The place an organism lives and obtains everything it needs to survive.
Habitat
Streams and small rivers that feed into a main river.
Tributaries
True or False: If a material is permeable, water cannot pass through it; if it is impermeable, water can pass through it easily.
False; impermeable, permeable
The amount of dissolved salt in a sample of water.
Salinity
The movement of energy through a body of water.
Wave
A large stream of moving water that flows through the oceans.
Current
Water that fills the cracks and spaces in underground soil and rock layers.
Groundwater
The land area that supplies water to a river system.
Watershed
True or False: The saturated zone contains more water than the unsaturated zone.
True
Short for "sound navigation and ranging"-- a mapping technology that uses sound waves to calculate the distance to an object.
Sonar
Horizontal distance between crests of a wave.
Wavelength
Climate
The continuous process by which water moves from Earth's surface to the atmosphere and back, driven by energy from the sun and gravity.
The Water Cycle
A ridge of land separating watersheds.
Divide
The top of the saturated zone is known by this name.
The Water Table
A rush of water that flows rapidly back to sea through a narrow opening.
Rip Current
The vertical distance from a wave's crest to its trough.
Wave height
A climate event that occurs every two to seven years in the Pacific Ocean, causing a shift in weather patterns.
El Niño
Water that falls to Earth as rain, snow, sleet, or hail.
Precipitation
A lake that stores water for human use.
Reservoir
Any underground layer of permeable rock that holds water and allows it to flow.
Groin
A massive wave caused by earthquakes that subsequently form far below the ocean's surface.
Tsunami
A shift in climate caused when waters in the eastern Pacific are colder than usual. The opposite of an El Niño.
La Niña
True or False: Evaporation is the process by which water molecules absorb enough energy to change into water vapor, where transpiration is the process by which the leaves of plants give off water vapor.
True
The buildup of nutrients in a lake.
Eutrophication
A well in which water rises on its own because of pressure within an aquifer.
Artesian Well
Match the following labels in the image with their definitions:
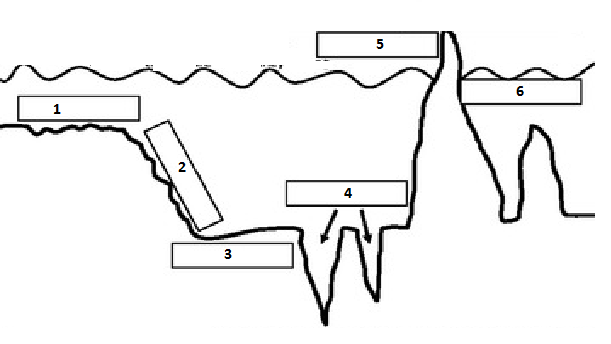 Word Bank: Seamount (in this picture, it is a Seamount Island), Trench, Continental Slope, Continental Shelf, Abyssal Plain, Mid-Ocean Ridges
Word Bank: Seamount (in this picture, it is a Seamount Island), Trench, Continental Slope, Continental Shelf, Abyssal Plain, Mid-Ocean Ridges
1. Continental Shelf
2. Continental Slope
3. Abyssal Plain
4. Trenches
5. Seamount Island
6. Mid-Ocean Ridge
The movement of sand along a beach as a result of waves.
Longshore Drift
The effect of Earth's rotation on winds and currents.
Coriolis Effect