Which enzyme adds DNA primers to the template DNA during DNA replication?
What is... DNA primase?
What happens during transcription?
What is... The DNA template (the antisense strand) is transcribed/converted into a sequence of RNA called mRNA (messenger RNA)?
What happens during translation?
What is... mRNA (messenger RNA) is translated/converted into a chain of amino acids (a polypeptide)?
What is a gene?
What is... A sequence of DNA that codes for a gene product like a polypeptide?
Where does translation occur in the cell?
What is... In the cytoplasm?
Is the arrow pointing to the leading or lagging strand? AND how do you know?
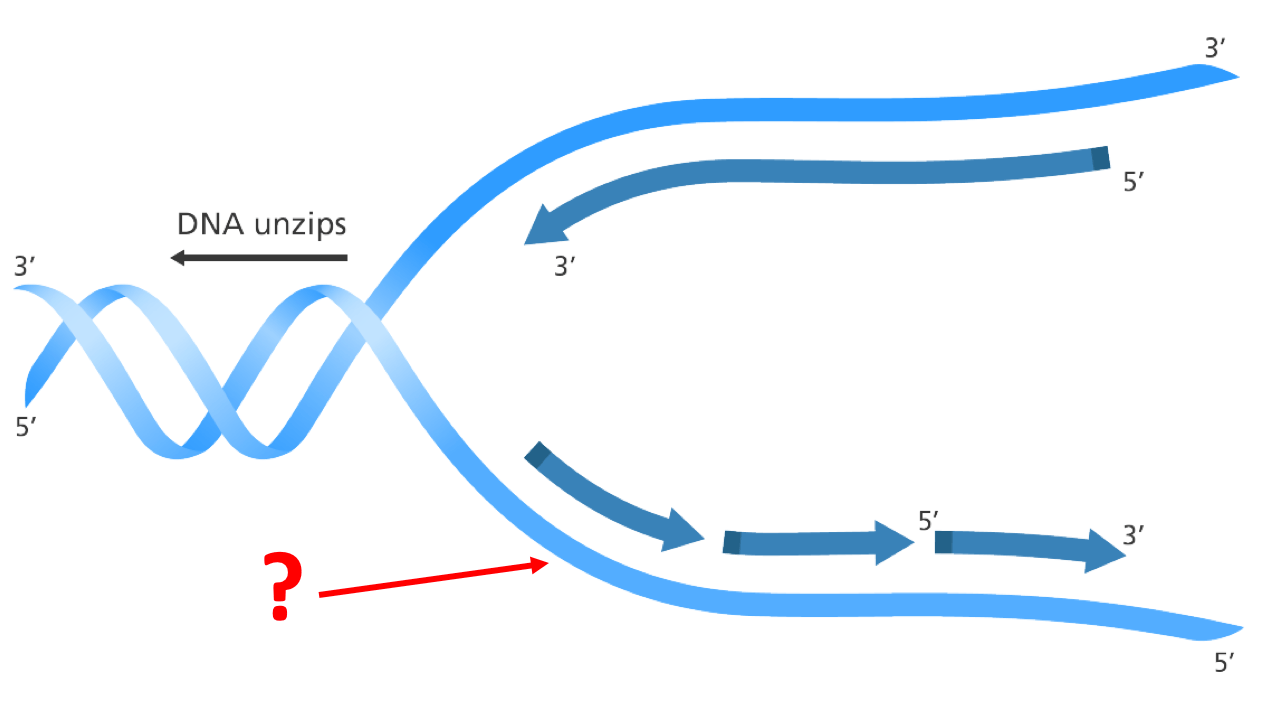
What is the lagging strand? Because there are Okazaki fragments, OR because it is going opposite to the direction of replication.
What is the function of RNA polymerase?
What is... unwinds the DNA, and extends the RNA sequence (by adding RNA nucleotides to the 3' end of the growing strand) ?
The codon of mRNA is: GGA
The anticodon on tRNA is: ________
What is.. CCU?
Why do cells need to replicate their DNA?
What is... DNA replication must occur for growth or repair of damaged tissues?
When does DNA replication occur in the cell cycle?
What is.. during the Synthesis phase of interphase?
What is the function of helicase? BE AS SPECIFIC AS POSSIBLE.
What is... unwinding the DNA, and breaking hydrogen bonds between nitrogenous bases?
The template DNA sequence is as follows:
3' - ATAACGGCT - 5'
What is the resulting mRNA sequence? YOU MUST MENTION THE 5' and 3' ENDS!
What is...
5' - UAUUGCCGA - 3' ?
The anticodon is: GCU
What is the resulting amino acid?
What is.. Arginine?
Which enzyme during DNA replication joins adjacent okazaki fragments together in the lagging strand?
What is.. ligase?
The strand of DNA that is not used as a template for transcription is called the ___________ strand.
What is... sense strand?
What is the function of DNA polymerase I?
What is.. replacing the RNA primers with DNA nucleotides?
During mRNA splicing, the _____________ are spliced out, while the _____________ are joined together.
what is... introns? And what is... exons?
The codon is: GAA
What is the resulting amino acid?
What is... Glutamine?
what is... peptide bonds?
Adjacent RNA nucleotides in mRNA are linked together via ___________ _________.
what is... covalent bonds?
DNA polymerase III can replicate DNA in what direction on the template DNA strand?
What is...
3' to 5' direction on the template DNA strand ?
5' to 3' direction on the growing DNA strand!
During mRNA modification: a ____________ and a __________ are added to either ends of the mRNA sequence.
what is...
A 5' cap and a 3' poly A-tail
A charged tRNA with a complementary anticodon enters the ribosome through the ______ site.
What is... A site?
What happens during the initiation stage of transcription?
What is...
RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region upstream (before) a gene.
What happens during the termination step of transcription?
What is...
RNA polymerase reaches the terminator region of the gene. The RNA polymerase detaches from the DNA and DNA rewinds. The mRNA and RNA polymerase dissociate.
What is the function of:
- DNA gyrase (topoisomerase)
AND
- Single stranded binding (SBB) protein?
What is...
Bind to the DNA near helicase to prevent super coiling of DNA
AND
Stabilizes DNA and keeps the DNA strands separated
When does transcription occur in the cell?
What is.. All the time!! Our cells are constantly making proteins for our bodies and cells to function
What happens during the termination step of translation?
What is...
1) ribosome reaches stop codon
2) protein called release factor binds to the stop codon in the A site
3) This causes the ribosome, mRNA, and polypeptide to dissociate
What happens in the P site of a ribosome during the elongation step of translation?
The ribosome moves forward another codon, and the tRNA in the P site is now moved to the E site and can leave.
Describe two features of tRNA, that is crucial for protein translation.
What is..
1) amino acid
2) anticodon