This type of fracture involves a clean break across the root and often results in crown mobility
What is a root fracture?
This periapical condition results in a painful, throbbing sensation and is caused by pulpal death
What is acute periapical abscess?
How far from the CEJ is the healthy alveolar crest normally found?
What is 1.5-2 mm
This radiographic technique is preferred for periodontal evaluation
Which type of resorption shortens the length of a tooth's root?
What is External Resporption?
This type of trauma results in the tooth appearing longer than adjacent teeth.
What is extrusion?
Calcification of the pulp chamber, that decreases the size of the pulp chamber.
What is Pulpal Sclerosis?
This bone loss pattern appears uneven and slanted on radiographs.
What is Vertical Bone loss?
This structure appears as a thin radiopaque line surrounding the tooth root?
What is the lamina dura?
This furcation class can be visually seen on a radiograph.
What is Class III and or Class IV?
This condition refers to partial displacement of teeth due to trauma.
What is luxation?
Which pulpal lesion appears radiographically as round, ovoid radiopacities within the pulp?
What is Pupal Stones?
Which grading level indicatesWhich grading level indicates rapid rate of progression?
What is Grade C
This radiopaque lesion is found in nonvital teeth with long-standing pulpitis
This type of trauma results in the tooth appearing shorter than adjacent teeth.
What is Intrusion?
This traumatic injury involves the labial and palatal plates and may show a radiolucent line on a radiograph.
What is a maxillary fracture?
A nonvital tooth with radiographic radiolucency but no symptoms likely has this lesion.
What is a periapical granuloma?
This periodontal stage involves furcation involvement and vertical bone loss.
What is Stage III
This condition appears as a well-defined radiopacity below the apex of a vital tooth
What is sclerotic bone?
What should be documented in the patient chart when it comes to Lesions.
What is appearance, location and size?
This type of Radiograph is the only way to see a mandibular fracture
What is a panoramic radiograph?
Which pulpal lesion results in no visible pulp chamber or canals?
What is pulpal obliteration?
Name this Stage of Periodontal disease
What is Stage II
What condition is present on #19
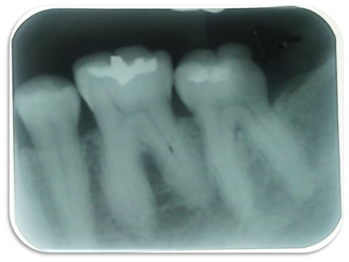
What is Hypercementosis?
This stage of periodontal disease can be seen as an indistinct fuzziness of the crestal lamina dura.
What is Stage I?