Which picture correctly shows how DNA replicates?
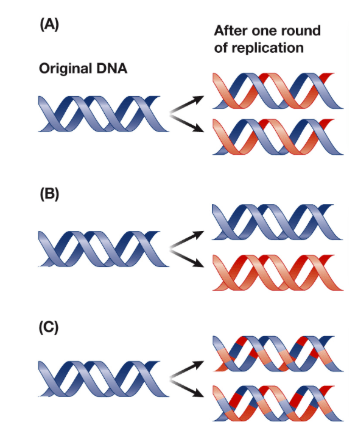
A.
What do we call the basic unit of DNA?
A nucleotide
Tell me the rules for nitrogenous base pairing.
Adenine pairs with thymine and cytosine pairs with guanine.
What is the name of the science teacher that drives the magic school bus?
Ms. Frizzle!
Sometimes DNA replication doesn’t go the way it is supposed to and the original DNA sequence is changed. What do we call it when this happens?
A mutation
What term can we use to describe how DNA replicates?
Semi-conservative
Covalent bonds hold together the backbone of DNA. What type of bonds hold together the nitrogenous bases in DNA?
Hydrogen Bonds
If the left strand of a DNA molecule is GATTACCA, what would the right strand of this DNA molecule be?
CTAATGGT
Name the female scientist that played a large part in the discovery of DNA, but never really got the credit due to her until very recently.
Rosalind Franklin; will accept just last name Franklin too
This term refers to any environmental trigger that may cause a mutation. Examples include viruses and exposure to harmful substances.
Mutagen
Explain why we call the method of DNA replication "semi-conservative."
Anything along the lines of "in each new molecule of DNA that is synthesized, one strand is from the original molecule of DNA and one strand is new."
What are the three molecules that make up every nucleotide?
A phosphate group, a five carbon sugar/deoxyribose, and a nitrogenous base.
If a molecule of DNA has 40% thymine and adenine, what percent of it is cytosine?
30%
Which two scientists contributed the theoretical part of the discovery of DNA?
Watson & Crick
Which type of mutation is shown below?
A C T G A
T G T C T
A substitution
Tell me all four steps of DNA replication.
Step 1: The DNA helix untwists into a straight-line.
Step 2: The hydrogen bonds holding the nitrogenous bases together break, leaving two half strands of DNA rather than one whole strand.
Step 3: Each half strand of DNA serves as a template that free-floating nucleotides attach to. This forms two new strands.
Step 4: Each of the two new strands winds back up into the double helix.
What is another name for deoxyribose? (Hint thinking of the shape of deoxyribose might help you answer this).
Pentose
Using your knowledge of the base pairing rules, tell me if this strand of DNA replicated correctly or if it underwent a mutation.
A T G C T C G A T T A
T A C G A G G T A A T
A mutation must've occurred because the nitrogenous base G is paired with another G. It should be paired with C.
Which scientist came up with the rule for using base pairing to figure out the percent composition of each nitrogenous base in DNA?
What are the four types of DNA level mutations?
Insertion, deletion, substitution, inversion.
We learned that in step 3 of DNA replication, free-floating nitrogenous bases come in and pair with the two template strands of the original DNA. Where do these free-floating nitrogenous bases actually come from though?
A. They are stored in the nucleus where the DNA is
B. They are floating around in the cytoplasm
C. They get built during replication to ensure that there is an exact match for each base in the template strand
D. They come from other strands of DNA that got broken down over time.
B. They are floating around in the cytoplasm
In the nucleus of the cell, there are chromosomes. Chromosomes are made up of genes. What are genes made up of?
DNA
Daily Double
Daily Double
Which two scientists discovered the method by which DNA replicates through the use of radioactive isotope labels?
Meselson and Stahl
What type of mutation is shown below?
A T C G A T T C G A
T A G C T A T C G A
An inversion