This is the minimum frequency for turning or repositioning a patient to reduce friction and shear
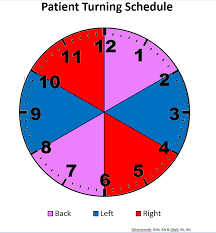
What is every 2 hours?
This technique must be used when changing central line dressings to prevent infection.
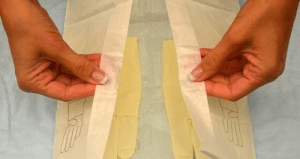 What is sterile technique?
What is sterile technique?
This is the most effective strategy to prevent CAUTI in hospitalized patients.
What is avoiding unnecessary catheter use?
These are 3 signs/symptoms of infection.
What are fever, purulent drainage, redness, warmth, induration, or swelling?
The amount of time the nurse waits to recheck blood sugar after intervening for a low reading.
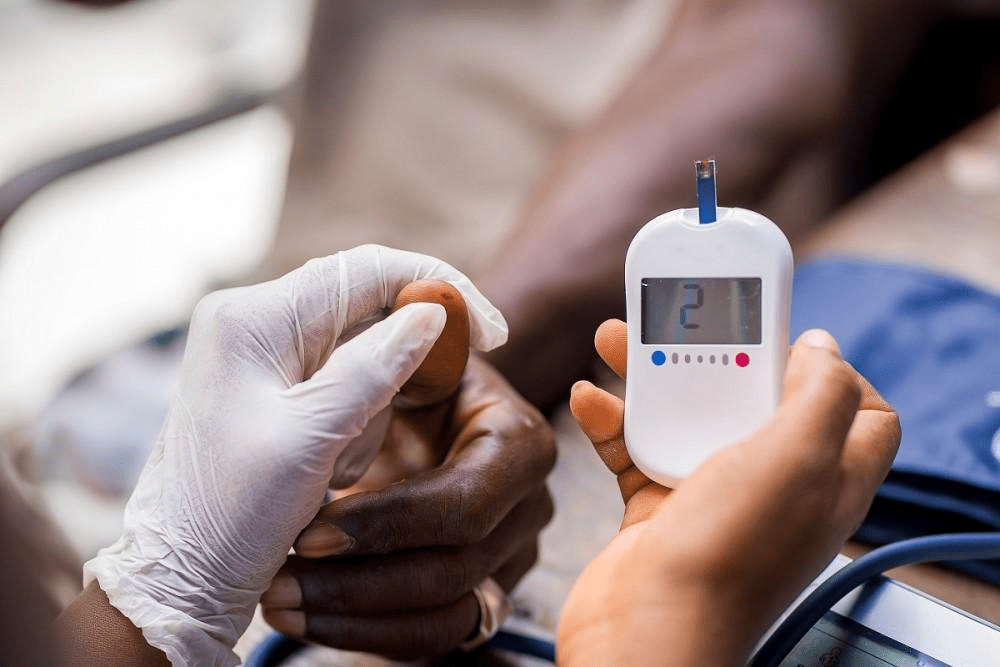
What is 15 minutes?
This is where you chart admissions and discharges in EPIC.
What is the Navigator?
A Braden score at or below this number requires escalation of pressure injury prevention methods.
What is 18 or less?
This is the minimum amount of time that you should "scrub the hub"
What is 5-15 seconds?
Name 2 risk factors for CAUTI.
What are being biologically female, having a urinary catheter in place for more than 48hrs, being an older adult?
What are using electric clippers to remove hair at the surgical site, removal of all jewelry, bathing the patient using CHG wipes, administration of antibiotics?
This is the first step in treating hypoglycemia in an unconscious patient.
What is administering IV dextrose or glucagon?

This is considered a self-care activity.
What is anything that helps you to relax and feel good?
This assessment/screening should be performed every shift, upon admission, and whenever there is a change affecting skin integrity.
What is the Braden Scale assessment?
What are blood cultures?
The nurse recommends this for the 24hr post-operative patient who is ambulating independently and has a urinary catheter.
What is removal of the urinary catheter?
Name one environmental factor in the operating room that can increase the risk of surgical site infection.
 What is poor air filtration or high traffic in the OR?
What is poor air filtration or high traffic in the OR?
This overload of ketones in the blood usually occurs in type 1 diabetics and can lead to diabetic coma and death.
What is Diabetic Ketoacidosis?
This is the person that the nurse resident should reach out to when they have a problem they don't know how to solve.
Who is the Clinical Site Coordinator?
These three body areas are the most common pressure points for developing pressure injuries.
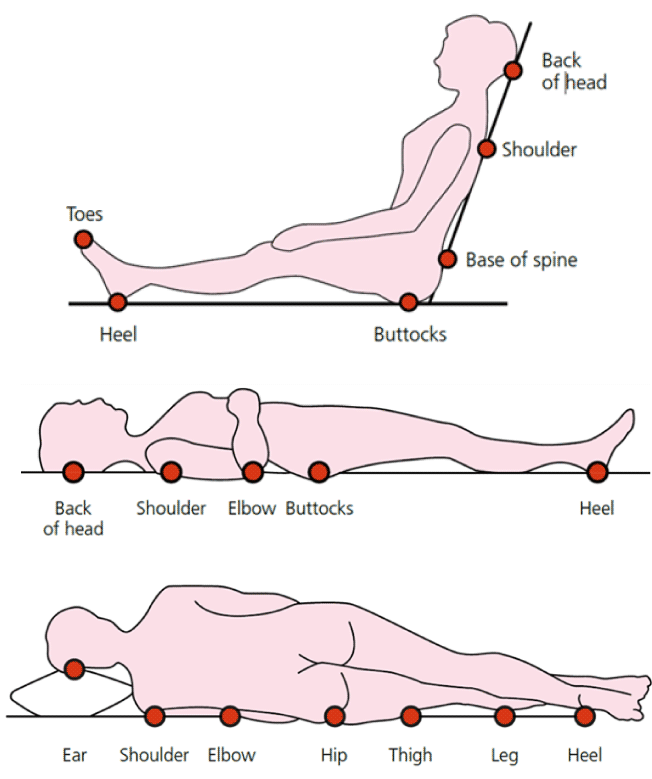
What are the sacrum, heels, and occiput?

Name one reason why a femoral central line is considered higher risk compared to other sites.
What is increased risk of infection due to proximity to groin?
These are 3 indications for insertion of a urinary catheter.
What are comfort/end of life, continuous bladder irrigation, GU surgery, post void residual greater than 300.
Name two patient-related risk factors for surgical site infection.
What are length of surgery, inadequate skin preparation, immunosuppression, higher BMI, smoking, or elevated blood glucose.?
These are usually treatments for both Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic Nonketotic Syndrome.
What are fluids and insulin?
Moisture management is critical in preventing pressure injuries. Name two interventions to reduce moisture-related skin breakdown.
What are using moisture barriers and frequent incontinence care?
This state entity collects CLABSI hospital rates and makes the information available to the public.
What is the California Department of Public Health?
Name two alternatives to indwelling urinary catheters for managing urinary retention.
What are intermittent catheterization and external catheters?
This is the recommended time frame for administering prophylactic antibiotics before incision.
What is within 60 minutes prior to incision?
Name one key lab value monitored during treatment of DKA.
What is serum potassium?
Nurse residents are considered ready for independent practice when they can effectively and continuously do this.

What is safely manage a full patient assignment?