This ratio (provide the numerator and denominator, along with the cutoff values) can help grade the severity and predict mortality in a patient with ARDS (acute respiratory distress syndrome).
What is the P/F ratio (PaO2/FiO2)?
Normal >400

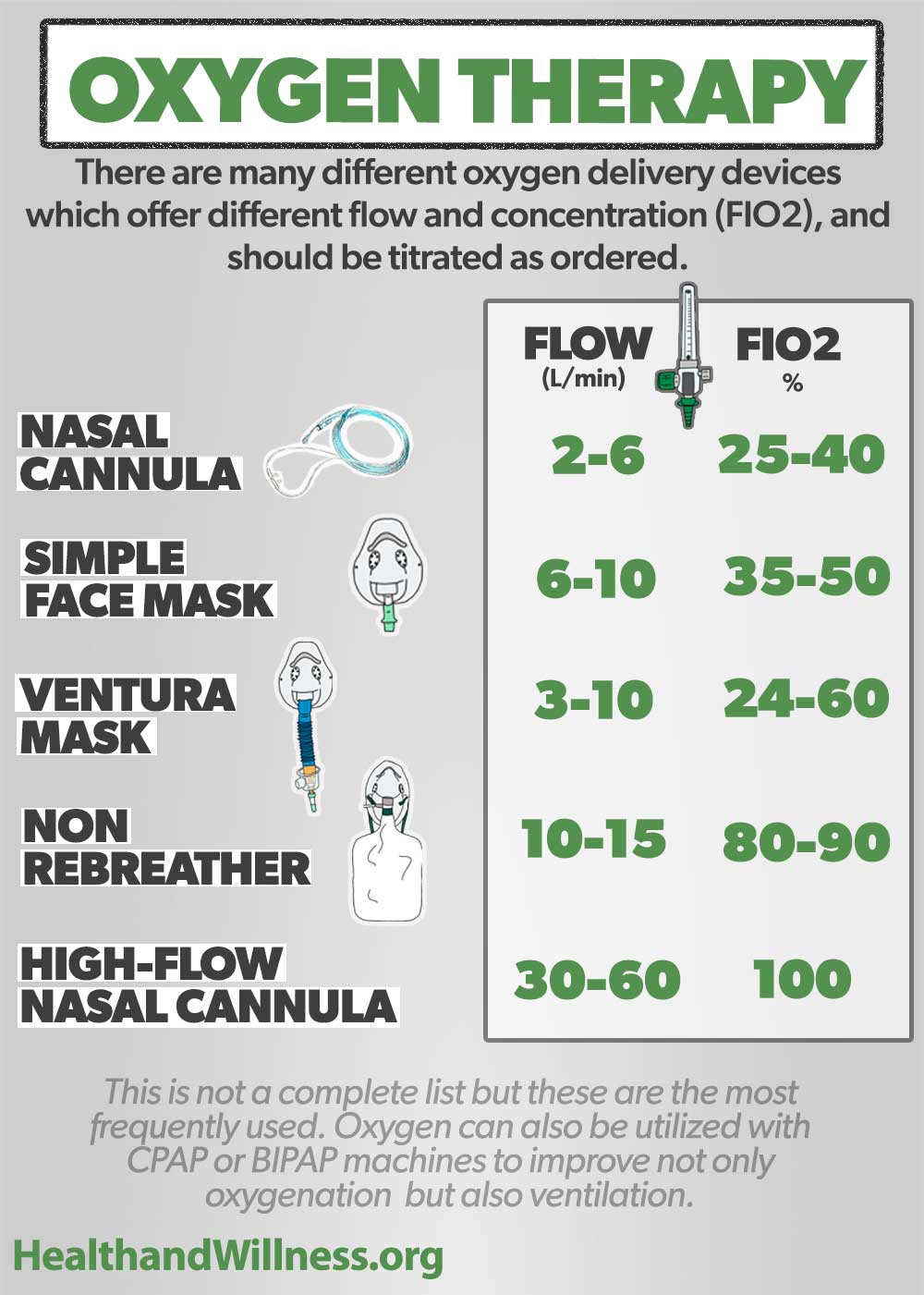
These are the three cutoffs, only one of three needed, to diagnose an exudative pleural effusion.
What is:
1) pleural fluid protein-serum protein ratio >0.5
2) pleural fluid LDH >200 (or >2/3 ULN)
3) pleural fluid LDH-serum LDH ratio >0.6
This FEV1/FVC ratio is indicative of obstructive lung disease.
What is <0.7?
This is the diagnosis for an immunologic pulmonary disorder caused by hypersensitivity to Aspergillus fumigatus, classically seen most in patients with chronic asthma or cystic fibrosis. Common associated findings are fleeting infiltrates on CXR, skin testing positive for Aspergillus fumigatus, eosinophilia >500/microL, IgE >417 IU/mL.
What is allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA)?
The triad of hematuria, hemoptysis, and strong linear IgG deposition along the GBM.
What is Goodpasture/Anti-GBM disease?
These two respiratory parameters (with cutoff values) can be used during a spontaneous breathing trial to assess safety for extubation on an mechanically ventilated patient that is on minimal O2 support (FiO2 <0.4) and PEEP <5-8 cm H2O.
What are the rapid shallow breathing index (RSBI) and negative inspiratory force (NIF)?
RSBI <105 [RSBI = RR/TV]
NIF <-30cm H2O (some studies suggest <-20 to -25)
The FEV1 improvement threshold that confirms reversibility in asthma.
What is >12% or 200mL increase in FEV1?
When 100% FiO2 fails to correct hypoxia, this mechanism is likely possible.
What is shunt physiology?

This is the cutoff, either in A-a gradient or arterial PO2, for glucocorticoid addition in the treatment of P. jirovecii pneumonia.
What is an indication for glucocorticoids within 72 hours with an A-a >/= 35mmHg OR arterial PO2 <70mmHg? (In addition to high-dose TMP-SMX)
These drug classes make up SMART therapy for asthma treatment for both maintenance and rescue relief.
What is a combination of ICS-LABA for both daily maintenance and as-needed symptom relief?
Describe the hemodynamic changes of Obstructive Shock due to a massive PE-
CO, CVP, PCWP, SVR, Central Venous O2
CO Down, CVP Up, PCWP Normal/Down, SVR Up, CVO2 down

This antifibrotic agent can slow the progression of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF).
Pirfenidone
Downregulates the production of growth factors and procollagens I and II
This lab abnormality (Bonus 100 pts: with the cutoff value) is the hallmark of Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome
What is daytime hypercapnia, (Bonus: defined as an arterial PCO2 greater than 45mmHg)?
This is the induration cutoff on a tuberculin screening skin test that would be concerning for an HIV-positive healthcare provider working within the prison system.
What is >/= 5mm induration after 48-72 hours?

According to the Fleischner Society, in low risk patients what is the interval for follow up CT of a 7mm solitary solid lung nodule?
CT in 6-12 months
If the nodule is stable, can consider CT at 18-24 months thereafter
This key bedside measurements (2 possibilities), which reflects diaphragmatic strength, helps determine the need for mechanical ventilation in a 35-year-old woman who recently recovered from sepsis and who has positive antibodies against acetylcholine receptor (anti-AChR) that is currently experiencing respiratory distress.
What is negative inspiratory force/maximal inspiratory pressure and vital capacity?
Cutoffs
NIF/MIP: > -25 to -30cm H2O (ie, between 0 to -30)
VC: < 15 to 20 mL/kg of ideal body weight


These are the two indications/situations for when empiric coverage of Pseudomonas is indicated in the treatment of community-acquired pneumonia.
What are: 1) Pseudomonal growth from a respiratory tract culture within the last year OR 2) hospitalization and parenteral antibiotics in the preceding 3 months?
Pseudomonas accounts for less than 5% of all CAP infections; however, previous isolation of the organism from sputum is associated with a 16-fold increased risk of subsequent infection. Other risk factors for Pseudomonas CAP include previous tracheostomy, bronchiectasis, and severe COPD. In patients who have been hospitalized in the preceding 3 months and received parenteral antibiotics, empiric therapy for both Pseudomonas and MRSA is recommended for severe (e.g., requiring ICU care) CAP.
After two days of intense skiing the Alps, Frank develops cough and hemoptysis and crackles on exam. In addition to supp oxygen and descent from altitude, this medication will help his hypoxia improve.
What is Nifedipine or PDE-5 inhibitors?
Decease the pulmonary vasculature constriction due to high altitude hypoxia leading to High-Altitude Pulmonary Edema
What is the diagnosis in a patient who presents with cough and fever for months non responsive to antibiotics, CT scan that demonstrated consolidation of a single lobe, and histopathology showing granulation tissue primarily affecting the terminal bronchioles?
Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia
Nonresolving symptoms and failure of response to antibiotics should raise suspicion for COP. Glucocorticoids is the mainstay of treatment.
What is the diagnosis in a patient who presents with recurrent asthma exacerbations that do not respond to steroids and has the following flow volume loop?
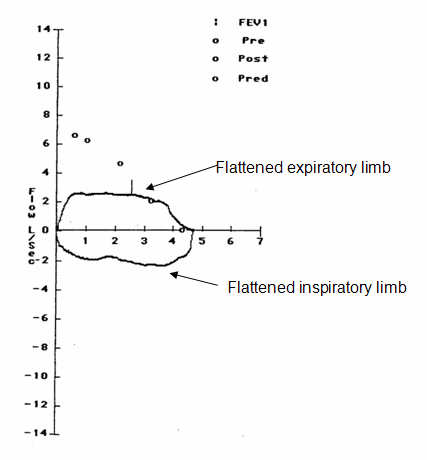
Fixed airway obstruction (or tracheomalacia)
Treated with chest physio, bronchodilators, and IP consult for consideration of stenting
A patient in the MICU on linezolid and ertapenem for undifferentiated shock has increasing levo and vasopressin requirements, so you are considering starting methylene blue. However, Dr Scully cautions you on this potential drug interaction.
Serotonin Syndrome
Linezolid and Methylene Blue, also must have caution in patients with Methylene Blue with patients on SSRIs, MAOs, tramadol, and zofran
Name 2 out of the 4 tumor markers utilized for targeted therapy in advanced-stage lung adenocarcinoma
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) mutation, Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PDL 1), Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (ALK) translocation, and ROS proto-oncogene 1 receptor tyrosine kinase (ROS1) translocation
What is the alveolar gas equation for PAO?
(Used for calculating A-a gradient)
PAO = (FiO2 x [Patm - PH20]) - (PaCO2 / R)
FiO2 = 0.21 at room air, Patm is atmospheric pressure (760mmHg at sea level), PH2O is the partial pressure of water (47 mmHg at 37 degrees C), PaCO2 is the arterial carbon dioxide tension (from ABG), and R is the respiratory quotient (normally 0.8)
This is the three-drug regimen and its duration of therapy indicated for a patient with 5 months of worsening cough with 10-lb weight loss, fatigue and decreased appetite, who has two separate sputum cultures growing Mycobacterium avium complex.
What is a combination of a macrolide (ie, clarithromycin, azithromycin), ethambutol, and a rifamycin (ie, rifampin, rifabutin)? Treatment duration of at least one year?
This is the only approved therapy (drug and/or class) for a patient with a hx of recurrent PEs, a mean PAP >20mmHg and a PWP <15mmH on RHC.
What is Riociguat?
Pulmonary vasodilator that acts on the nitric oxide pathway, is currently the only approved PH therapy available for CTEPH treatment. Works by directly stimulating guanylate cyclase receptor, independent of endogenous NO, to promote pulmonary artery vasodilation.