Which does not change with high and low tides?
A. local sea level
B. mean sea level
C. median sea level
b. mean sea level
Seawater has a ______ freezing point than freshwater.
(higher / lower)
BONUS: Why do people put salt on the roads in the winter?
lower; salt makes water freeze at a colder temperature, so it melts the ice
Identify zone 1:
A. intertidal
B. photic
C. aphotic
D. littoral
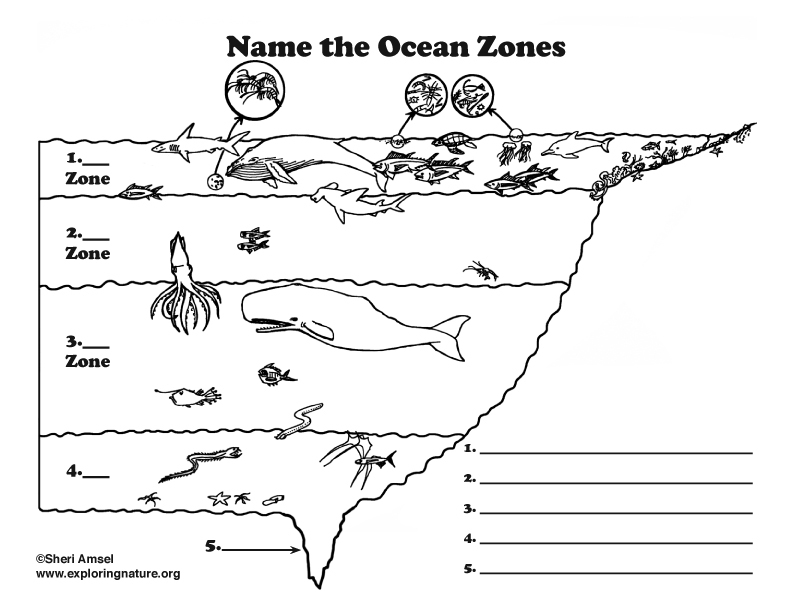
B. photic
______ is the main chemical building block of all living things.
A. nitrogen
B. hydrogen
C. carbon
D. oxygen
C. carbon
What is the largest ocean basin?
Pacific
Mid ocean ridges are often found at _______ boundaries, and fracture zones are often found to cross them at _________ boundaries (convergent, divergent, transform)
divergent, transform
Sound travels faster in _______ than in _______ (air / water).
BONUS: What do dolphins use to "see" underwater using sound?
water, air
ECHOLOCATION
Upper regions of the ocean have more dissolved _________ than lower regions.
oxygen
Carbon in the atmosphere is typically in the form of _________________________.
carbon dioxide
True or False: Mean sea level is slowly rising in most locations around the world.
True
An island atoll could have formed when...
A. a volcanic island collapsed into a flooded caldera on whose rim coral reefs grew
B. a shallow seamount sank or sea level rose above the seamount, forcing corals to grow upward from the crater rim and forming shallow reefs
C. either A or B happened
D. neither A nor B happened
C. either A or B happened
How does salinity change throughout a narrow bay fed by a river, such as the Chesapeake bay?
salinity is lower near the mouth of the river, and higher towards the ocean edge of the bay
What zone would you find coral in?
A. intertidal
B. photic
C. aphotic
D. littoral
![]()
D. littoral
Name three places where carbon is stored in the carbon cycle.
BONUS: What form does the carbon take in each location?
atmosphere - carbon dioxide
ocean water - carbonates
rock - fossil fuels
organisms - biomolecules
Why is the current salinity of the world’s oceans a problem for old-earth geologists?
If the earth were that old, the oceans would be far saltier.
BONUS: Give one location where you would find this form.
island arcs; Alaska (the Aleutian islands), Japan, the Philippines
As you go from surface to ocean bottom, the temperature _________, the pressure __________, and the density __________.
(increases / decreases)
decreases, increases, increases
What is the difference between the littoral zone and the photic zone?
littoral zone - sunlit zone over the continental shelf
photic zone - sunlit zone of open ocean
What organisms help out the nitrogen cycle by converting it to a form usable by living organisms?
cyanobacteria
What is the scientific name for the most common salt found in the ocean?
BONUS: Can you write the chemical formula too?
sodium chloride
NaCl
Describe two ways the ocean could have formed according to old-earth geologists.
Water was retained from the nebular cloud
Icy meteorites brought water
How do minerals enter ocean water? How do they leave?
Salt In - Rivers carry some dissolved minerals
Salt Out: - Living things use them
- Clumping and settling to the seafloor
- Precipitate and form sediments
What is one creature that could produce bioluminescence?
firefly, angle fish, comb jellyfish, lantern fish, glow worm, bobtail squid
How does an excess of fertilizer in ocean water kill fish?
Fertilizers cause algal blooms
Algae die and decompose
Bacteria use up oxygen
Fish die
About what percentage of the earth’s surface is covered by oceans?
(Closest guess gets the points!)
71 %