For the following situations involving sampling, identify—as precisely as possible—the population that the sample represents.
An insurance company wants to monitor the quality of its procedures for handling loss claims from its auto insurance policyholders. Each month the company selects an SRS of all auto insurance claims filed that month to examine them for accuracy and promptness.
Population is all auto claims filed in a given month for this insurance company
A medical study of heart surgery investigates the effect of a drug called a beta-blocker on the pulse rate of the patient during surgery. The pulse rate will be measured at a specific point during the operation. The investigators will use 20 patients facing heart surgery as subjects. You have a list of these patients, numbered 1 to 20, in alphabetical order.
Use the section from the random digits table below to carry out the randomization required by your design and list the outcome of the randomization.
96746 12149 37823 71868 18442 35119 62103 39244
96927 19931 36809 74192 77567 88741 48409 41903
43909 99477 25330 64359 40085 16925 85117 36071
15689 14227 06565 14374 13352 49367 81982 87209
36759 58984 68288 22913 18638 54303 00795 08727
The first 10 patient numbers are 18, 19, 10, 03, 06, 08, 11, 15, 13, 09. These patients will constitute the treatment group. The remaining 10 patients will be in the control group.
For the study described below, comment on the extent to which inferences can be drawn about a larger population and whether cause and effect can be established.
A football coach thinks lessons in yoga will improve the flexibility of his players and thereby reduce injuries. To test his theory, he randomly divides the players on the team into two groups. One group has 45 minutes of yoga training each day. The players in the other group do the standard stretching routine the team has used in the past. He compares flexibility in the two groups at the end of the experiment.
Random assignment-->cause and effect can be inferred. No random sampling-->Cannot generalize beyond the subjects of the study.
Is "final grade of a course (A, B, C, D, F)" a categorical or quantitative variable?
Categorical
The actor who plays Elf in the 2003 movie.
Will Farrell
In late 1995, a Gallup survey reported that about 46% Americans approved of sending troops to Bosnia. The poll did not mention that 20,000 U.S. troops were committed to go. A CBS News poll mentioned the 20,000 figure and got a different outcome—an approval rate of only 33%. Briefly explain why the mention of the number of troops would cause such a big difference in the poll results. Write the name of the kind of bias that is at work here.
This is bias arising from the wording of a question. Knowledge of how many troops were going to be deployed increased people’s concerns about troop safety.
A family restaurant chain wants to test the market for a new menu item: a grilled chicken sandwich with chipotle salsa. They are interested in both how to market the item and the right price to charge for it. They decide to offer the sandwich at 60 different restaurants in the chain, using two different descriptions on the menu. Half the restaurants’ menus will emphasize ―healthy eating (and half will emphasize ―value). These two groups of restaurants will be further divided in three groups, each charging either a High, Medium, or Low price for the sandwich. After a month, they will measure what proportion of customers order the new sandwich.
Suppose the company plans to conduct a completely randomized design. List the experimental units, factors (explanatory variables), and treatments in this experimental design (there are 6 of them).
Experimental units: the 60 restaurants. Factors: menu description and price. Treatments: Healthy-High price, Healthy-Medium price, Healthy-Low price, Value-High price, Value-Medium price, Value-Low price.
For the study described below, comment on the extent to which inferences can be drawn about a larger population and whether cause and effect can be established.
Does lack of sleep affect your academic performance? A student explores this question by asking everyone in his statistics class to write down on a piece of paper his or her score on a recent test and total number of hours of sleep he or she got on the last three nights before taking the test.
No random assignment-->cause and effect cannot be inferred. No random sampling-->Cannot generalize beyond the subjects of the study.
Suppose that you have a least squares regression line of y = 1.65 - 2.2x and that we have a point (10, -19). Find the residual.
1.35
The Charles Dickens' classic, A Christmas Carol, recounts the story of an elderly miser named . . .
Ebenezer Scrooge
A church group interested in promoting volunteerism in a community chooses an SRS of 200 community addresses and sends members to visit these addresses during weekday working hours to inquire about the residents’ attitudes toward volunteer work. Sixty percent of all respondents say that they would be willing to donate at least an hour a week to some volunteer organization. Bias is present in this sample design. Identify the type of bias involved and state whether you think the sample percent obtained is higher or lower than the true population percent.
Sampling only during workday hours meant that only people without regular daytime jobs were available to answer the door—the poll suffered from undercoverage of people who were employed. Since those who are not employed may be more likely to have time to volunteer, the poll probably overestimated the proportion of potential volunteers. There is also potential response bias: a people is likely to say he or she will volunteer to look like a good person.
A family restaurant chain wants to test the market for a new menu item: a grilled chicken sandwich with chipotle salsa. They are interested in both how to market the item and the right price to charge for it. They decide to offer the sandwich at 60 different restaurants in the chain, using two different descriptions on the menu. Half the restaurants’ menus will emphasize ―healthy eating (and half will emphasize ―value). These two groups of restaurants will be further divided in three groups, each charging either a High, Medium, or Low price for the sandwich. After a month, they will measure what proportion of customers order the new sandwich.
Suppose that 30 of the restaurants in the study are free-standing buildings and the other 30 are located inside malls. The company suspects that the different building types may have impact on how people respond to the advertising campaign and the price. How might they alter the design of this experiment to take this into account?
Block for building type: randomly assign the six different treatments to the 30 free-standing buildings, the do the same to the 30 mall restaurants, so that there are exactly five of each building type assigned to each treatment.
For the study described below, comment on the extent to which inferences can be drawn about a larger population and whether cause and effect can be established.
Does ―Cold-Cut, a popular over-the-counter cold remedy that claims to reduce the length and severity of colds really work? A consumer advocacy group addresses this question by asking a random sample of 400 adults how many colds they’d had in the last six months, how long each cold lasted, and if they took "Cold-Cut" to treat the cold.
No random assignment-->cause and effect cannot be inferred. Random sampling-->Can generalize to population from which the random sample was selected.
A data set has only positive values. If the largest value of a data set is doubled, which of the following is NOT true?
a) The mean increases
b) The range increases
c) The IQR increases
d) The standard deviation increases
In the 2004 movie, The Polar Express, how did the hero boy lose the bell?
He has a hole in his pocket that it falls through
Each state conducts an annual study of seat belt use by drivers following guidelines set by the federal government. Seat belt use is observed at randomly chosen road locations at random times during daylight hours. The locations are based on counties within each state. In Hawaii, the counties are the islands that make up the state’s territory, and the survey is conducted on the 4 most populated islands: Oahu, Maui, Hawaii (referred to as ―The Big Island‖), and Kauai. The sample sizes on the islands are proportional to the amount of road traffic., so each location is equally likely to be selected.
Is this a SRS of road locations in the state of Hawaii? Explain.
No. Not every group of locations is equally likely to be selected. It’s impossible, for example, to have a sample of locations that are all on Oahu. This is a stratified random sample.
A medical study of heart surgery investigates the effect of a drug called a beta-blocker on the pulse rate of the patient during surgery. The pulse rate will be measured at a specific point during the operation. The investigators will use 20 patients facing heart surgery as subjects. You have a list of these patients, numbered 1 to 20, in alphabetical order.
Describe the design of a completely randomized, controlled experiment to test the effect of beta-blockers on pulse rate during surgery.
Use a random number table to choose ten 2-digit numbers from 01 to 20, ignoring repeats. The patients with these numbers will receive the beta-blocker during their operation. The remaining 10 people will act as a control group and will not receive the beta blocker. Measure pulse rate of all patients at the specified point in the operation, and compare the difference in mean pulse rate for the two groups.
Do abandoned children placed in foster homes do better than similar children placed in an institution? The Bucharest Early Intervention Project found that the answer is a clear “Yes.” The subjects were 136 young children abandoned at birth and living in orphanages in Bucharest, Romania. Half of the children, chosen at random, were placed in foster homes. The other half remained in the orphanages.55 (Foster care was not easily available in Romania at the time and so was paid for by the study.) What conclusion can we draw from this study? Explain.
Because this study involved random assignment to the treatments, we can infer that the difference between foster care or institutional care caused the difference in response.
Does the following graph show any outliers? Discuss.
No, the 1.5(IQR) test shows there are no outliers.
In the 1983 movie, A Christmas Story, which Christmas gift does Ralphie want so badly?
A red rider BB gun
Suppose there are 476 possible road locations on Kauai, Hawaii and we need to randomly select 22 of them to be in a sample. Use the random digits table below, choose the first 3 road locations for the seat belt survey sample. Explain your method clearly.
35476 55972 39421 65850 04266 35435 43742 11937
71487 09984 29077 14863 61683 47052 62224 51025
13873 81598 95052 90908 73592 75186 87136 95761
Make sure assigned digits are all the same length and that sampling is done without replacement. If we selected the first three 3-digit numbers between 001 and 476, they will be 354, 239, and 421.
A college fitness center offers an exercise program for staff members who choose to participate. The program assesses each participant’s fitness using a treadmill test, and also administers a personality questionnaire. There is a moderately strong positive correlation between fitness score and score for self-confidence. Explain why it would not be possible to conclude from this study that the exercise program increases one’s self-confidence.
Since this was an observational study, we cannot establish cause and effect. It’s possible, for instance, that people with more self-confidence are more likely to choose to exercise. That is, people’s personality might be a confounding variable.
According to Louann Brizendine, author of The Female Brain, women say nearly three times as many words per day as men. Skeptical researchers devised a study to test this claim. They used electronic devices to record the talking patterns of 396 university students who volunteered to participate in the study. The device was programmed to record 30 seconds of sound every 12.5 minutes without the carrier’s knowledge. According to a published report of the study in Scientific American, “Men showed a slightly wider variability in words uttered.... But in the end, the sexes came out just about even in the daily averages: women at 16,215 words and men at 15,669.” This difference was not statistically significant. What conclusion can we draw from this study? Explain.
Because this study did not involve random assignment to a treatment, we cannot infer cause and effect. Also, because the individuals were not randomly chosen, we cannot generalize to a larger population.
Compare the following distributions:
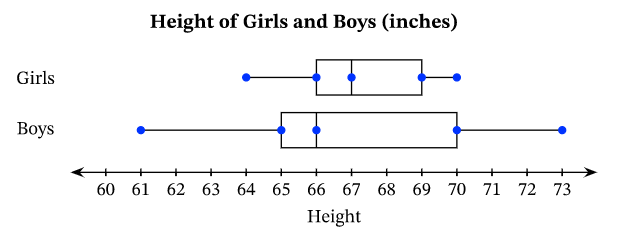
SOCS in context with comparative terms.
In the 1989 comedy National Lampoon's Christmas Vacation, what had Clark Griswold been planning to buy with the Christmas bonus he expected from work?
A swimming pool