What is otitis externa and its causes.
Inflammation and/or infection of the external auditory canal.
Causes:
•Moisture (ex: swimming)
•Trauma/irritation
•Foreign body in EAC
•Dermatological conditions (ex: eczema)
•Streptococcus pneumoniae
•Haemophilus Influenzae
•Moraxella Catarrhalis (less common)
What are signs and symptoms of an infected pre-auricular pit/sinus?
•Redness
•Swelling
•Warmth
•Exudate/pus
•Visible lump that’s painful
•Fever
What syndrome is associated with choanal atresia?
CHARGE syndrome
Treacher Collins Syndrome
What are ways to prevent AOM?
Proper vaccination
•Scheduled vaccines
•Influenza (flu) vaccine
•Pneumococcal vaccine
Reduce household smoke exposure
•Secondhand smoke
Encourage breastfeeding
•Maternal antibodies
Encourage proper hand hygiene
Reduce the use of the pacifier after 6 months old
•Can impact the function of the Eustachian tube
What is the first line antibiotic used to treat acute bacterial sinusitis?
> 2 years: Amoxicillin
< 2 years: Amox-Clav
Name a non-surgical treatment option for prominauris in infants. When should it be initiated?
•Ear molding
Use ear molders to help mold the babies' ear into the appropriate shape
Timing: ideally, first few weeks (less than 6 weeks) of the babie’s life
Why? Increase in estrogen allows for infant's ears to be more moldable
Define cyclic cyanosis.
Cyanosis is worse during feeding and rest/sleep
Cyanosis improves when crying
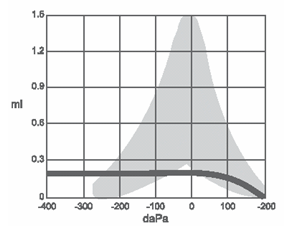
What can cause this?
MEE, PET, TM Perforation
What diagnostic tests and/or laboratory studies should be ordered when mastoiditis is suspected and why?
Labs:
•CBC and CRP: inflammatory markers
Imaging: CT scan temporal bones
•Mastoid air cell opacification
•Loss of the mastoid air cell wall visibility/clarity***
•Mastoid air cells septum destruction/erosion
•Mastoid cortex destruction
•Abscess formation
Treatment for viral rhinitis?
•Rest
•Hydration
•Analgesia
•Tylenol
•Advil
•Intranasal corticosteroids
•Saline nasal sprays
What kind of hearing loss do you have with aural atresia and how can we improve it?
Conductive hearing loss
Use of a BAHA
Why should we obtain and MRI/CT scan when a child has a nasal dermoid cyst?
Determine the extent of the lesion + any intracranial involvement
What is acute mastoiditis?
•A complication that arises from an AOM.
•A bacterial infection of the mastoid bone, spread via the mastoid antrum.
My ear tubes are leaking (otorrhea), what should I do?
•Ciprodex drops ( 4-5 drops BID) x 7days
•No improvement, move onto oral antibiotics (ex: Amoxicillin)
•Still leaking, have leakage swabbed to assess if bacteria or fungus is resistant to antibiotic of choice. Treat with appropriate antibiotic/fungal.
What is the treatment for neonatal rhinitis?
Steroid drops x1 week and NS rinses
Name the otoscopic findings with cholesteatoma.
•White/yellow pearly mass located behind the TM, in the retraction pocket
•Retraction pocket with accumulation of debris in the retraction pocket.
Location: attic or postero-superior quadrant
•Otorrhea
•Granulation tissue
What is the difference between choanal atresia and pyriform aperture stenosis?
Nasal choana is obstructed by bone and/or tissue
Narrow or blocked nasal passage/opening caused by overgrowth of upper jaw
How do you treat otitis externa?
Topical antibiotic/steroid drops to the affected ear
•Ex: Ciprodex drops
•Usually, 4 drops BID x 7 days (but can vary depending on the severity)
•These drops are only effective if the infection is bacterial.
If fungal, the patient will require antifungal ear drops
•Ex: clotrimazole
Analgesia:
•Over the counter medications (ex: NSAIDS)
May require systemic antibiotics if no improvement with the topical treatments, more severe cases, necrotizing otitis externa or contains risk factors (view next slides)
3 or more AOM in 6 months
OR
4 AOM in 12 months with at least 1 in the preceding 6 months
OR
Refractory AOM despite IV antibiotics
OR
Persistent MEE (> 3 months) with documented hearing loss
What are the diagnostic criteria for acute bacterial sinusitis (3)?
No improvement in URTI symptoms beyond 10 days.
Cough (needs to be present during the day)
Nasal congestion/discharge
OR
Fever (>39) for 3+ days
Nasal discharge: thick, purulent for 3+ days
Facial pain and/or periorbital edema
OR
Initial improvement in URTI symptoms, but then progressive worsening in symptoms (cough, nasal congestions/discharge)
Name the Levenson's Criteria for Congenital Cholesteatoma?
•White/pearly mass medial to a normal tympanic membrane
•Pars flaccida and pars tensa are normal
•No previous history of otorrhea
•No previous history of any ear related surgeries
•No previous history of any tympanic membrane perforations
•Children with previous otitis media are no longer excluded from this category
Is a nasal dermoid cyst associate with a + Furstenberg sign?
No!
Theres no enlargement in mass when straining, crying, compression of jugular vein (internal) (negative Furstenberg sign)
Bezolds abscess is a complication of what ENT infection or conditions?
Mastoiditis