What does DNA stand for and where is it located in eukaryotes?
DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic Acid and is located in the nucleus
In what phase does "crossing over" occur?
Prophase I
Name the phase:

Prophase II
What is the result of Meiosis?
Four haploid cells
Which Nitrogenous base pairs with Adenine?
Thymine.
What is the structure of DNA and what does is resemble?
The structure is a double helix, and resembles a twisted ladder.
What is the order of the phases in Meiosis?
1. Interphase, Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I Telophase I, Cytokinesis
2. Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, Telophase II, Cytokinesis
How many times does interphase occur?
1 time
A diploid zygote.
What is the purpose of meiosis?
The purpose is for the production of gametes.
What are the three components that make up DNA?
The three components that make up DNA are a 5 carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
In what phase do the tetrads line up in the middle of the cell?
Metaphase I
Name this phase:
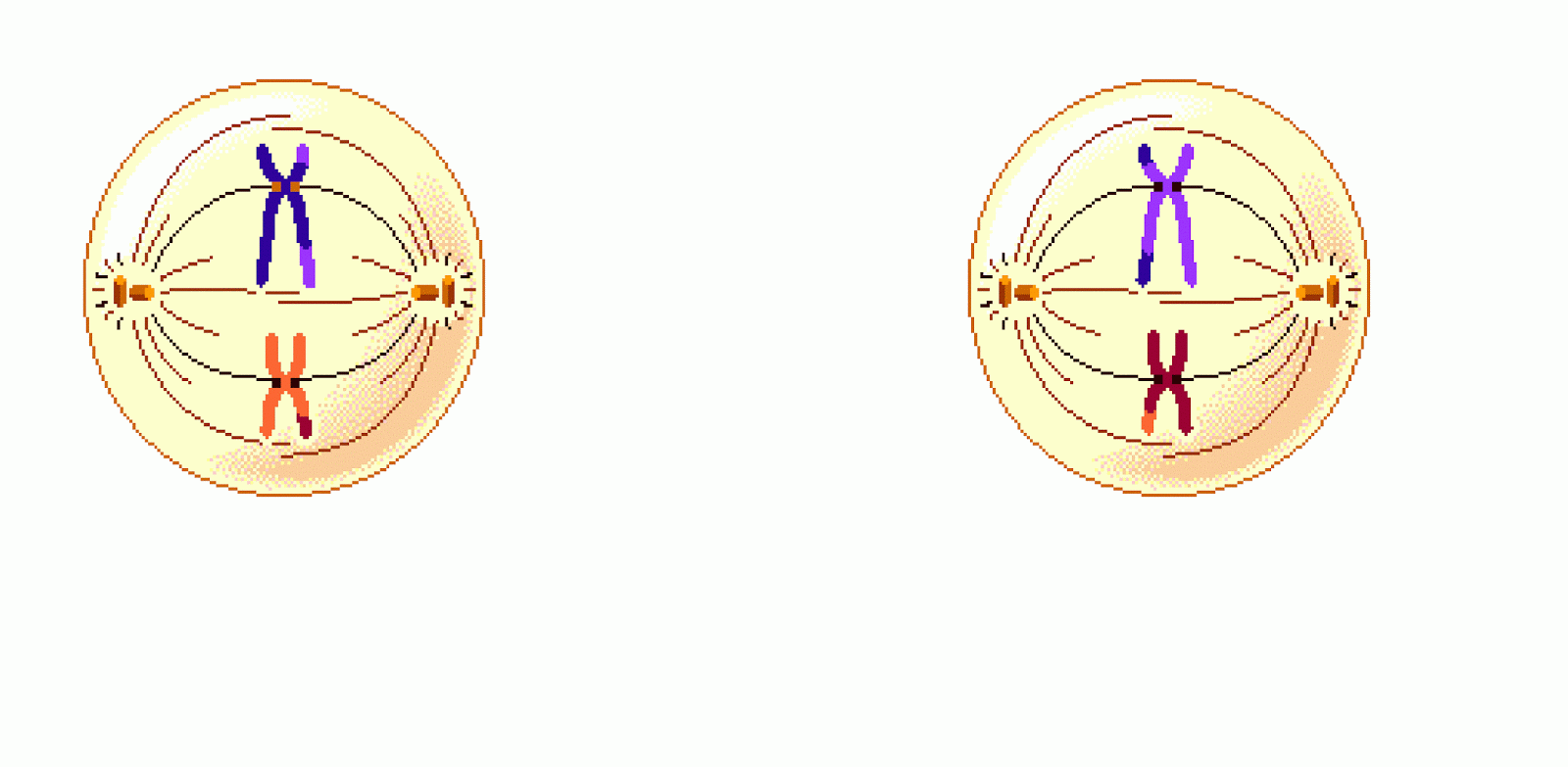
Metaphase II
What are the three sources of genetic variability?
1. Crossing Over
2. Independent Orientation of Chromosomes
3. Ramdom Fertilization
How many times does the DNA replicate and the nucleus divide?
The DNA replicates once and the nucleus divides twice.
What is the function of DNA?
The function of DNA provides genetic information for characteristics or traits
In what phases does the cell divide?
Cytokinesis
Name this Phase:

Telophase II
Where does crossing over occur on a pair of homologous chromosomes?
Chiasma
Which bonds connect the sugars and phosphate molecules?
Phosphodiester bond
What type of bond holds the nitrogenous bases pairs together?
Hydrogen bonds hold the nitrogenous bases together.
Describe anaphase I and anaphase II
Anaphase I:
The homologous chromosomes are pulled apart.
Anaphase II:
The sister chromatids are pulled apart.
Where do the spindle microtubules attach in Metaphase I.
They attach to the centromere with a kinetochore.
What is the disorder called due to a trisomy and which chromosome does it occur?
Down Syndrome and chromosome 21
What is the term when the individual strands form a right-handed double helix?
Antiparallel