This benign neonatal rash presents with erythematous macules and papules with central pustules, sparing palms and soles.
What is erythema toxicum neonatorum?
A benign newborn rash characterized by red macules, papules, and pustules—often described as “flea‑bitten” appearance. Typically appears within the first week of life and resolves without treatment
This genetic condition causes blisters with minimal trauma.

What is epidermolysis bullosa?
Group of genetic skin disorders characterized by extremely fragile skin that blisters and tears easily from minor friction or trauma
"Honey-colored crusts" are classic for this condition.
What is impetigo?
This periorbital rash with proximal muscle weakness suggests an autoimmune connective tissue disease.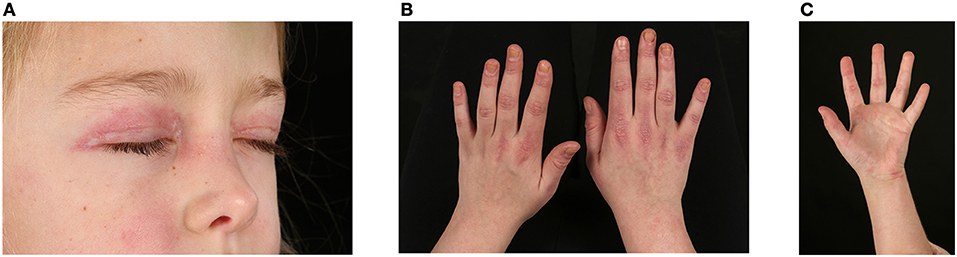
What is juvenile dermatomyositis?
Skin rash: A characteristic sign of JDM is a skin rash, which can be reddish or purplish and appear around the eyelids, knuckles, finger joints, elbows, and knees. It can also occur on the face, chest, and back.
First-line topical treatment for mild acne.
What is benzoyl peroxide and topical retinoids?
Mild: Topical retinoids (tretinoin, adapalene) and benzoyl peroxide.
Moderate: Combination therapy with topical retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, and topical or oral antibiotics (doxycycline, minocycline).
Severe: Oral isotretinoin for nodulocystic and treatment-resistant acne, requiring monitoring for side effects and teratogenicity.
Diaper dermatitis with satellite lesions is caused by this fungus.
What is Candida albicans?
This viral infection causes grouped vesicles on an erythematous base, often around the mouth.
What is herpes simplex virus (HSV)?
This dermatophyte infection affects the scalp and may require oral antifungals.
What is tinea capitis?
More than 6 Café-au-lait macules are associated with this genetic disorder.
What is neurofibromatosis type 1?
The diagnosis requires the presence of two or more of the NF1 diagnostic criteria.
Other criteria include:
-Skin-fold freckling (in the armpits or groin),
- Neurofibromas,
-Lisch nodules (on the iris of the eye),
-Optic pathway gliomas,
-Distinctive bone lesions,
-Having a family history of NF1.
Emollients are the cornerstone of management for this chronic itchy condition.
What is atopic dermatitis (eczema)?

What is harlequin color change?
Harlequin color change (HCC), also known as the harlequin sign, is a temporary and harmless skin condition in newborns where one half of the body appears red or flushed, while the other half is pale. This occurs due to a temporary imbalance in the regulation of blood vessel tone, likely related to the immaturity of the newborn's nervous system. The color change is usually well-defined at the midline and is typically seen between the second and fifth days of life, though it can appear as late as three weeks. The episode is brief, lasting from seconds to minutes, and may recur.
Target lesions are the hallmark of this condition often triggered by infections.
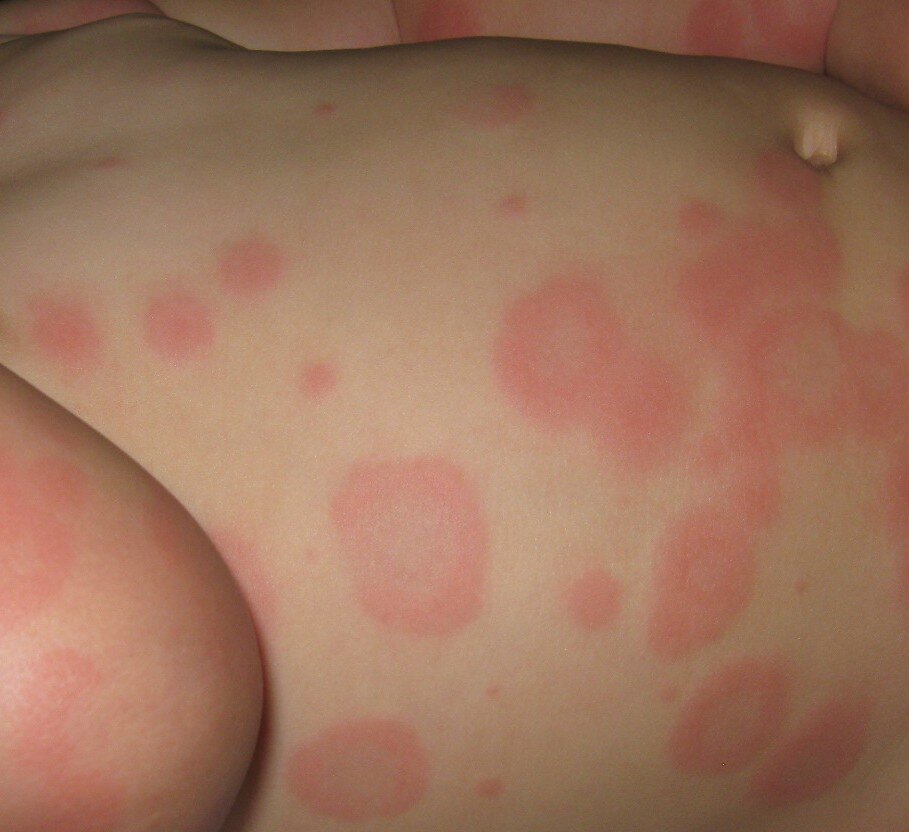
What is erythema multiforme?
A "Christmas tree pattern" of pink plaques on the trunk is typical of this condition.
What is pityriasis rosea?
This “slapped cheek” rash is caused by ...
What is parvovirus B19?
First-line treatment for tinea corporis.
What is topical antifungal (clotrimazole)?
What is transient neonatal pustular melanosis?
Self-limited condition presents with vesicles and pustules on a hyperpigmented base in darker-skinned newborns.
Widespread blistering and mucosal involvement in a febrile child suggests this severe reaction.
What is Stevens-Johnson syndrome?
Molluscum contagiosum is caused by this virus family.
What is poxvirus?
Lacy reticular rash on the extremities may indicate this autoimmune disease.
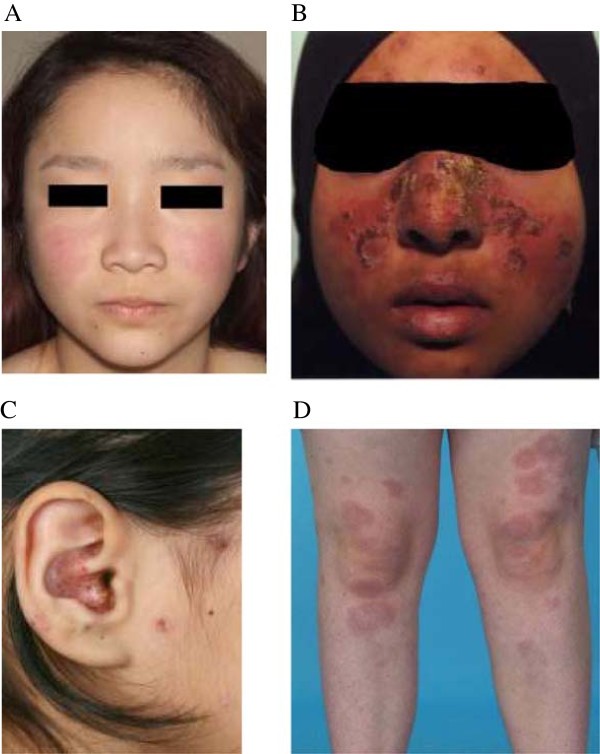
What is lupus erythematosus?
LE specific skin lesions: (A) Malar (butterfly) rash (mild symptom); (B) Malar rash with interface dermatitis; (C) Crusting and interface changes affecting the ear; and (D) Generalized ACLE or maculopapular lupus rash at both knees.

This medication is contraindicated in children <8 years due to dental staining.
What is doxycycline?
This life-threatening condition presents in neonates with generalized redness and blistering due to exfoliative toxin.
What is staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome?

This condition has linear vesicles following Blaschko’s lines in infants.

What is incontinentia pigmenti?
Incontinentia Pigmenti (IP) is a rare genetic disorder primarily affecting females, characterized by distinctive skin changes, and can also impact hair, teeth, eyes, and the nervous system. It's caused by a mutation in the IKBKG gene on the X chromosome and inherited in an X-linked dominant manner. Males with IP are rare, often due to Klinefelter syndrome or genetic mosaicism.
This sexually transmitted disease can present with condyloma lata in children due to congenital infection or abuse.
What is syphilis?
A child with petechiae, hepatosplenomegaly, and pancytopenia may have this underlying condition.

What is leukemia?
Systemic retinoid used for severe nodulocystic acne with teratogenicity concerns.
What is isotretinoin?