Is when the rock breaks.
What is Fracture?
Deadly ocean waves from an earthquake
What are Tsunamis?
An Instrument used to create seismograms.
What is a seismograph?
Why all structures in earthquakes zones aren’t constructed for maximum safety.
What is cost?
The force per unit area that is placed on a rock.
What is Stress?
The initial point where the rocks rupture in the crust creating an Earthquake.
What is the Focus?
The number of seismographs require to locate the epicenter of an earthquake.
What is three?
On what to build or anchor your house to make it safest from earthquakes.
What is bedrock?
The most common stress at transform plate boundaries
What is Shear Stress?
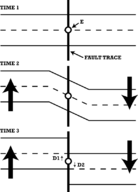
What Theory of Earthquakes does this show?
What is Elastic Rebound Theory?
What it means if a seismogram records P-waves and surface waves but not S-waves.
The Earthquake was on the other side of the Earth
Three things that kill people most in earthquakes
Fires, Building Collapse, Tsunamis.
A rock fold that bends downward.
What is a Syncline?
The height of a wave from the center line to its crest
What is the Amplitude?
The earliest scale use to measure earthquake strength.
What is the Mercalli scale?
What its called when loose sand or soil acts like quicksand when shaken.
What is Liquifaction?
When stress causes a material to change shape
What is Strain or Deformation?
About 80% of all earthquakes strike around here.
What is the Pacific Ocean?
How does the energy release of a magnitude 5 earthquake compare with the energy release of a magnitude 8 earthquake on the moment magnitude scale?
What is 27000 times?
What its called to make older buildings earthquake safe
What is retrofitting?