What is the definition of psychology?
Psychology is the study of behaviour and mental processes
Define happiness
Happiness is the state of well-being and contentment, characterised by positive emotions and life satisfaction.
What is the first step in the scientific method used in psychological research?
Identify the research question
What is phrenology and how was it used?
Study of the shape and size of the skull. It was thought to determine character traits and mental abilities.
What is the main manual used to diagnose mental disorders?
DSM-5
Which school of thought in psychology focuses on unconscious processes and early childhood experiences?
Psychodynamic Perspective
What is the difference between subjective and objective happiness?
Subjective refers to an individual's personal assessment of their own well-being, while objective happiness refers to external indicators such as income, health, and social connections that can influence happiness.
What is the difference between a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis?
The null hypothesis states that there is no effect or relationship, while the alternative hypothesis suggests that there is an effect or relationship.
Why were split brain studies important in understanding brain function?
Split-brain studies, split the left and right hemisphere through the corpus callosum. It showed that they have distinct functions and can operate independently.
Describe the mental health continuum
The mental health continuum represents the range of mental health, from optimal well-being to mental illness, acknowledging that mental health can fluctuate over time.
Which psychological approach emphasises observable behaviour and the role of the environment in shaping behaviour?
Behavioural approach
What are some factors that can impact an individual's happiness?
(List 3)
Genetics, social relationships, income, physical health, work, life events, personality traits.
What is the difference between quantitative and qualitative research methods?
Quantitative methods involve numerical data and statistical analysis (e.g., surveys, experiments), while qualitative methods focus on non-numerical data, such as interviews or focus groups, to understand experiences and meanings.
What is the role of the synapse in neuron communication?
The synapse is the gap between two neurons where neurotransmitters are released from one neuron and receied by receptors on another neuron
How is mental health different from mental illness?
Mental health refers to a person’s overall emotional and psychological well-being, while mental illness refers to diagnosable conditions that affect mood, thinking, and behavior, often requiring treatment.
Which psychological process focuses on mental processes such as thinking, memory, and problem-solving?
The cognitive perspective
Methods include:
- self-report surveys
- behaviour observations
- measuring of external/environmental factors
What is a control group and why is it important in psychology experiments?
A control group is a group in an experiment that does not receive the experimental treatment, serving as a baseline for comparison. It is important because it helps researchers determine if changes in the experimental group are due to the treatment rather than other factors.
What is the forebrain made up of?
Cerebrum, Thalamus, Hypothalamus
What are risk and protective factors that contribute to mental illness?
Risk factors include genetic predisposition, trauma, and chronic stress. Protective factors include strong social support, resilience, and healthy coping mechanisms.
The biological approach to psychology focuses on the influence of what on human behaviour?
(List at least 2 things)
Brain, nervous system, genetics and other bioogical factors.
Which neurotransmitters are involved in contributing to happiness?
Dopamine
Oxytocin
Serotonin
Endorphins
What is a descriptive research method, and how does naturalistic observation fit into this?
Descriptive research methods aim to describe behavior without manipulating variables. Naturalistic observation involves observing and recording behavior in its natural environment without interference.
Label the parts of the neuron
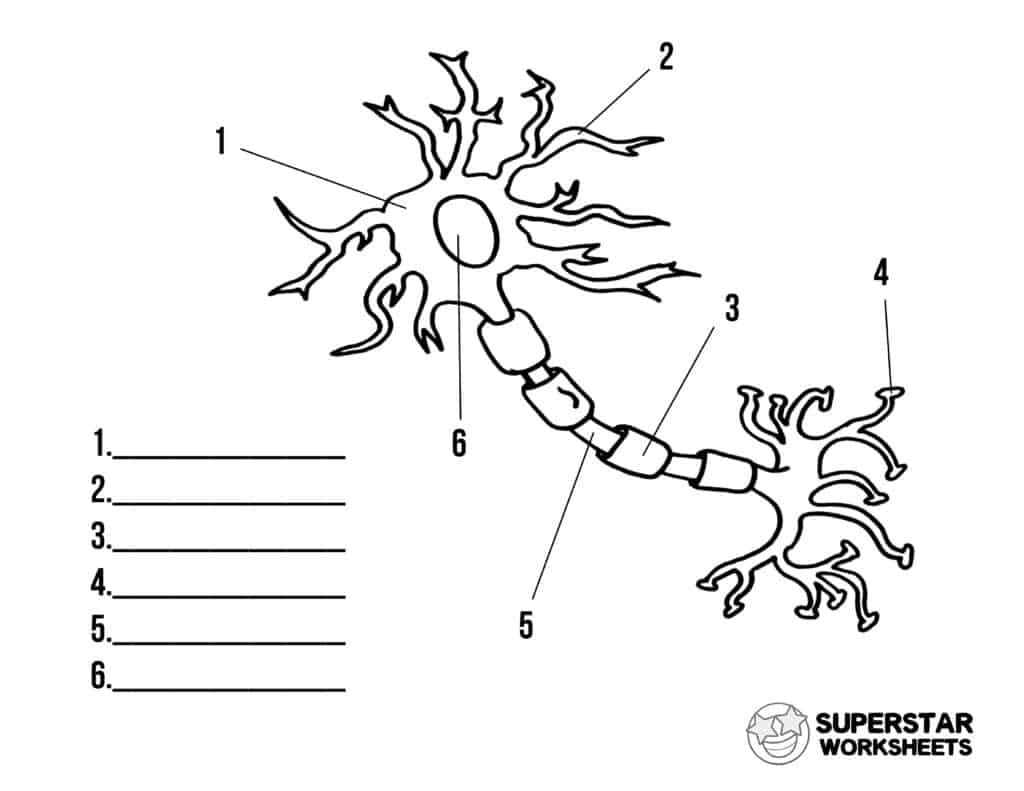
1. Cell body (Soma)
2. Dendrites
3. Myelin Sheath
4. Axon terminal
5. Axon
6. Nucleus
What are the 4Ps?
Predisposing risk factors
Precipitating risk factors
Perpetuating risk factors
Protective factors
Name one type of specialty in psychology and explain their role
Examples:
- Research
- Clinical
- Cognitive
- Community
- Counselling
- Developmental
- Educational
- Evolutionary
- Forensic
- Health
- Neuroscience
- Sport psychology
How does Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs relate to happiness?
Maslow’s Hierarchy suggests that happiness can only be fully achieved once lower-level needs (like physiological and safety needs) are met, with self-actualization at the top, representing the realization of one’s potential.

What are the ethical considerations in psychological research involving human participants, and how do they protect participants from harm?
Ethical considerations include informed consent (ensuring participants understand the study and agree to participate), confidentiality (protecting participants' private information), debriefing (informing participants about the study's true nature afterward if deception was used), and the right to withdraw at any time. These protect participants from physical, emotional, or psychological harm and ensure that their participation is voluntary and respectful of their rights.
Describe the concept of neuroplasticity,and explain how it can affect recovery following brain injury.
Neuroplasticity is the brain's ability to reorganize and form new neural connections, allowing it to adapt to injury. For example, if one area of the brain is damaged, nearby neurons may take over some functions of the damaged neurons, or another area of the brain may strengthen to compensate for the loss. This adaptability is crucial in rehabilitation, as it can enable patients to regain skills and functions through targeted therapies that promote neural reorganization.
Identify and describe two strategies for promoting positive mental health at a societal level, and explain how they can help reduce stigma around mental illness.
- Public Education Campaigns: These campaigns aim to educate the public about mental health, dispel myths, and provide accurate information. By increasing awareness, they reduce stigma by normalizing mental health issues as common and manageable.
- Mental Health Support Programs in Schools and Workplaces: Providing accessible mental health resources and support services within institutions helps people seek help early, creates a culture of openness, and reduces the stigma by integrating mental health care into everyday life.
Teacher Discretion
Final Jeopardy
Tom has recently been having trouble with his balance, coordination, and muscle control. He also experiences difficulty with breathing and heart rate regulation. Based on these symptoms, which part of Tom’s brain is most likely impacted, and why?
The hindbrain, specifically the medulla and cerebellum, is likely impacted. The medulla controls vital functions like breathing and heart rate, while the cerebellum is responsible for coordination and balance.