Outline why the rate of the reaction decreases with time.
What is that the limiting reactant is used up and less product is formed?
-log[H+]
What is pH?
The gain of electrons by a species
What is reduction
Magnesium has three stable isotopes, Mg-24, Mg-25 and Mg-26. The lightest isotope, Mg-24, has a percentage abundance of 78.9%. Calculate the percentage abundance of the heaviest isotope to one decimal place.
9.9%
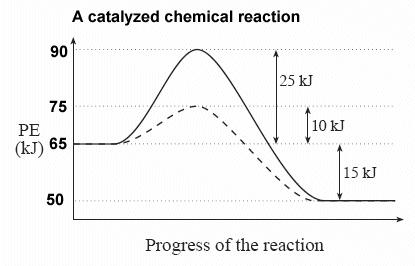
Explain, in terms of the function of a catalyst, why the curves on the potential energy diagram for the catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions are different
The curves are different because in a catalyzed reaction, the activation energy is less than an uncatalyzed reaction.
These do not affect Kc.
What is concentration, pressure, and catalyst?
The polyatomic ion that all strong bases have in common.
What is a Hydroxide group (OH-)?
What is the oxidation number for each element in the following compound? CaCO3
Ca = +2
C = +4
O = -2
What does this equation represent?
X --> X+ + e-
The first ioniztion energy.
Explain, in terms of kinetic energy and collision, how increasing the temperature of a reaction will increase the rate of that reaction.
As you increase the temperature of a reaction, the kinetic energy (speed) of particles increases and therefore increases the frequency and effectiveness of collisions.
Name two ways to change the pressure of the system
What is add or remove a gaseous product or reactant, change the temperature or change the volume of the container
Products in a chemical neutralization
Salt and water
Is this a redox reaction or not?:
2KClO3 --> 2KCl + 3O2
Yes; redox
Decomposition
Explain in terms of intermolecular forces, why water has a higher boiling point than sulfur dioxide.
Water has: London dispersion forces, permanent dipole, and hydrogen bonding.
Sulfur dioxide only has London dispersion forces and permanent dipole.
three things that must happen for the collision theory to happen
What is Particles must collide, Collisions must have the correct orientation, Collisions must have sufficient energy?
Balance this equation and determine its equilibrium expression: Hydrogen + Bromine yields Hydrobromic Acid. All of these elements are gases.
What is ([HBr]2)/([H2][Br2])
[OH-] = 6.4x10-10
pH = ?
What is 4.8?
Which species is being oxidized and which one is being reduced and by how much?
2H2O2 --> 2H2O + O2
Oxygen reduced: -1 to -2
Oxygen oxidized: -1 to 0
Determine the concentration of the solution when 4.00 grams of sodium hydroxide, Mr = 40.0 g mol-1 is dissolved in 200 cm3 of water.
0.50 mol dm-3
In what type of reaction do the products of the reaction always possess more potential energy than the reactants?
Endothermic
The reaction, N2 + 3H2 --> 2 NH3, produced -543 kJ of heat. If the energy is increased, this happens to the equilibrium.
What is the equilibrium shifts left. For an exothermic system, energy is a product. The system will shift to the left to use up the excess energy
An acid is a hydrogen ion donor, and a base is a hydrogen ion acceptor.
What is Brønsted-Lowry model?
What is always moving from the anode to the cathode in a electrolytic cell?
Electrons
Use the average bond enthalpies given in the IB Data Booklet to calculate the enthalpy change for the combustion of ethanol vapour, according to the equation:
C2H5OH (g) + 3 O2 (g) → 2 CO2 (g) + 3 H2O (g)
- 1032 kJ mol-1