Karyotype (47,XXY)
Klinefelter Syndrome
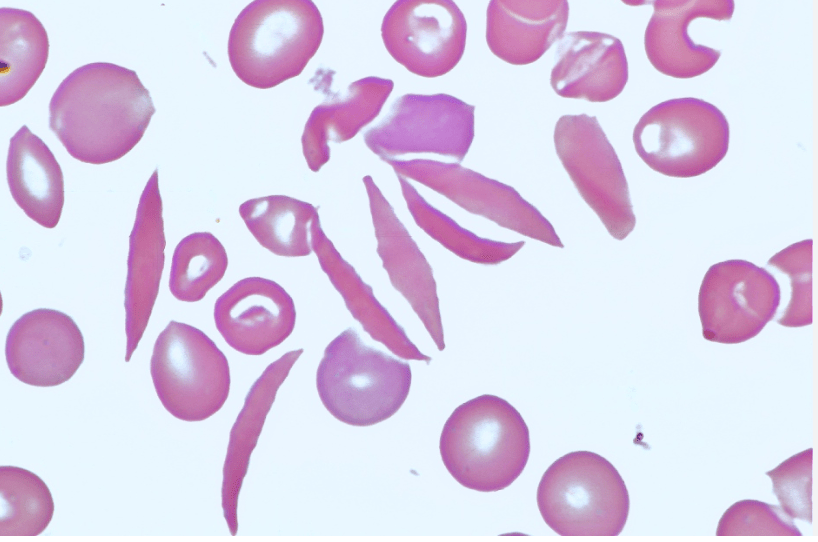
This is a disease caused by a single point mutation and is treated by...
Gene therapy to increase expression of y globin in red blood cells
Presents with lighter skin and hair, rapid loss of intelligence during the first year of life.
This disease is caused from the inability for PAH to catalyze this reaction
Conversion of phenylalanine to tyrosine
(PKU)
X linked disorder that causes progressive muscle weakness, Gower maneuver to stand up
Duchenne's/Becker Muscular Dystrophy
Inheritance:AR
Etilogy: beta hexoaminidase A deficiency
Presentation: cherry red spot, progressive neurodegeneration
Tay-Sachs Disease
Bonus Point: What the main difference between this and Niemann-Pick disease?
Presents 3-6 months of age with hepatomegaly, sever fasting hypoglycemia, protuberant abdomen poor growth. This is caused by a deficiency on glucose-6-phosphatase
Von Gierke disease
Kids should be screened for these two familial cancer syndromes
Familial Adenomatous Polyposis and Li Fraumeni Syndrome
This disease presents with elevated sweat chloride, frequent lung infections, difficulty clearing mucus and pancreatic insufficiency. What is the most common mutation for this condition?
F508del
(Cystic Fibrosis)
Interitance: X linked
Etiology: impaired formation of NADPH.
Clinical Presentation: varies depending on residual enzyme activity
Severe: Chronic Hemolytic anemia, hemoglobinuria, jaundice
Acute hemolytic anemia to exposure to oxidants
Glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
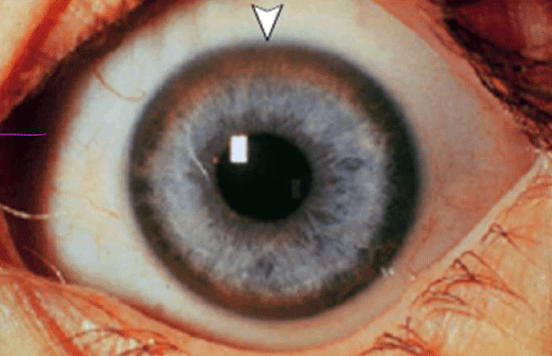 This is known as the Layser Fleischer Ring. This is a characteristic finding of what disease.
This is known as the Layser Fleischer Ring. This is a characteristic finding of what disease.
Wilson's Disease
Autoantibodies for cancer cells or autoimmune diseases that mimic Voltage gated calcium channels cause this disease.
LEMS (Lambert Eaton)
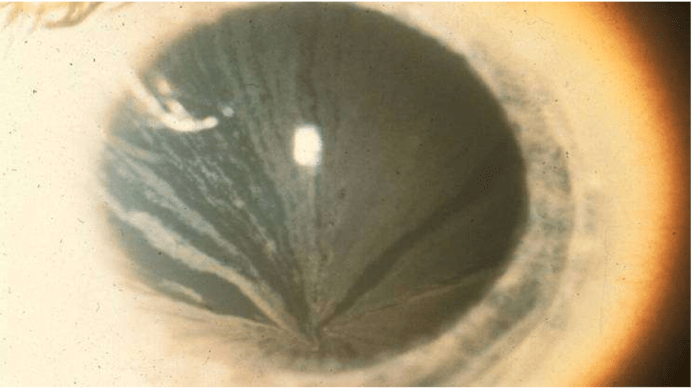
This X linked disorder causes the condition above due to a deficiency in Alpha-galactosidase A
Fabry Disease
This is caused by a deficiency in the glycogen debrancher enzyme
Cori Disease
Caused by a genetic defect that affects normal function of fibrillin.
Individuals tend to be tall, slender, and with long limbs and digits. Tha fatigue rapidly during exercise
Marfan Syndrom
This autosomal recessive disease presents with failure to thrive, developmental delay UV sensitivity, cataracts and a progeria like appearance
Cockayne Syndrome
Inheritance: AR
Etiology: mutation in beta globin gene
Presentation: pale conjunctiva, microcytic anemia, chipmunk face
Treatment: depends on severity (none-transfusions-splenectomy, iron chelation therapy)
Beta Thalassemia
X linked recessive disorder that is caused by a deficiency in hypoxanthine-guaninephosphoribosyltransferase. This disease is caused by an up regulation of what pathway
Synthesis of purines
Bonus Points: Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome
Auto antibodies that attach nicotinic ACh receptors causing muscle weakness
Myasthenia Gravis
Hunter and Hurler's syndrome cause a build up of what substance
Dermatan Sulfate, heparan Sulfate
This presents with fasting hypoglycemia in infancy but No muscle weakness. Tolerance also seems to improve with age. This disease is also consider less severe than other GSDs
Glycogen Storage Disease type 0
AKA Hepatic Glycogen Synthase Deficiency
Presents with soft stretchable skin, hypermobile joints, poorly healing wounds. This is caused by a defect in assembly of what type of connective tissue
Type 3 collagen (some more sever types have type 1 involvement)
Ehlers-danlos
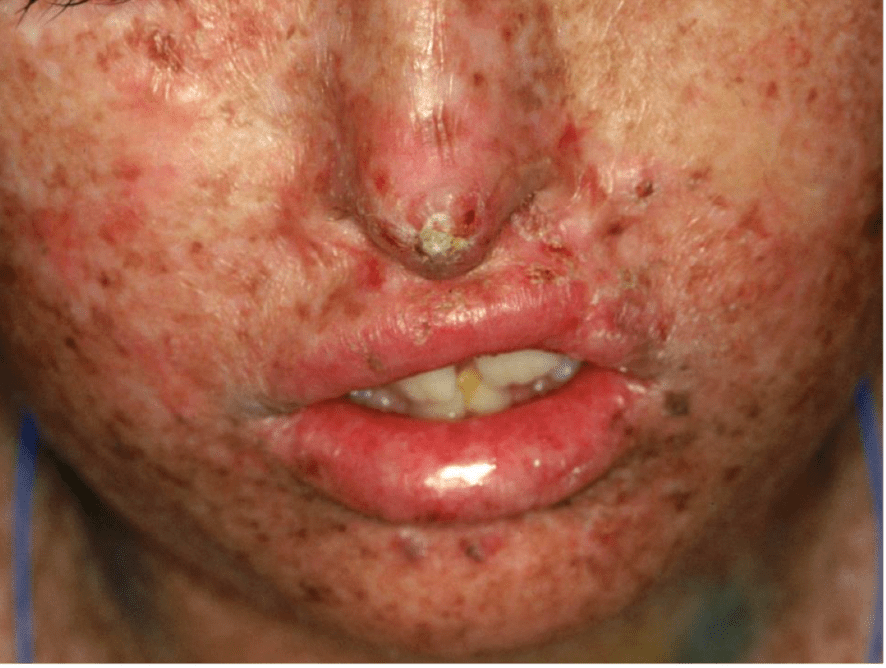
This is disease is caused by a genetic defect in...
DNA repair pathways.. specifically Nucleotide Excision Repair
This disease primarily affects Red blood cells due to the lack of ATP from glycolysis. Causes hemolytic anemia, jaundice, enlarged spleen
Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency
This is how to differentiate between a pyrimidine synthesis cycle defect or a urea cycle defect
Hint: difference between OTC deficiency and Orotic Aciduria
Urea Cycle- increase orotic acid and increase ammonia
Pyrimidine Synthesis Cycle: just orotic acid
Presents with elevation in the cerebrospinal fluid protein levels but NO elevated white blood cell count in CSF
Also-ascending symmetrical paresthesia and paralysis
Guillain Barre
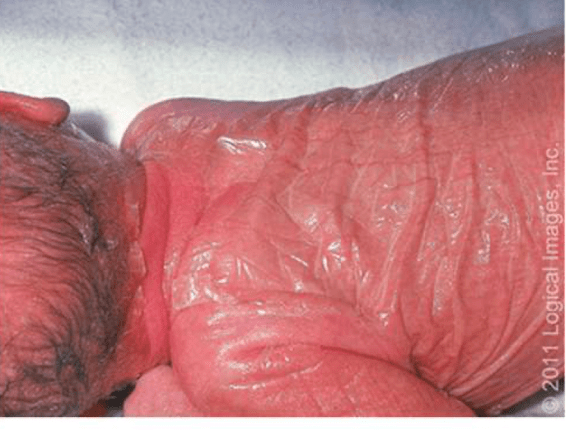
Type 2 of this disease causes this presentation known as Collodion Baby. Additionally, this disease causes hepatosplenomegaly, pancytopenia and a specific type of macrophage
Gaucher Disease
This disease only affects muscle tissue Lab values show increased CPK and,+Myoglobinuria and increased muscle glycogen. It is caused by a defect in this enzyme
Muscle phosphorylase
Bonus Points (McArdle Disease)
This is a rare storage disease that is caused by a mutation that prevents the phosphorylation of mannose in the cis golgi
I Cell Disease
Inheritance: AD (usually de novo)
Etiology: Lamin A Point Mutation
Presentation: age related changes in skin i.e loss of subcutaneous fat, joint contractures, bone abnormalities (premature aging syndrome)
Treatment: farnosyl transferase inhibitors
Hutchinson Gilford Progeria Syndrome
This disease is caused by a deficiency in HMB synthase. This is induced by the 4 M's-meds, malnutrition, menstruation, maladies and ETOH
This is treated with repleting heme after an acute attack and down regulating ALA synthase.
Acute Intermittent Porphyria
This disease presents with growth failure and developmental delay, progressive neurological and neuromuscular degeneration. It can be caused by a genetic defect (X-Linked) or from a deficiency in cofactors.
It can be diagnosed by the elevation of these labs..
Pyruvate, lactate/lactic acidosis, alanine
I.e Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex deficiency
Etiology: Mutation in SMN1 gene
Presentation: Progressive weakness due to loss of spinal cord neurons
Spinal Muscular Atrophy
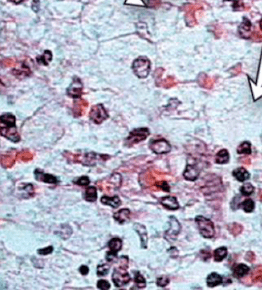 This disease presents with a deficiency is what enzyme?
This disease presents with a deficiency is what enzyme?
Sphingomyelinase
Infantile onset presents with cardiomyopathy, muscular hypotonia feeding difficulties and failure to thrive. Lab values include increase CPK, no myoglobinuria and increased lysosomal glycogen
This disease is caused by a deficiency in which two enzymes
Lysosomal acid alpha glucosidase
acid maltase enzyme
Bonus Point: Pompe Disease
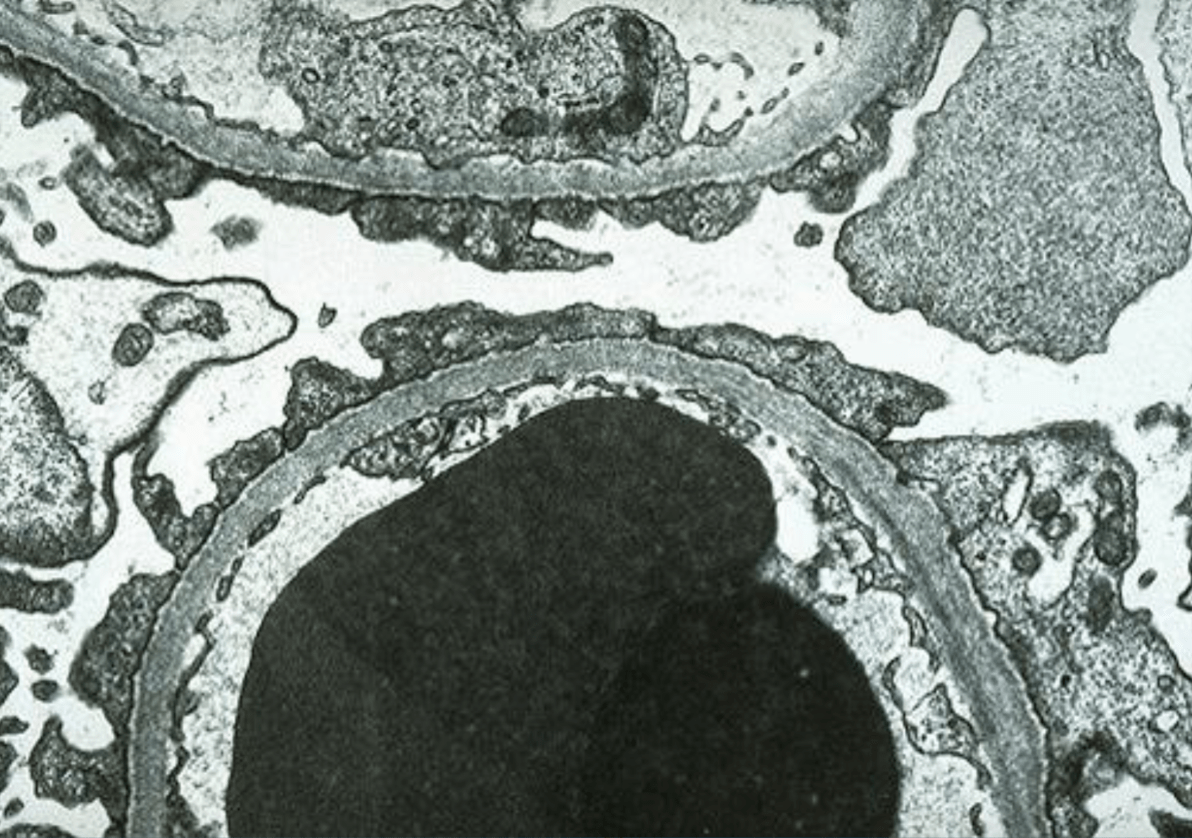 This disease presents with a defect in this type of cell. Presents with edema, proteinuria and hypoalbuminemia
This disease presents with a defect in this type of cell. Presents with edema, proteinuria and hypoalbuminemia
Name organelle above and syndrome
Glomerulus, Nephrotic Syndrome