What is the formula of copper (I) sulfide?
Cu2S
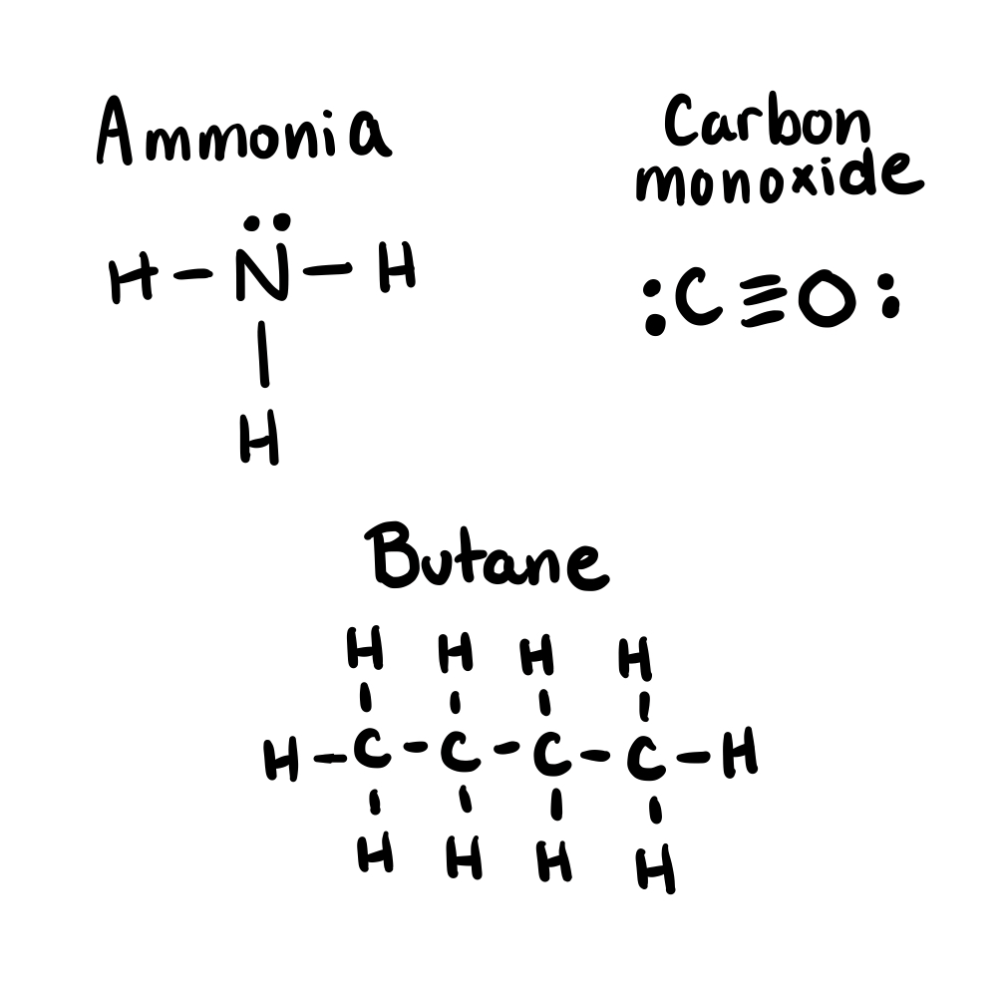
Draw the lewis formula for : Ammonia , Carbon monoxide and Butane
Draw the Lewis diagram of CO2
State its molecular geomtery
State whether is is polar or non-polar

Linear
Non-Polar
How can the electrons in a metallic bond be described?
"Sea of elestrons" "Free floating" "Delocalized"
List the intermolecular forces in order of increasing strength
London dispersion forces < dipole induced dipole < dipole-dipole < hydrogen bonding
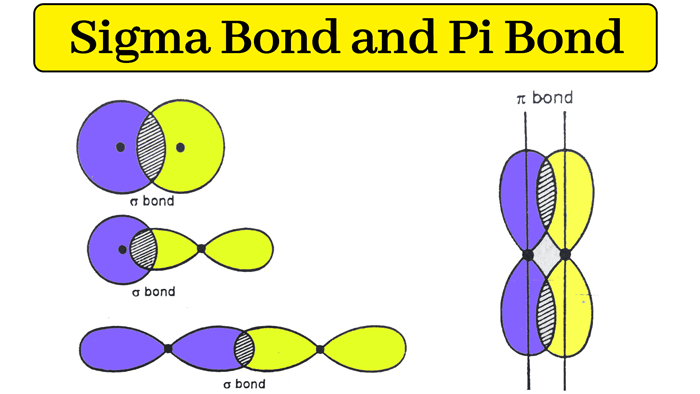
Draw a sketch of a sigma and pi bond.
Name two physical properties of solid ionic compounds
Poor electrical conductivity, Good solubility in water, High boiling point
Draw any polar covalent compound, indicate the dipole or partial positive / negative charges
Examples: water, ammonia, sulfur dioxide, etc.
What is the molecular geometry and bond angle in methane (CH₄)?
Tetrahedral
109.3º
Why does adding small amounts of carbon to iron make the metal harder? What is the resulting substance called?
Disrupts the regular arrangement of iron atoms/ions, reduces ability for atoms to slide over one another.
Called Steel / Aloy
What is the main interaction between ethanol molecules (C2H5OH)
Hydrogen bonding
What is the formal charge of the carbon atom

zero 0
Which two factors impact the relative strength of an ionic bond and how?
Difference in ionic radius (small = stronger) Difference in charge (bigger = stronger)
Draw an ozone molecule (O3) and describe the bond lengths and strengths

Single bond: Longer and weaker
Double bond: shorter and stronger
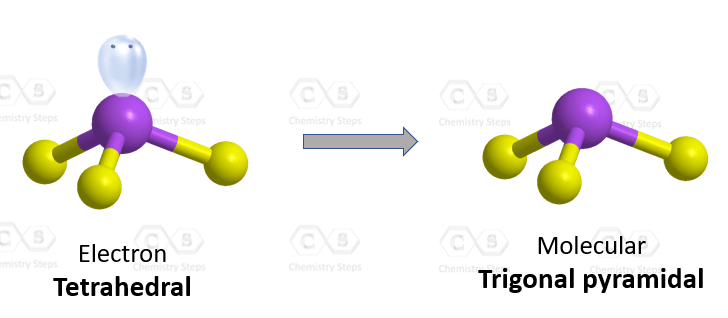
Draw a molecule where its molecular geometry is different to its electron geometry.
Name the molecular geometry and electron geometry.
Example:
Describe malleability
The ability of a metal or metal alloy to be formed into a variety of shapes by hammering it or rolling it into thin sheets.
How does increasing the amount of carbons in an alkane impact their boiling point?
Boiling point increases
Molecule gets longer, more points of contact for intermolecular forces, stronger intermolecular forces.
List 3 pieces of evidence disproving the kekulé structure of benzene
Same bond length and strength,
Bond length and strength halves,
enthalpy of hydrogenation halves,
undergoes substitution reactions,
only one isomer of benzene exists
Write the equation for the lattice enthalpy of magnesium sulfide including state symbols
MgS (s) → Mg2+ (g) + S2– (g)
State which allotrope(s) of carbon do not conduct electricity. Explain why.
diamond, no delocalized electrons (carbon has 4 covalent bonds)
Draw the 3 dimentional Lewis diagram and identify the molecular geometry of PCl3

Trigonal pyramidal
Place the following in order from weakest to strongest metallic bond: Mg, Na, K, Ca
K<Na<Ca<Mg
List 3 effects of hydrogen bonding in water
Cohesion, adhesion, surface tension, low density of solid water, high specific heat capacity, etc.
Count the number of sigma and pi bonds in the molecule below:

Sigma bonds: 6
Pi bonds: 1
Which has a more exothermic lattice enthalpy: NaBr or NaF ?
NaF (same cation (Na), Fluorine ion is smaller than brom
Draw and name 2 covalent molecules that are exceptions to the octet rule
(2 molecules)
Rank these molecules in order of increasing bond angle;
Ammonia, Boron trifluoride, Water
Water (104.5º)<Ammonia(107º)<Boron trifluoride(120º)
Which metal has the weakest metallic bonds?
Mercury (Hg)
What are the strongest intermolecular forces between molecules of propanone, CH3COCH3, in the liquid phase? (drawing recommended)
Dipole–dipole forces
Describe the type of hybridization of the oxygen atom in
sp hybridization