
This plate boundary is associated with new crust formation.
What is a Divergent Plate Boundary?
This term refers to the point inside the Earth where an earthquake originates.
What is an epicenter?
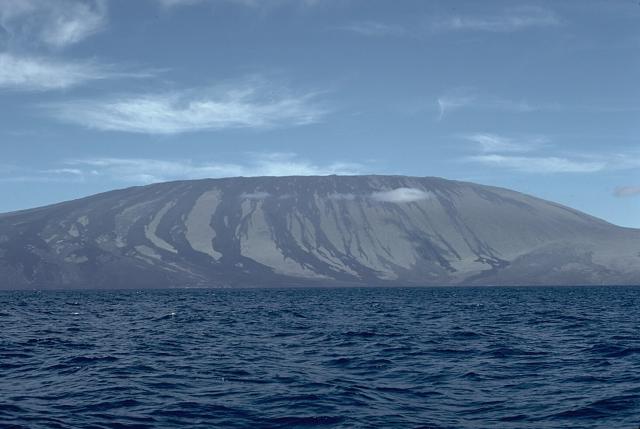 These volcanoes are categorized by gentle slopes and low-viscosity lava flows.
These volcanoes are categorized by gentle slopes and low-viscosity lava flows.
What are Shield Volcanoes?
The outermost layer of Earth. There are two types: Continental and Oceanic.
What is the crust?
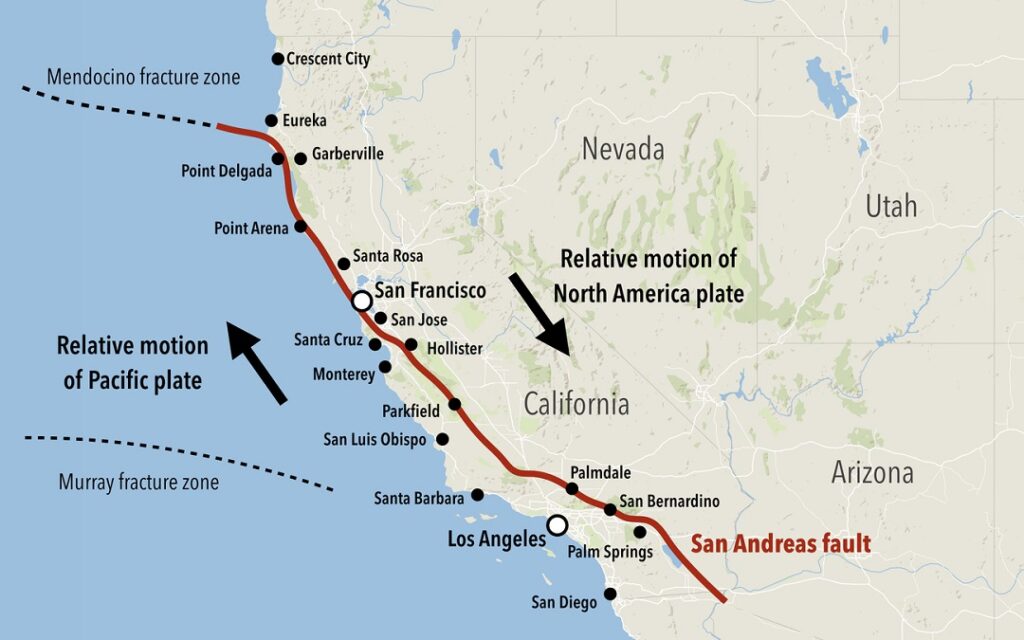 The San Andreas Fault is an example of this type of boundary where plates slide past one another.
The San Andreas Fault is an example of this type of boundary where plates slide past one another.
What is a Transform Plate Boundary?
This scale is used to measure the magnitude of an earthquake.
What is the Richter Scale?
Mount St. Helens is an example of this type of volcano, known for their steep slopes and more explosive eruptions.
What is a Stratovolcano?
Tectonic Plates rest on top of this layer and convection currents within the layer cause the plates to shift and move slowly over time.
What is the mantle?
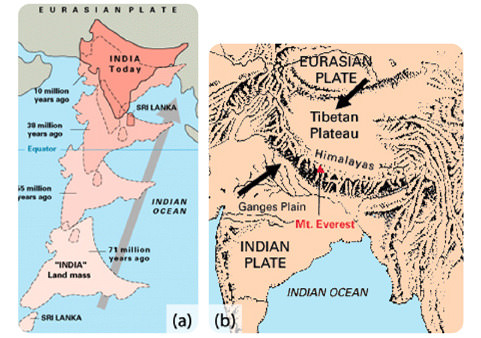 The Himalayan Mountains were built as a result of this type of plate boundary.
The Himalayan Mountains were built as a result of this type of plate boundary.
What is a Continental-Continental Convergent Boundary?
Earthquakes tend to occur at these plate boundaries.
What are all of them? Convergent, Divergent, and Transform.
When intrusive magma erupts from a volcano and flows outside of the volcano it is now considered this instead.
What is lava?
Heat from this layer generates the convection currents that drive the movement of Tectonic Plates.
What is the Core?
One of the proposed 'mechanisms' for how/why plates move.
What is Mantle Convection?
This many seismic stations are needed to triangulate the epicenter of an earthquake.
What is at least three?
Batholiths and Laccoliths are examples of plutons, present in extinct volcanoes which no longer have access to this feature.
What is a magma chamber?
What is water?
Oceanic plates tend to subduct underneath Continental plates due to this property.
What is density?
The faster seismic wave that is capable of traveling through solids, liquids, and gasses. Typically arrives first to the seismometer.
What are P-waves or Primary Waves?
What are Hotspots?
Experts believe that Earth has a liquid outer core that surrounds a solid inner core because this type of seismic wave cannot travel through liquids and seems to 'disappear' as it travels through the earth.
What are S-waves, or Secondary Waves?