The acronym DNA stands for what?
What is Deoxyribonucleic Acid
This enzyme can be found unzipping the DNA strand prior to DNA replication.
What is Helicase.
The acronym RNA stands for what?
What is Ribonucleic Acid
This type of RNA is produced by DNA being copied during transcription.
What is mRNA.
This type of mutation results in the shifting of a DNA sequence?
What is a frameshift mutation.
The structure of a DNA is different than an RNA because of this feature?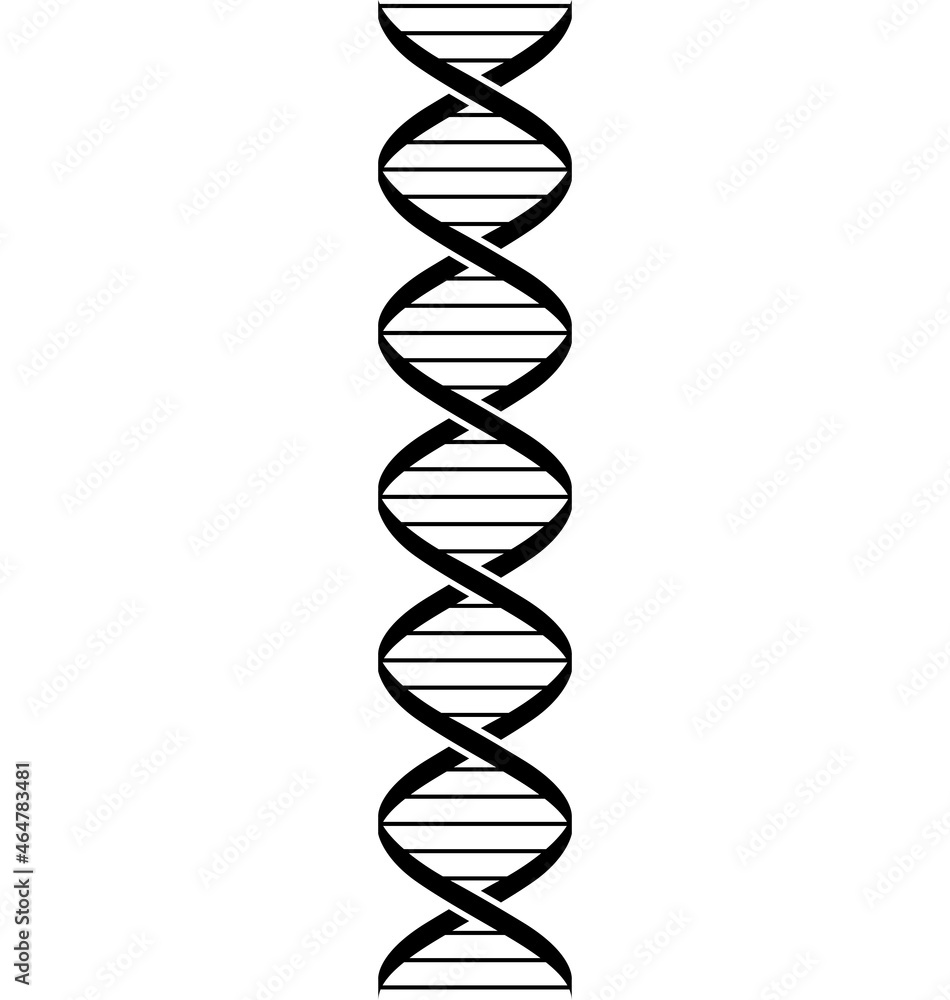
What is a DNA double helix
This enzyme is used to start the process of DNA replication by placing primers at the beginning of the original DNA strand.
What is Primase.
This base is different in RNA compared to DNA and what is it replaced by what other base?
What is Thymine and it is replaced by Uracil.
Briefly describe the process of translation.
The mRNA places itself on the ribosome where correct tRNA with its anti-codon join the mRNA to release amino acids to be strung together to ultimately make proteins.
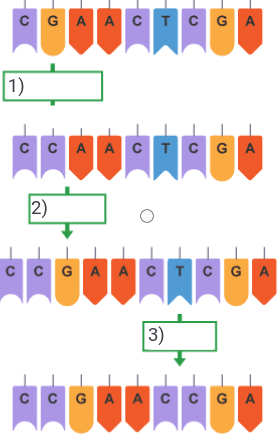
1) Substitution
2) Insertion
3) Deletion
These are the three main parts of a DNA nucleotide?
What is the Nitrogenous base, phosphate group and a pentose sugar.
This enzyme is used to glue Okazaki fragments back together.
Which strand can the Okazaki fragments be found?
What is Ligase and the lagging strand.
Identify the three types of RNA and their functions.
The mRNA codon CCA codes for what amino acid?
What is Proline.
What is effect on protein synthesis when the repressor protein binds to the operator?
Protein synthesis is stopped.
What does a single DNA strand serve as for mRNA.
What is a template for base pairs.
Identify the leading strand and lagging strand.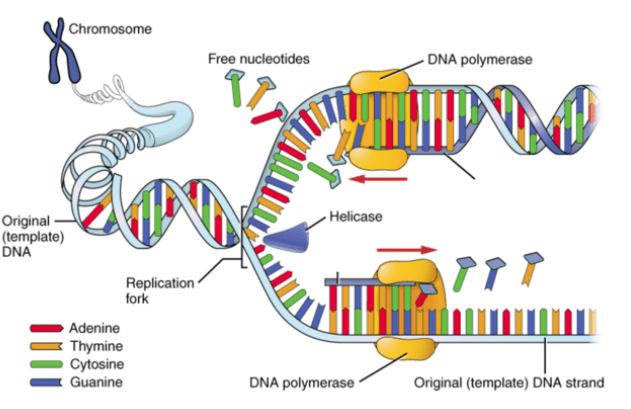
Top is leading and bottom is lagging.
The central dogma of molecular biology is that DNA makes RNA and RNA makes what?
What is proteins.
A strand DNA is copied to make proteins. The strand is as follows: TAC GGT CAC TTA. What are the four codons for the mRNA and what amino acids do they code for?
What is AUG CCA GUG AAU and Start, Proline, Histidine, and Asparginine.
The first person to stand up and sing the chorus to Taylor Swift song earns these points.

Name the four nitrogenous bases in DNA and how they pair up.
What is
Cytosine=Guanine
Adenine=Thymine
Helicase unzips, replication fork formed, primase adds primer at the origin, DNA polymerase copies the DNA and proofreads, ligase connects the okazaki fragments.
These are the two processes RNA carries out to make proteins?
What is transcription and translation.
What is Leucine.
Sickle Cell Anemia is caused by the change in the 7th codon in a DNA strand. The correct codon is GAG, but the mutation results in GUG. Identify the amino acid that should be present and the one that is present in Sickle Cell. Also identify if it is a silent, missense, or nonsense mutation.
What is Glutamic Acid and Valine. It is a missense mutation.