This field studies Earth's materials, history, and processes.
What is Earth Science (or Geoscience)
This famous geoscientist developed laws to understand the relative age of sedimentary rocks (first and last name)
Nicolas Steno AKA Nicolaus Stenonius AKA Niels Steensen
The outermost layer of Earth is called this.
What is the crust?
The Earth and the solar system formed from a cloud of gas and this material.
What is dust?
This process in the mantle causes less dense material to rise and denser material to sink.
What is convection?
Three subdisciplines in Earth Science.
What are: Geology, meteorology, oceanography, astronomy, environmental science. paleontology, geophysics, geochemistry, volcanology, seismology, hydrology, hydrogeology, soil science, planetary science, climate science, biogeochemistry
According to this law, rock layers are deposited in flat, horizontal layers.
What is the Law of Original Horizontality?
This is the thickest layer of Earth
What is the mantle
The age of the earth.
What is 4.54 billion years old
(4.6 is ok)
Heat driving mantle convection comes from this source deep within Earth.
What is the core?
These lifeless, natural features can tell stories about Earth's history, including its age and past environments.
What are rocks?
This law states that geological features cutting across layers are younger than the layers they cut through.
What is the Law of Cross-Cutting Relationships?
The inner core is made mostly of these metals, which remains solid due to immense pressure.
Iron and Nickle
The property defined by the amount of mass in a given space or volume.
What is density?
Rigid pieces of Earth's crust that move are called this.
What are tectonic plates?
Ways geoscientists can further understand rocks (list 2 ways)
What are: radiometric dating, stratigraphy, mineral and rock composition/texture, fossil content
This law suggests that sedimentary layers extend outward in all directions until they thin out or meet a barrier.
What is the Law of Lateral Continuity?
The mantle behaves differently with depth; near the crust, it is brittle, but deeper, it acts like this.
What is plastic or ductile?
The moon is thought to have formed when this happened
What is a Mars-sized body collided with Earth, sending out material that eventually coalesced (clumped up) into the moon.
Mantle convection is responsible for these surface phenomena (name 3)
What are: plate motion, ocean basins, mountains, earthquakes, volcanoes, valleys, tsunamis
Describe how a rock can go through the rock cycle and become all 3 different rock types throughout its existence.
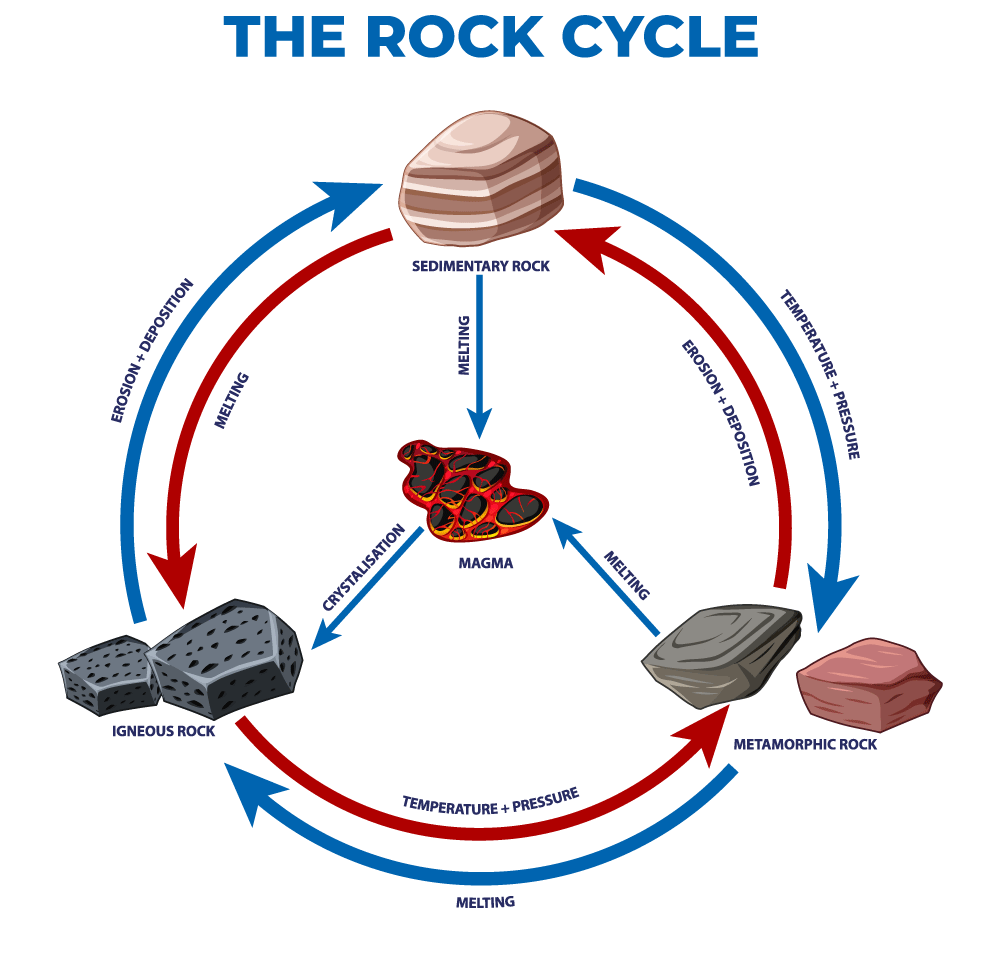
What is: BDAECHIGJFKLM
This process of separation by density led to the formation of Earth’s distinct layers.
What is differentiation?
The force that pulled together gas and dust to form Earth and the solar system depends on the mass of objects. The greater the mass, the stronger this force.
What is gravity?
Why applying heat causes materials to be less dense.
Applying heat (aka thermal) energy causes particles within the material to spread apart. This makes the material occupy more volume but still have the same mass, resulting in less density.