During a femoral artery insertion of the IAB, this is proper placement of the IAB tip.
What is: Just distal to the left subclavian artery or between 2nd and 3rd intercostal space.
The amount of heparin to be added to one liter of NS to prepare anticoagulant solution for ATS cases.
What do BTR and BTT stand for?
BTR: Bridge to recovery
BBT: Bridge to transplant
What does eCCO2R stand for?
Extracorporeal carbon dioxide removal
True or false: In order for central cannulation, the chest needs to remain open.
True
What are three complications of ECMO?
Bleeding, hemorrhage, stroke (air or clots), SIRS, kidney injury (or failure), hemolysis, infections, neurologic injury
This determines the correct catheter size.
What is the height of the patient?
In a centrifugal ATS bowl, when blood components separate, red blood cells comprised this layer of the bowl.
What is the outermost layer?
What are two common complications of VAD use/ support?
Stoke (embolized clot), infections, bleeding, hemolysis, arrhythmias
What is the dicrotic notch?
Type of ECMO used for ARF
VV (veno-venous ecmo)
What does "chugging" mean during ECMO, and what are the two possible causes?
The vessel or RA collapsing around the drainage cannula, either because of malposition, hypovolemia, or both.
Inflation of the IAB increases myocardial oxygen supply by increasing these two events.
What is diastolic augmentation and coronary artery perfusion?
When separating blood components via centrifugation for platelet rich plasma, these components comprise the center layer.
What are platelets and buffy coat?
What is "Ecpella", and why would one use it?
ECMO + Impella-- ECMO for systemic support, and Impella to unload the LV
Reduction of the power expenditure of the ventricle when on an LVAD is referred to as...
(LV) unloading)
This type and location of cannulation requires a DLP.
Femoral VA ECMO
What is the appropriate RPM to establish ECMO flows, and why?
1800-2000 to overcome the initial afterload of the patient
The primary effects of IABP counterpulsation are (2 answers)
What is decrease myocardial oxygen demand and increase myocardial oxygen supply?
The time in which processed ATS blood must be reinfused.
What is 6 hours from processing?
What is an example of a centrifugal VAD?
Heartmate III, Heartware
What year was the first successful ECMO? Hint: It was on a neonate
1975
Type of ECMO for failure to wean from cardiopulmonary bypass
VA (veno-arterial) ECMO
Regarding ECMO, what does "delta P" describe?
Change in pressure between the "PreOxy" pressure and "PostOxy" pressure to describe the resistance (and therefore the presumed clot) within the oxygenator.
The preferred trigger while using IABP.
What is ECG?
To form platelet gel, this is required to activate the platelet rich plasma (2 items).
What are thrombin and calcium chloride?
This VAD drains blood flow from the LA via an external pump, and reinfuses it to the femoral artery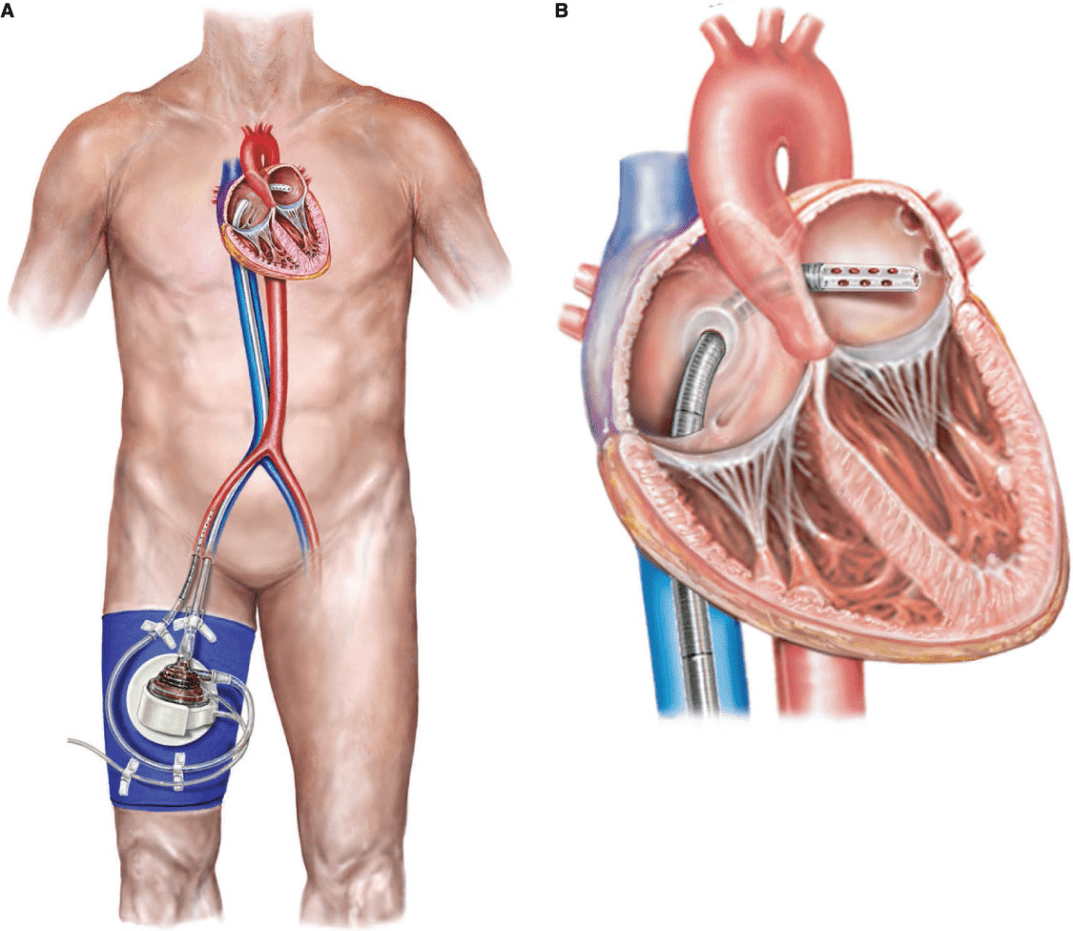
The TandemHeart
21-100% FiO2, and 0-10 LPM sweep (with the potential of an extra LPM for a total of 11 LPM)
The surgeon wants to this VV ECMO patient to be able to be ambulated in the ICU. What cannulation strategy would you recommend?
Neck cannulation, with a dual-lumen cannula
You put a respiratory failure patient on ECMO. The drainage cannula and the reinfusion cannula are both bright red. What are your next steps, and why?
Check the pulse oximetry of the patient, draw a patient VBG, PreOxy gas, Post oxy gas to calculate recirculation. Concern for recirculation >20%
Regarding IAB timing, there is an increase in LV afterload AND a decrease in cardiac output.
What is early inflation?
This is the minimum micron size for ATS blood reinfusion filter.
What is 40 microns?
Heartmate II, Impella
This was the first commercially available autotransfusion device.
What is the Bentley ATS 100?
This cannulation strategy provides both pulmonary and cardiac support, but divides the inflow between the venous side and the arterial side.
VAV
Parallel (as opposed to series)
Regarding IAB timing, minimal diastolic augmentation, lack of reduction in myocardial oxygen demand and LV afterload.
What is early delfation?
A contraindication to using ATS, Floseal (or any hemostatic agent) causes this.
What is platelet aggregation/clot formation?
What is a difference between the Impella 5.5 and the Impella CP?
Higher flow capabilities with the 5.5 (up to 5.5LPM versus 4.3 LPM)
5.5 is implanted surgically through the axillary artery, whereas the CP is percutaneous
5.5 is typically longer term VAD support, CP is typically shorter term/ rescue
What was name of the commonly referenced trial that showed that ECMO shows advantages over conventional ventilatory support for severe respiratory failure?
CESAR (Conventional ventilatory support vs. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for Severe Adult Respiratory failure)
Clot in the right heart mobilized and wedged in a distal pulmonary artery. Which type of ECMO would be more appropriate?
What is VV ECMO
When on ECMO, what is the appropriate therapeutic ACT, aPTT, and Anti-Xa?
ACT, goal is typically 180- 220 sec
aPTT goal is 1.5-2.5 x baseline (40 to 80 seconds)
Anti-Xa goal is 0.3-0.7 IU/ mL