The amount of space and object takes up
What is volume?
The Earth’s outermost layer made up of a mixture of gases
What is the atmosphere?
The affects of melting glaciers on the geosphere (the ground), the hydrosphere (glaciers) and atmosphere (climate) is an example of this
What is feedback?
A group of parts that work together as a whole
What is a system?
The huge broken pieces of rock that make up the lithosphere
What are plates?
Earth’s thinnest layer
What is the crust?
This deeper inside the Earth, the greater the pressure, so this increases
What is temperature?
This layer groups together the uppermost part of the mantle and the crust because their characteristics are the same; made of brittle rock, strong, hard and rigid
What is the lithosphere?
The movement of energy from a warmer object to a cooler object
What is heat transfer?
Cooler, denser liquid does this
What is sinks?
Using your five senses to collect factual evidence
What is making accurate observations?
The sphere that contains all of the Earth’s water
What is the hydrosphere?
This is considered to be a part of the Earth system because it is a source of energy for Earth’s processes
What is the sun?
The forces that erode mountains
What are destructive forces?
The slow movement of Earth’s plates
What is plate tectonics?
Geologists use these 2 main types of evidence to learn about Earth’s interior
What are direct evidence (from rock samples) and indirect evidence (from seismic waves)?
This is the layer of rock that forms the Earth’s outer skin, including both dry land and the ocean floor
What is the crust?
The layer of the mantle under the lithosphere that is solid, but so hot it can bend like a spoon
What is the asthenosphere?
The type of heat that is transferred in rays, like sunlight
What is radiation?
Hotter, less dense liquid does this
What is rises?
The attempted explanations followed by a scientists observation
What are inferences?
This sphere contains 3 main parts: a metal core, a solid middle layer and a rocky outer layer
What is the geosphere?
The atmosphere is mostly made up of these 2 gases
What are nitrogen and oxygen?
The wearing down and carrying away of land by natural forces such as water, ice or wind
What is erosion?
The type of forces that raised the Himalaya Mountains
What are constructive forces?
Produced by earthquakes, geologists use the speed and paths these take to get clues about the structure of the Earth
What are seismic waves?
The crust that lies beneath the ocean
What is oceanic crust?
The deepest (hot, but rigid) layer of the mantle that contains the transition zone
What is the mesosphere?
Heat transfer by the movement of a fluid is called
What is convection?
Name the correct order of the 4 main layers of the Earth’s interior starting from the innermost layer
What is the inner core, the outer core, the mantle and the crust?
Descriptions of a scientific observation that does not include numbers
What are qualitative observations?
There are 4 of these main “parts” that make up the Earth system
What are spheres?
The ability to do work
What is energy?
These forces shape the land’s surface by building up mountains and other land masses
What are constructive forces?
Ice, rain, wind and changing temperatures are these type of forces
What are destructive forces?
These are the 3 layers of the Earth’s interior
What are the crust, the mantle and the core?
The crust that forms the continents
What is continental crusts?
A dense ball describes this part of the Earth’s interior
What is the inner core?
Heat that transfers between materials that are touching
What is conduction?
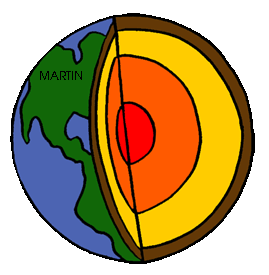 Name the brown layer; specifically, the part of the brown layer that is under the green
Name the brown layer; specifically, the part of the brown layer that is under the green
What is the continental crust?
If you count or measure objects using standard units, you will be making this type of observation
What is a quantitative observation?
The only sphere that contains living organisms
What is the biosphere?
The 2 main sources of energy that drive the Earth system
What are heat from the sun and heat flowing out of the Earth as it cools?
Earth’s top layer of thick, solid rock
What is the lithosphere?
This process demonstrates how one part of the Earth system might affect the other parts
What is feedback?
The result of a force pressing on an area
What is pressure?
The layer of the Earth’s interior that is made up of very hot, but solid rock; about 3000km thick
What is the mantle?
Scientists think that movements in the liquid outer core of the Earth create this (hint: it has a north and a south pole)
What is the Earth’s magnetic field?
Convection currents occur in these 2 layers of the Earth’s interior
What are the mantle and the outer core?
Rock samples collected from drilling holes several kilometers into the Earth provide this type of evidence about the Earth’s interior
What is direct evidence?