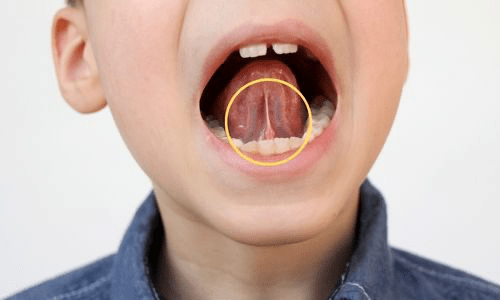
Lingual Frenum
How many primary teeth are there? How many permanent teeth are there?
Use the D-A-Q-T system to identify tooth #1.
Permanent Maxillary Right 3rd Molar
Xero
Dry
How many probing depth measurements are taken for each tooth?
6 (3 on the lingual + 3 on the facial/buccal)
What plane divides the body into superior and inferior?
Horizontal/Transverse Plane
What is this name for the outside border of the lips (where one would place lip-liner)?
Vermillion Border
What is the function of incisors?
Biting/Cutting
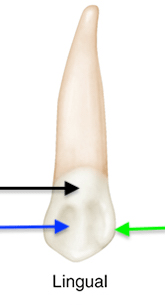
What anatomical structure is the black arrow pointing to?
How often should health histories be updated? (Ex/ new medications or new medical conditions)
At every office visit.
This slender, calibrated dental instrument is used to measure the depth of the gingival sulcus or periodontal pockets around each tooth.
Periodontal Probe
The Frontal/Coronal plane divides the body into what? Use anatomical directional terminology.
Anterior + Posterior
What intraoral structure is this?
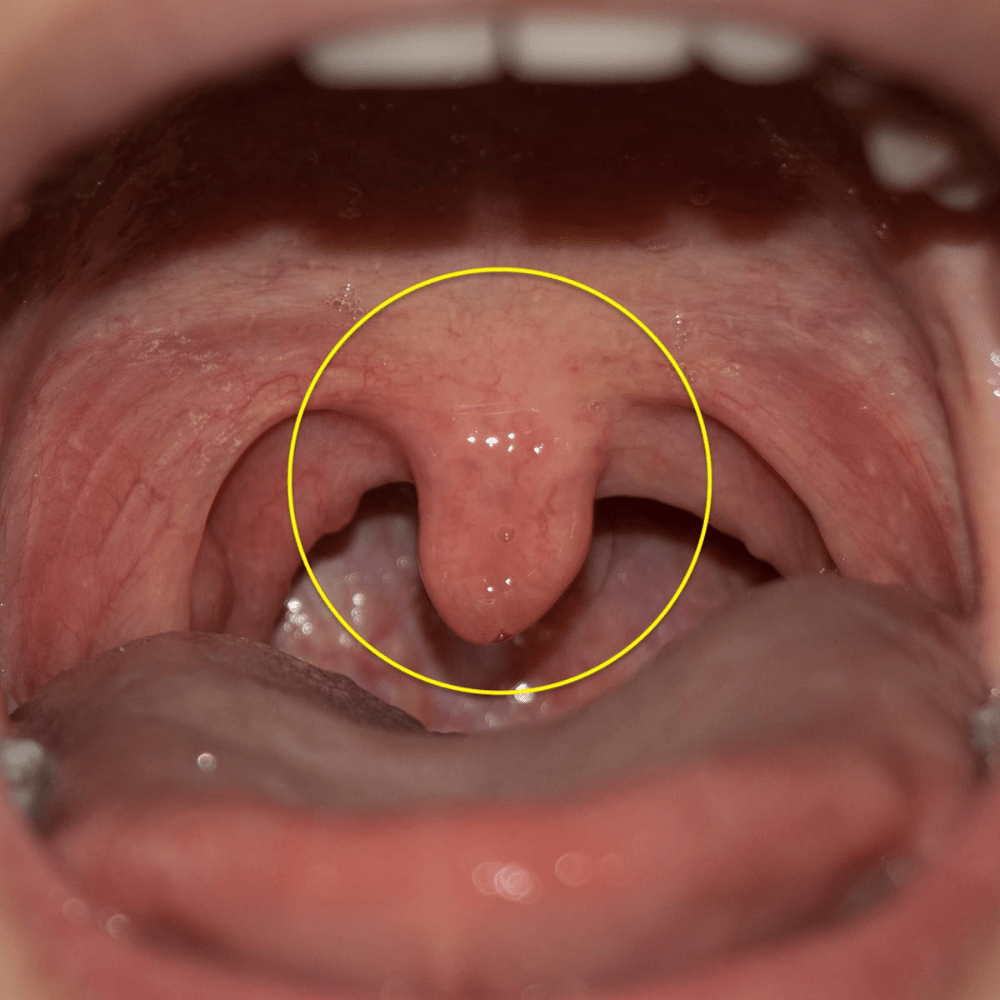
Uvula
What type of teeth are considered anterior teeth?
Which permanent teeth are bilaterally the smallest and most symmetric?
Permanent Mandibular Incisors
If a mistake was made while paper charting, how would you fix the error?
Use a single line to cross out the mistake, then inital/date the entry.
Bleeding on Probing indicates active gum inflammation.
What are the 4 structural units of the body in order from the smallest to largest?
Cells, Tissues, Organs, Body Systems
These papillae at the back of the tongue help with taste perception. 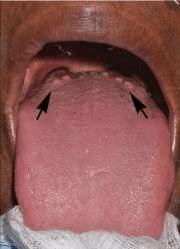
Which teeth are nonsuccedaneous?
All permanent molars.
What anatomical feature is highlighted in this photo?
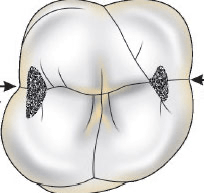
Triangular Fossa
What does HIPAA require all dental practices to have?
A written privacy policy.
To test for this, a clinician gently applies pressure in the buccal-lingual direction with two instrument handles.
Tooth Mobility
Which type of tissue lines the oral cavity?
Epithelial Tissue (Oral Mucosa)
What is the name of the line where pink gingiva meets more red alveolar mucosa?
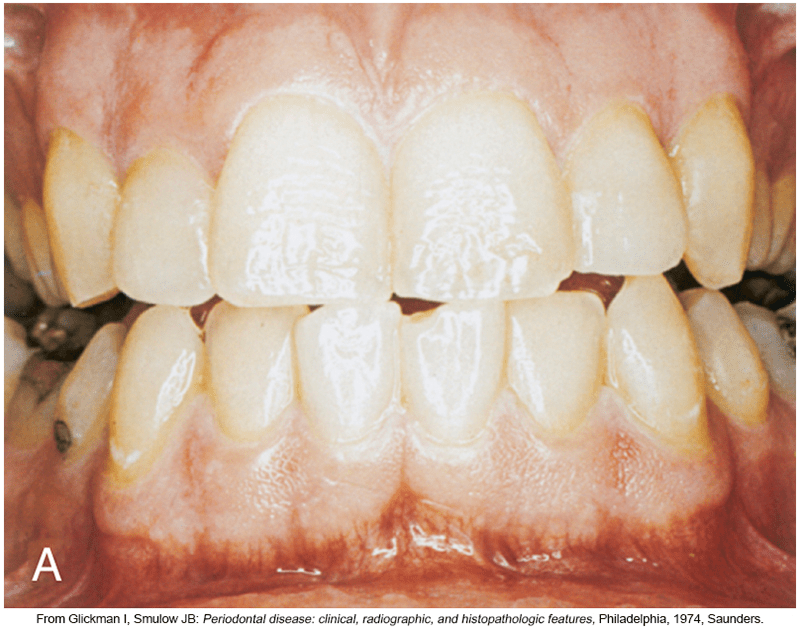
Mucogingival Junction (MGJ)
What are the 5 tooth surfaces of the permanent maxillary right second premolar?
Mesial, Distal, Buccal, Lingual, Occlusal
Which premolar has 2 roots?
Maxillary 1st Premolars
Pyo
Pus
To measure recession, the clinician records the distance between the gingival margin and this anatomical landmark.
Cementoenamel Junction (CEJ)
What is included within the axial region?
Head, Neck, & Trunk
The oral cavity can be divided into two major areas. What are their names?
Vestibule + Oral Cavity Proper
Using Angle's Classifications, what class is this? 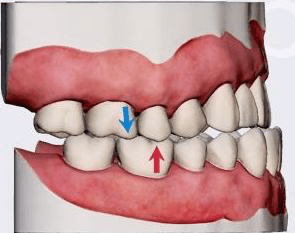
Class III
What is often the first permanent tooth to erupt in the oral cavity?
Permanent 1st Molars
What are the two areas of personal health information (PHI)?
Personal Information (Ex/ Tax information, credit card number, SS) + Health Information (Ex/ Any medical/dental history or treatment notes)
This term describes the tissues that surround and support the teeth, including the gums, periodontal ligament, cementum, and alveolar bone.
Periodontium