This is the most common acute gastrointestinal complication of radiation therapy for prostate cancer.
Acute proctitis (Acute radiation proctitis)
Andexanet alpha is a reversal agent for this class of direct oral anticoagulants.
Factor Xa inhibitors: Apixaban (Eliquis) or Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)
This statistical term describes how close two or more repeated measurements are to each other
Precision
This is the most common non-neoplastic polyp of the colon
Hyperplastic polyp

This is the term for objects or materials which can transmit infection if contaminated
Fomite (accept fomes)
Relative effect of vitamin A derivatives (β-carotene and retinol) or vitamin E (α-tocopherol) given prophylactically to prevent lung cancer.
Increased incidence and mortality
"Do not prescribe vitamin A derivatives (β-carotene and retinol) or vitamin E (α-tocopherol) to prevent lung cancer." - MKSAP
Smoking cessation is the most effective preventive measure for lung cancer.
Annual screening with low-dose CT in patients aged 50 to 80 years who have a 20-pack-year history of smoking is associated with a decrease in lung cancer and all-cause mortality.
This clinical condition is characterized by cyclic episodes of nausea and vomiting associated with marijuana use
Cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome (cannabis hyperemesis syndrome)
List three reportable diseases
HIV infection, chlamydia, gonorrhea, and botulism are examples
This condition is characterized by ascitic fluid infection without an evident intra-abdominal surgically treatable source
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
This is the name for a measles infection in patients with preexisting but incompletely protective anti-measles antibody
Modified measles
This syndrome is associated with these images
A is the current photograph
B is photographed 5 years previously
C is the current photograph of the upper chest
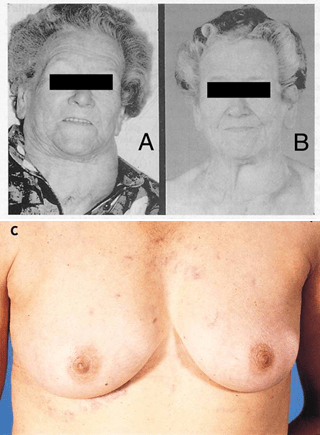
Superior vena cava syndrome
This is the cause of Saturnine gout
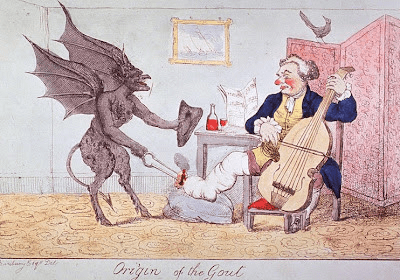
(Lead Poisoning) competes with uric acid for excretion in the distal tubule and is the probable mechanism of action leading to saturnine gout in lead-exposed patients
This type of bias occurs when specific individuals are more likely to be selected for a study group, resulting in a nonrandom sample, limiting generalizability
Selection Bias
The three original laboratory values needed to calculate the MELD score
The Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score model uses INR, bilirubin, creatinine, and history of dialysis to estimate the relative disease severity and the likelihood of survival after surgery.
This systemic reaction is characterized by endotoxin-like products released by the death of harmful microorganisms following initiation of antibiotic treatment
Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction
(commonly associated with initiating syphilis treatment)
This treatment is indicated for patients with recurrent MALT lymphoma.
Chemotherapy or gastrectomy
Involved site radiation therapy (ISRT) as the preferred first-line therapy or rituximab if ISRT is contraindicated. OR antibiotic therapy for H. pylori eradication is FIRST LINE
This enzyme is competitively inhibited by the reversal agent, fomepizole.
Alcohol dehydrogenase (used as an antidote for methanol or PEG poisoning)
Study structure of the following visual:
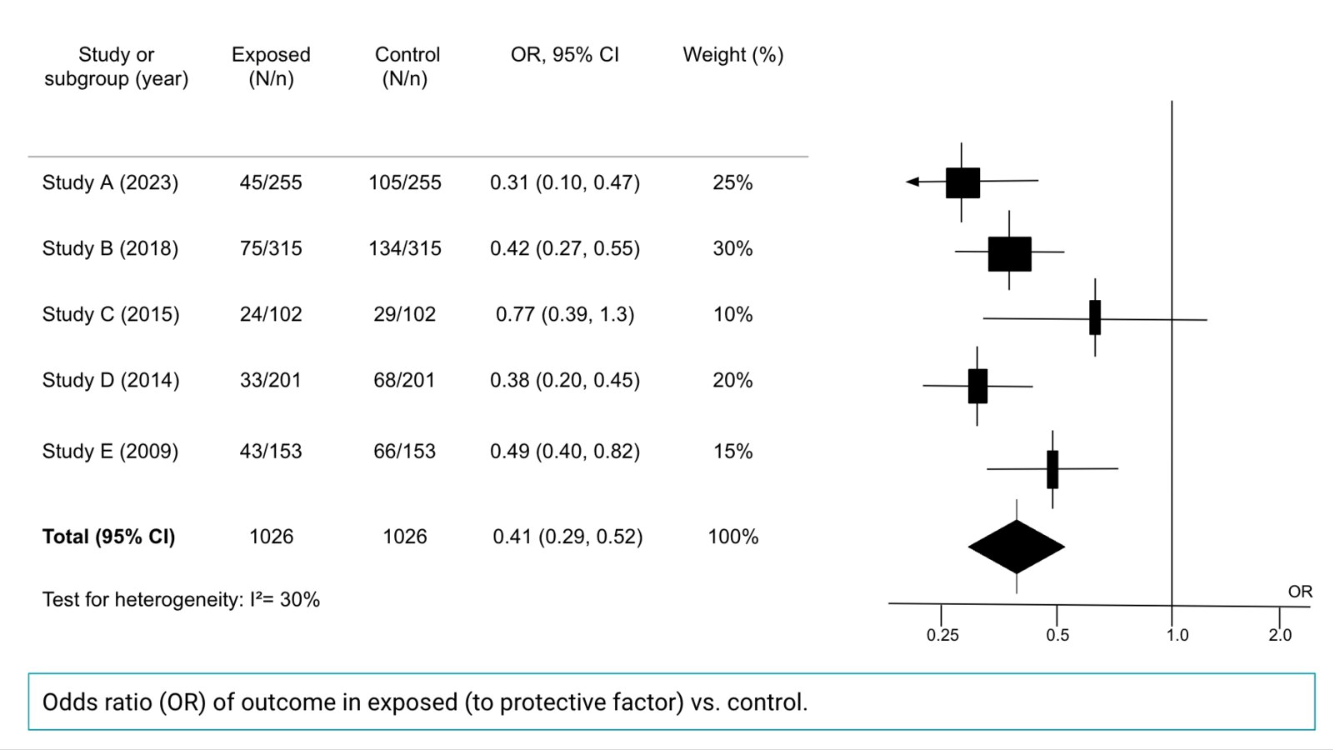
Forrest Plot
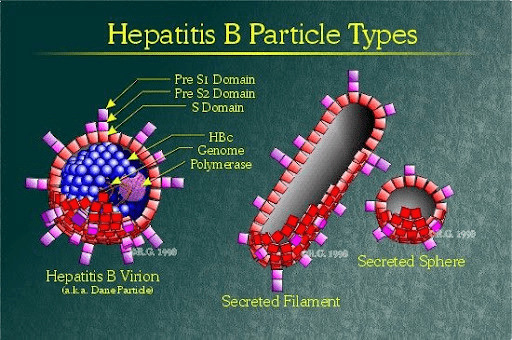
This hepatitis virus is associated with circulating Dane particles.
Hepatitis B (accept HBV)
This bacterial species is associated with the formation bacillary angiomatosis

Bartonella henselae (Cat-Scratch Disease)
This new class of anti-hormonal agent was found to be superior to tamoxifen in treating metastatic breast cancer and as adjuvant therapy for early-stage breast cancer
Third-generation aromatase inhibitors (i.e., letrozole, anastrozole)
N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine is the toxic metabolite associated with overdose of this agent.
Acetaminophen (APAP or paracetamol)
The proportion of the incidence of a disease in a population due to exposure that would be eliminated with removal of the exposure
Population attributable risk (attributable risk; population attributable fraction)
The proportion of disease incidence among exposed individuals that can be attributed to the risk factor to determine the proportion of cases in the exposed population that can be attributed to the risk factor
One of three indications to initiate steroids in alcoholic hepatitis (Two score thresholds or clinical symptoms)
≥ 32
Severe alcoholic hepatitis (Maddrey score ≥ 32 or MELD score > 20, or presence of hepatic encephalopathy)
This is the antibiotic treatment of choice for infection of the intestines with the coccidian parasite Cyclospora cayetanensis
trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole