This is the most common type of skin cancer and often presents as a pearly or waxy lesion with rolled edges and central ulceration.
What is basal cell carcinoma
You are visiting a patient who is bed bound in a rehabilitation facility on a dermatology consultation. The patient is noted to have a full thickness pressure ulcer on the left hip with loss of skin. What is the stage of this ulcer?
What is stage 3

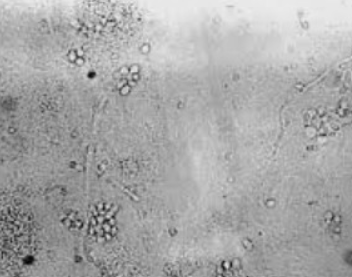
This fungal infection reveals a "spaghetti and meatball" type appearance with skin scraping under KOH prep.
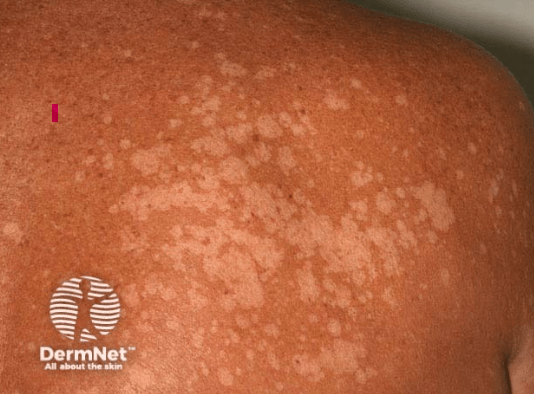
What is tinea versicolor/pityriasis versicolor
A 33 year old female presents to your office 3 weeks after returning from vacation in Mexico. She notes that her chronic condition flared after spending time "sipping margaritas on the beach"
On exam you appreciate the following and confirm this suspected diagnosis: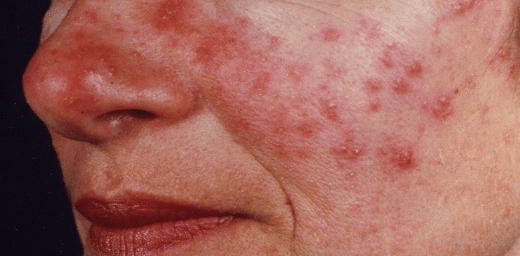
What is Rosacea
What is the trigger that is most common and most likely related to the patient's flare?
- Sun exposure
This sign, characterized by vesicles on the tip of the nose or the periorbital region, is a clinical clue for a viral infection involving this cranial nerve, which can indicate a serious risk of ocular complications.
Hutchinson's sign, CN V
The reason Hutchinson's sign is associated with eye involvement is that the nasociliary branch of the trigeminal nerve, which supplies sensation to the tip of the nose, also innervates parts of the eye.
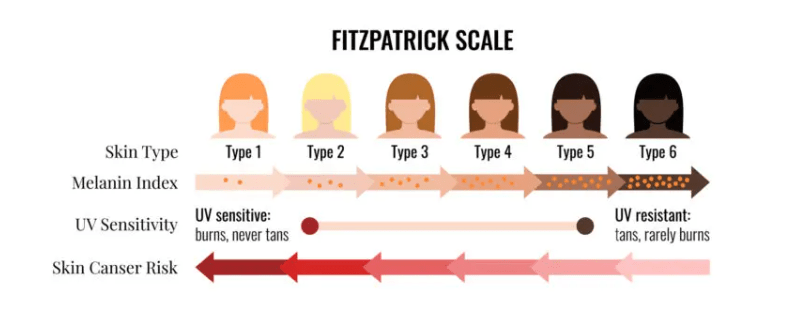
This scale is used to determine skin melanin index.
Fair skin with low melanin index is referred to as this Type.
Fitzpatrick
Fair skin, red hair, with low melanin index is referred to as this Type.
Type 1
This type of burn involves the epidermis and demonstrates erythema and minor microscopic changes.
• Pain is major complaint.
• No blister
• Dry
• No scar is left.
• Healing is complete in up to 10 days.
Classify this burn.
1st degree (superficial)
1st ---> 4th
less severe ---> more severe
This type of skin scraping preparation is used to better identify a fungal infection.
What is KOH
The exposure to this causes photoaging.
What are UVA Rays
This is the most common autoimmune blistering disorder of adult/elderly population and presents with sub epidermal blistering and negative Nikolsky sign
Bullous Pemphigoid
These are the 4 stages of what?
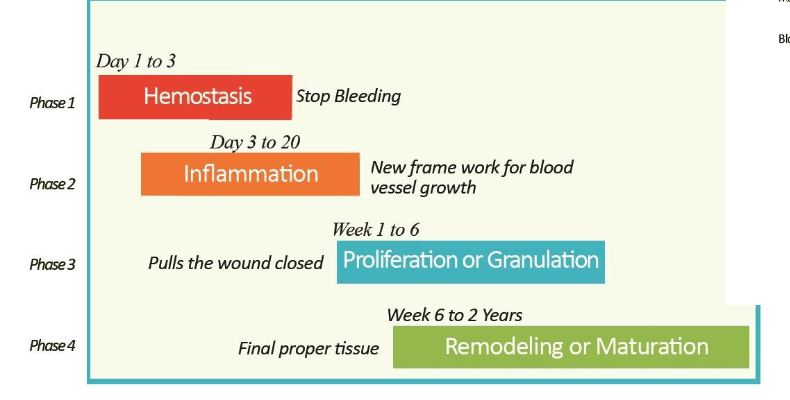
What is wound healing
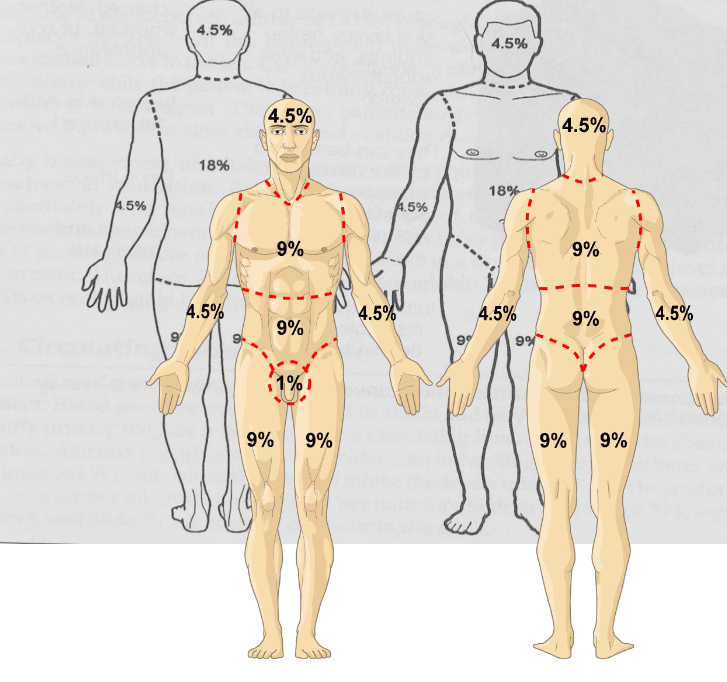
A patient sustained a burn to the entire left leg front and back. What is the percentage of body surface involved?
18%
This streptococcal cellulitis has a sharply defined and
slightly elevated border.
What is Erysipelas
This type of skin cancer often occurs in the sun exposed areas and can appear as a non-healing, friable, tender, nodule
Squamous cell carcinoma
This benign lesion is described as a superficial epidermal growth with a waxy, stuck-on appearance
What is Seborrheic keratosis
This single descriptor differentiates between a macule and a patch.
What is size
Macule: a flat colored lesion <1cm in diameter, non-palpable
Patch: a large flat colored lesion >1cm, non-palpable
Alyssa is a 27 year old female presenting with recurrent axillary abscesses. She has been seen 4 times in the last 12 mos for the same. On exam she has a single fluctuant, tender, erythematous mass under the left axilla. She does not have any appreciated tender inflammatory nodules, scars, or sinus tract formation. What is the diagnosis and what stage?
Hidradenitis supprativa
Hurley Stage I
This skin infection is caused by corynebacterium and glows coral red under woods lamp examination
This chronic autoimmune condition that primarily affects the skin, causes round, disc-shaped lesions. These lesions can become worse or be triggered by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light, such as sunlight or artificial UV light sources like tanning beds. One of the mainstays of treatment is photo-protection and avoidance of sunlight during peak hours.
What is discoid lupus
Franklin was camping over the weekend and is presenting with a pruritic, erythematous, vesicular rash on the right arm. On exam you note that the vesicles are in a linear pattern consistent with this most likely diagnosis.
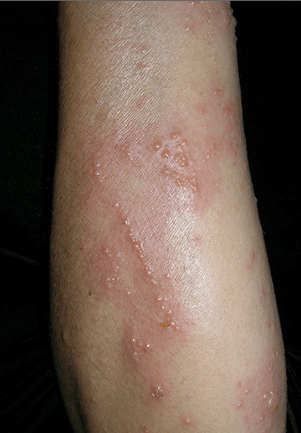
What is toxicodendron allergic contact dermatitis
Other common causes of allergic contact dermatitis?
Nickel (belt buckle or pant button common offender)
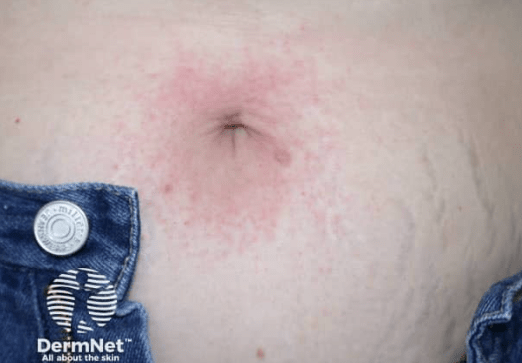
This primary lesion is described as a raised, erythematous, edematous papule or plaque with vasodilation, usually with well-defined borders. It is also involved in Darier sign.
What are wheals
also accept: hives, urticaria
A patient presents with recurrent episodes of vesicular lesions around the lips that ulcerate. They often occur after spending time outside.
Which of the following lab test can you order while the patient does not currently have symptoms to confirm your diagnosis?
HSV IgG antibodies
Which labs could you order if they have just recently been infected? IgM
What test could you do if there are vesicles present on exam? Tzank smear or viral culture
What are the first line treatments for mild acne
- comedonal
- papulopustular/mixed
Topical retinoid
Topical antimicrobial (salicylic acid, benzoyl peroxide, topical clindagel)
Also known as the "mask of pregnancy" this hyperpigmentation of the skin is often due to hormonal influence, genetics, and UV exposure.
What is Melasma
One component of treatment: avoid sun/photo-protection
A patient presented 1 week ago with a single, large, oval patch, pinkish red in color, with a slightly raised, scaly border. 2 days later they returned with a more diffuse rash confirming your suspected diagnosis
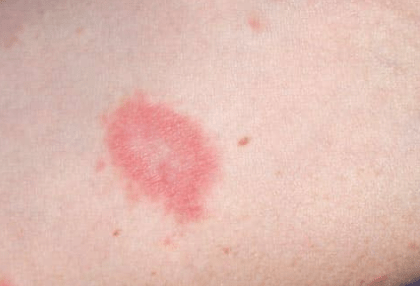
What is a herald patch/pityriasis rosea
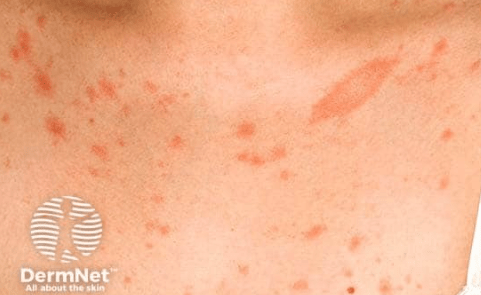
Name 3 types of secondary lesions
- Scale: Flakes of dead skin (e.g., dandruff or scaling in psoriasis/ excessive stratum corneum).
- Crust: Dried serum, blood, or pus on the surface (e.g., scab).
- Excoriation: Linear scratches or abrasions often caused by scratching.
- Lichenification: Thickened, leathery skin due to chronic scratching or rubbing.
- Ulcer: A deeper loss of skin tissue, sometimes reaching the dermis or subcutaneous layers.
- Scar: Fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin following injury or healing.
- Fissure
- Atrophy
Secondary lesions are changes that occur to primary lesions over time due to progression, healing, scratching, infection, or other external factors. Secondary lesions often reflect an evolution in the skin condition and may signal a chronic or worsening problem.
This acrosclerotic skin condition can lead to sclerodactyly or "claw deformities"
What is scleroderma
Gottron’s papules – pathognomonic for this condition are described as; red flat-topped papules over knuckles and sides of fingers.
What is dermatomyositis