This is the negatively charged subatomic particle.
What is the electron?
This refers to a gap in the geological record due to erosion.
What is an unconformity?
This refers to a map which uses lines to show elevation.
What is topographic?
This type of volcano creates ash in its eruptions.
What is explosive?
This type of wave is what we usually feel during an earthquake and arrive last.
What is a surface wave?
These subatomic particles are found together in the nucleus.
What are protons and neutrons?
This refers to the time is takes for half of an unstable material to decay into a stable material.
What is a half-life?
This refers to the level/depth groundwater reaches above bedrock.
What is the water table?
This type of volcano is mostly made of ash, small, and short-lived.
What is a cinder cone?
These type of waves occur within the Earth's interior.
What are body waves?
These processes lead to sediment.
What are weathering and erosion?
This type of energy source uses turbines places in the ocean.
What is tidal energy/power?
This Ocean is locates south of Asia and north of Australia.
What is the Indian Ocean?
This type of lava is medium viscosity and leaves a rough surface.
What is A'a?
This type of wave moves rock in a forward-back motion as it compresses it.
What is a P wave?
This is a property which states a mineral is formed without any components from plants or animals.
What is inorganic?
This refers to the process of determining a rock's age due to patterns in the layers.
What is relative age dating?
This results as water cools or becomes more salty.
This landform is the result of a volcano collapsing in on itself.
What is a caldera?
This refers to the point in the crust where an earthquake originates.
What is the hypocenter?
These are the 3 major types of mineral formation.
What are Evaporative, Hydrothermal, and Igneous formation?
The original amount of a material which takes 10 minutes to decay to 1g, with a half life of 2 minutes.
What is 32g?
The elevation of Point B on the map shown: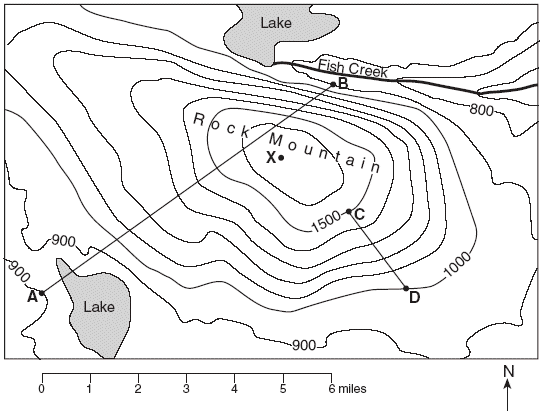
What is 900?
These two things cause an eruption to be more explosive.
What are water content and silica content?
A magnitude 4.0 quake is this many times stronger than a magnitude 2.0 quake.
What is 100?