Classic presenting symptoms of diabetes
polyphagia - increased hunger
polyuria- increased urination
polydipsia - increased thirst
weight loss
blurred vision
Increased intake of this food associated with increase in risk of type 2
Red meat
Tobacco use also increases risk
1st line treatment for Hgba1c >9 without symptoms
GLP-1 or Long Acting Insulin
If >10, Insulin or Sulfonylurea (if injection declined) - need something that has rapid onset of lowering blood sugars
Earliest finding of diabetic nephropathy
Increased urinary protein excretion
>30mg/day
Timing and Cut off value for Glucola
(50g 1 hr challenge)
24-28 weeks and 135
If positive, needs 3 hr GTT (100g)
fasting 95
1 hr 180
2 hr 135
3 hr 140
Screening guidelines per USPSTF
Adults 35-70 every 3 years for BMI>25
Every year for patients with prediabetes
Diet that has the most evidence for diabetes prevention
Mediterranean Diet
LDL goal for DM & CVD
<55 mg/dl
all diabetics are recommended to be on a moderate or high dose statin
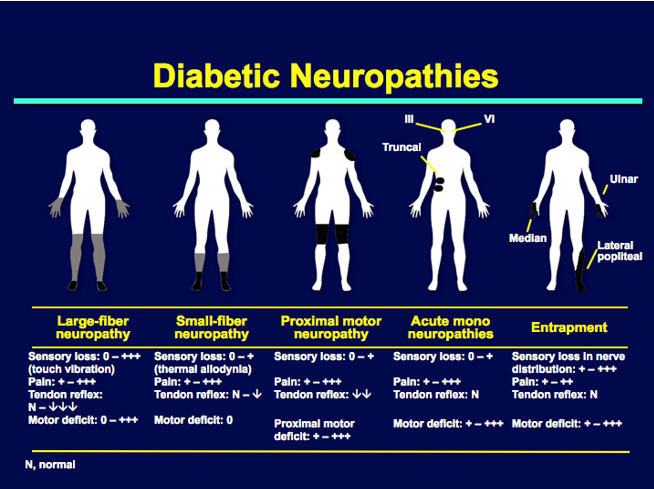
Symptoms of diabetic neuropathy
Burning, Numbness, tingling, poor balance, electric shocks, stabbing
Risks of untreated gestational diabetes
Large for gestational age infants (Shoulder dystocia, caesarean section)
Increased pre-eclampsia
Risk Factors for diabetes
1st degree relative
h/o CVD, PCOS, HIV, pancreatitis
HTN>130/80; HDL<35; TG>250
Minimum amount of exercise for potential diabetes prevention
150 minutes per week
1st line treatment recommended in patients with CKD or CHF
SGLT2 inhibitor
Recommended for secondary protection of CV events in diabetic patients
ASA 81-162 mg daily
SMOKING CESSATION!
Medications that can be used in pregnancy
Metformin
Glyburide
Insulin (preferred)
*all compatible with breastfeeding
Lab tests that distinguish between type 1 and type 2
Fasting C peptide level
Islet auto antibodies such as GAD65, Insulin, Tyrosine Phosphatase
Medication (name and dose) that has been studied in DPP trials
Metformin 850mg BID
Supplements that potentially help with diabetes
Chromium
Vitamin D
Most potent monotherapy in terms of a1c reduction
2-2.5 with combination monotherapy (GLP-1/GIP) once weekly injections
Findings of diabetic retinopathy
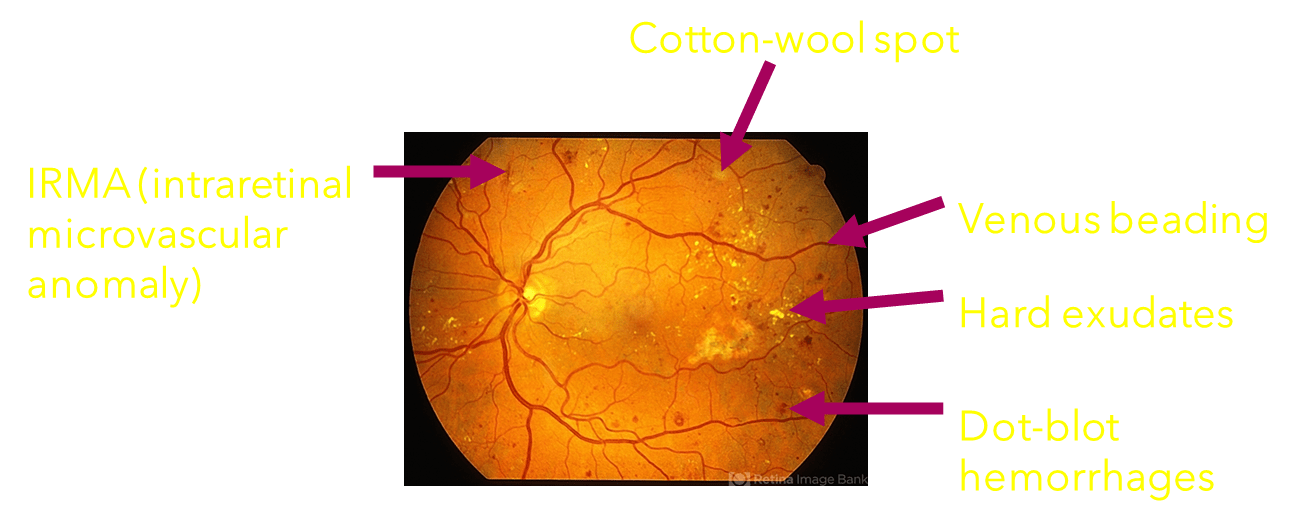
Proliferative and Non Proliferative Diabetic retinopathy
leading cause of preventable blindness among working adults between the ages of 20 and 74 years
Prior to conception
1st trimester
Postpartum
Diagnostic criteria for diabetes and prediabetes
FBG>126 (8 hrs); FBG 100-125
A1c >6.5; A1c 5.7-6.4
Random BG>200
Goals of prevention
Preventing/delaying onset of DM
Preserving B cell function
Delaying microvascular and cardiovascular complications
Minimal weight reduction goal to improve a1c
7% of current body weight
Vaccine recommended specifically for diabetics
Hepatitis B
Influenza, Pneumovax, Covid, Tdap
Recommended followup for patients diagnosed with gestational diabetes
Screening at postpartum visit (a1c or 75g GTT)
Lifelong screening every 3 years