Say or Sing (+100pts)
the Phases of the Moon
New Moon
Waxing Crescent
1st Quarter
Waxing Gibbous
Full Moon
Waning Gibbous
3rd Quarter
Waning Crescent
What are the layers of Soil?
Humus - Horizon O
Top Soil - Horizon A
Sub Soil- Horizon B
Parent Rock - Horizon C
Bed Rock - Horizon R
What type of volcano is the Mauna Loa in Hawaii?
Shield Volcano
What is the most abundant form of water on Earth? (S6E3a)
What is Saltwater/Ocean?
Deep currents are caused mostly by
differences in density.
Copernicus created this accurate solar system model, which was not accepted for several decades before proven correct.
What is the Heliocentric Solar System Model?
What are the (7) ways scientists identify minerals?
Fracture
Color
Luster
Streak
Texture
Hardness
Describe the Epicenter and the Focus of an Earthquake.
Epicenter - the point on the earth's surface above the focus where a seismic rupture begins
Focus- location where the earthquake begins
The height of a surface wave is NOT affected by the
...salinity of the water.
Where would you be likely to find a generator?
At a power plant that supplies electricity to an entire town
Order the planets from closest to farthest from the sun. Share two characteristics about one planet.
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, (Asteroid belt +50pts), Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune
Characteristics may vary
What are the 3 types of rocks?
Give (1) identifying characteristic for each rock type
Igneous (shiny, fine or coarse grains)
Metamorphic (ribbonlike bands, smooth)
Sedimentary (fossils, sediment composition)
What causes Earthquakes?
Transform Boundary- two tectonic plates sliding past each other
If you could descend from the surface to the ocean floor, what would you observe?
Higher salinity, extremely cold temperature
Hector is walking along the ocean floor from the beach. Which of the following features would he reach after the continental shelf?
continental slope
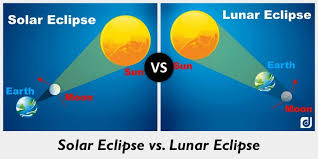
Draw a Solar & Lunar Eclipse
How is each rock type formed?
Igneous- Inside or Outside of a Volcano
Sedimentary- Weathering, Deposition, Compaction, Cementation
Metamorphic- Heat & Pressure
What geological event causes Volcanoes to form?
Magma rises to the surface through a divergent plate boundary
What are the two types of currents? Which one would move a bottle or help a ship the ocean?
Surface Currents- Help ship and bottle
Deep Currents
Sunlight is not currently used as a major source of energy. Why not?
Economical ways to capture and store large amounts of solar energy have not been developed.
Define the Big Bang Theory. What evidence have scientists researched to prove this theory occurred?
A singular point that exploded, created all of this universe, and left behind comic radiation
What is the difference between Weathering & Erosion?
Identify (3) examples of each type of weathering.
Identify the (4) Agents of Erosion
weathering occurs in one place, erosion involves movement to a new location
Mechanical (Abrasion, Frost Wedging, Plant Roots, Exfoliation)
Chemical (Oxidization, Hydrolysis, Carbonation, Lichen, Acid Rain)
Agents- Wind Water Gravity Ice... Erosion is really nice (+50pts)
Define the 3 types of volcanoes and identify 1 real world example.
Composite-
most common type of volcano, explosive eruptions, found Mt. St, Helena ;called stratavolcano
Shield-
built up of layers of lava, repetitive non explosive eruptions; gently sloping sides; found in Hawaii
Cinder-Cone
modern explosive & non-explosive eruptions; found near other volcanoes; found in Mexico
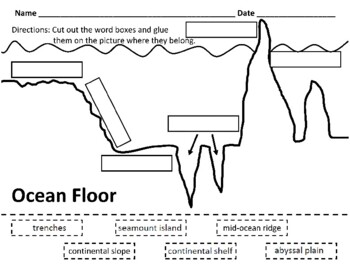
Continental Shelf
Continental Slope
Abyssal Plain
Trenches
Seamount Islands
When coal is burned to produce electricity, the electrical energy produced is less than the potential energy in the coal. Which best explains this observation?
Some of the potential energy in coal is converted into forms of energy other than electricity.