& Codon Chart
What is the structure of DNA?
Double Helix
Helicase splits the bases apart, the point at which the strand separate is called?
Replication Fork
DNA is transcribed into __________
RNA
Rna is translated into ___________
Proteins
What is the sugar in the RNA backbone?
Ribose
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine and Cytosine are what?
Nitrogenous Bases
Bases are connected to each other by this weak bond
Hydrogen bonds
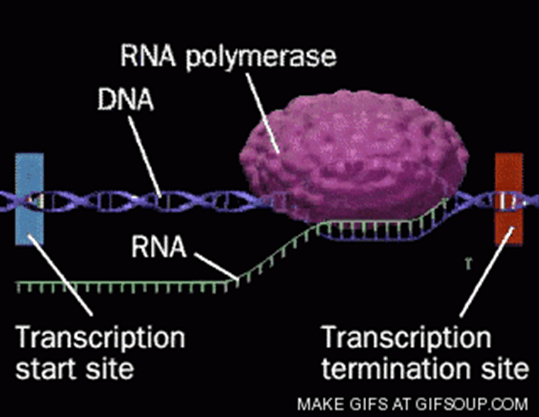
Where does Transcription occur?
In the Nucleus
Polypeptide chains (protein chains) are made up of what?
Amino Acids
3 bases "words" on consecutive nucleotides that code for a specific amino acid are called
Codons
Deoxyribose Sugar
Adenine (A) will pair with which base?
Cytosine (C) will pair with which base?
A pair with Thymine (T)
C pair with Guanine (G)
The base Thymine (T) is replaced by what base in RNA?
Uracil (U)
Where does Translation take place?
In the ______________ of the cell, At the ___________
Cytoplasm
Ribosome
What does AAU code for?
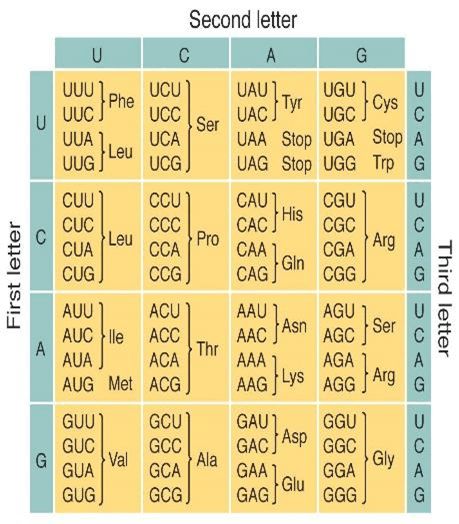
ASN
A Nucleotide is composed of what 3 parts?
Phosphate, (Deoxyribose) Sugar, Base (ATGC)
When DNA replicates and the two new DNA has one old (Parent) strand and one new (Daughter) strand is called?
Semi-Conservative
_____________________; not Helicase is responsible for unwinding DNA and building the compimentary strand of mRNA during transcription.
RNA Polymerase
Which type of RNA has the anticodons attached to specific amino acids?
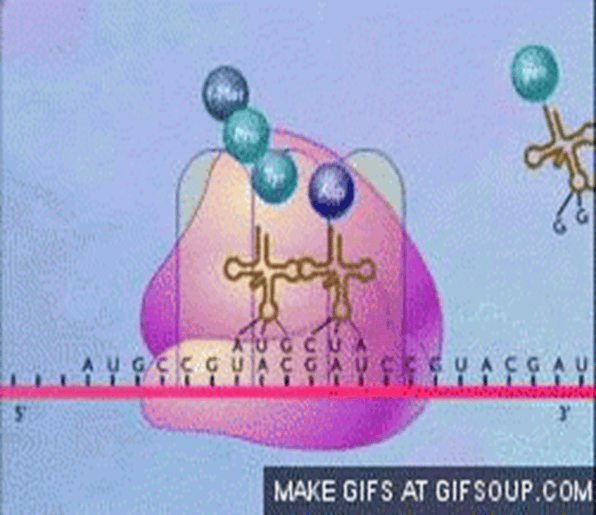
tRNA or Transfer RNA
What is the AUG code for?
MET or START amino acid
What bonds hold the sugar backbone together?
(Phosphodiester Bonds)
Strong Covalent Bonds
DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the parent strands in a _____ prime to ______prime direction
5' to 3'
What specifically is being copied during transcription?
What is a gene?
The RNA sequence will code for this polypeptide chain.
AUG GCC UUA UAG
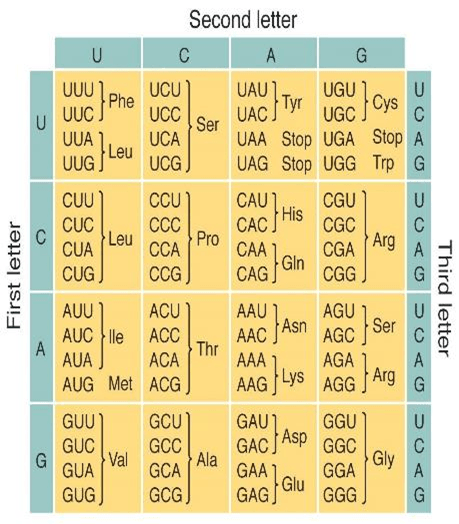
MET(START), ALA, LEU, STOP
How many Amino Acids are there?
20