Which sphere is made up of all living things?
Biosphere
The Earth has four layers with different properties. In which layer of the Earth would you find a semi-solid rock that flows like a liquid in convection currents?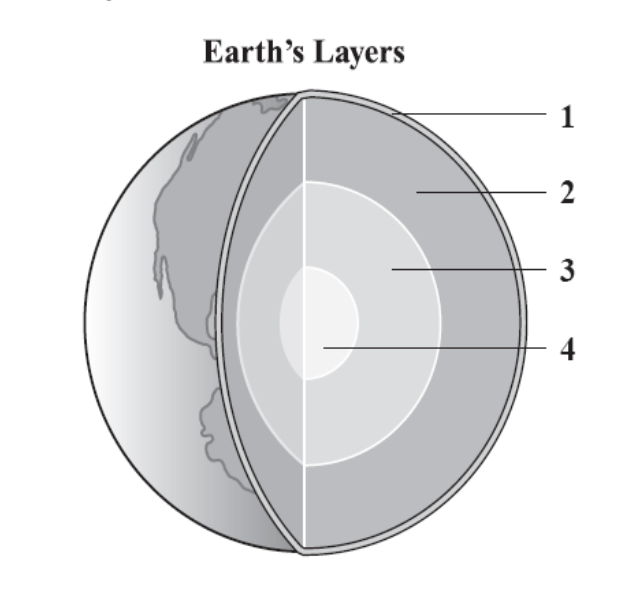
2. Mantle
What type of heat transfer travels through electromagnetic waves? Ex: the sun heats up the ground

Radiation
What is the process of rocks breaking down into smaller pieces (sediments)?
Weathering
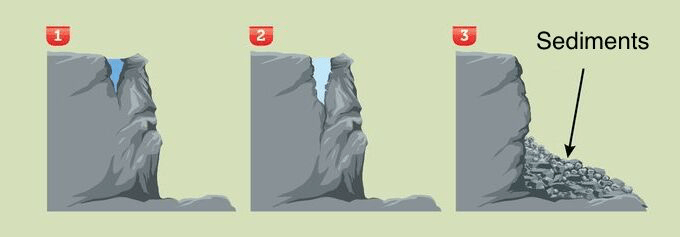
What are the three types of rocks present in the rock cycle?
Metamorphic, Igneous, and Sedimentary
During a wildfire, smoke gets carried by wind into highly populated areas, where humans and other animals have difficulty breathing. Which spheres of the Earth are interacting in this example?
Atmosphere and biosphere
The thinnest outermost layer of the Earth's interior?
The Crust
What type of heat transfer is through direct contact? Ex: when hot land heats up the air above it
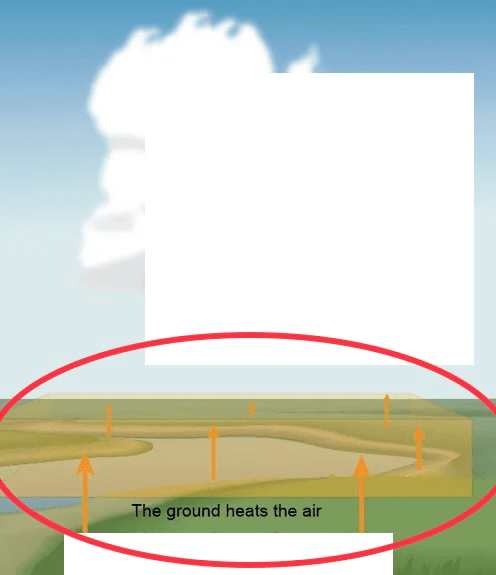

Conduction
What is the primary process by which natural agents like water, wind, or ice move and transport soil and rock debris from one place to another?
Erosion
What type of rock is formed through compaction and cementation? Fossils are usually found in this type of rock and it is known to have many layers.
Sedimentary
Which pair of Earth's spheres interact the most when ocean waves break onto a beach?
A. atmosphere and biosphere
B. geosphere and atmosphere
C. hydrosphere and biosphere
D. geosphere and hydrosphere
D. Geosphere and hydrosphere
A transform boundary is when two plates slide past one another. What natural disaster does this cause? 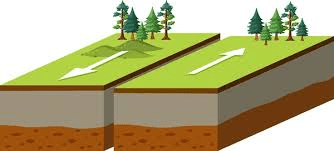
Earthquakes
When heat transfers in a circular motion in a fluid such as water or air. Ex: warm air rising, cold air sinking
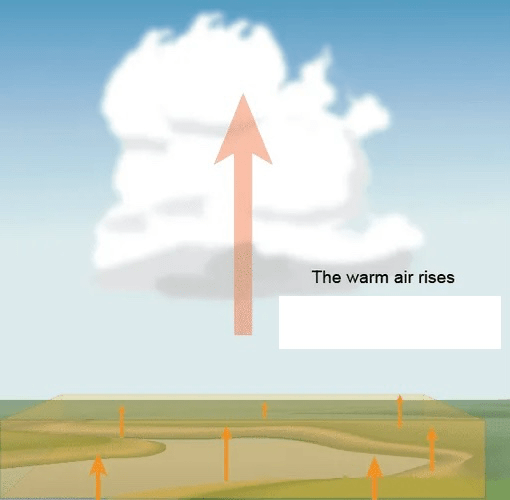

Convection
When particles carried by wind, water, or ice are dropped into another location
Deposition
What type of rock is made from intense heat and pressure deep inside the Earth's mantle?
Metamorphic
Which statement best describes the climate of Florida she lives?
A. It typically rains in the afternoon during the summer.
B. The average yearly temperature is 22°C (72°F).
C. Yesterday the temperature was 32°C (90°F) and it was raining.
D. It is usually hot at the beach.
The average yearly temperature is 22°C (72°F).
During a convergent boundary, tectonic plates move towards one another causing what type of landforms?
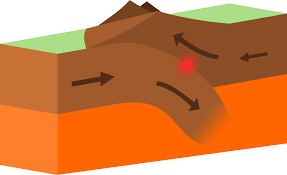
Mountains or Volcanoes
Where does the energy that creates global patterns of wind movement come from?
Radiation from the Sun
Earth's surface is constantly changing, and new landforms are constantly taking shape due to natural processes. Which landform is most likely caused by deposition?
A. caves
B. lakes
C. valleys
D. deltas
D. Deltas
What must happen in order for a metamorphic rock to be transformed into an igneous rock?
Melting & Cooling
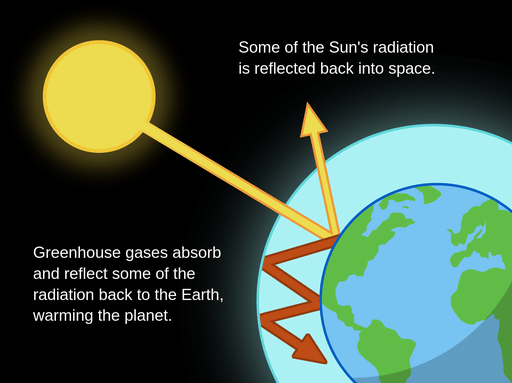
The atmosphere surrounding Earth helps to maintain the various climates found around the world and keeps Earth from becoming extremely cold all over. How does the atmosphere help to keep Earth insulated and warm?
The atmosphere helps trap heat energy from the Sun and energy radiated from Earth to maintain the climate
Under the ocean when two tectonic plates separate, magma rises causing sea floor spreading forming new oceanic crust. What type of plate boundary is occurring during this process? 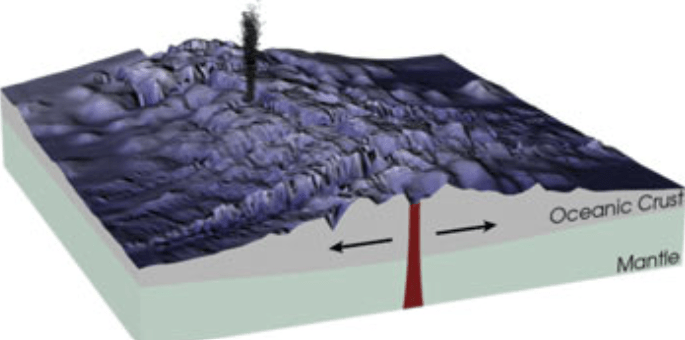
Divergent plate boundary
The Sun heats up Earth unevenly due to its spherical shape and tilt. What are the circular arrows shown in the picture below.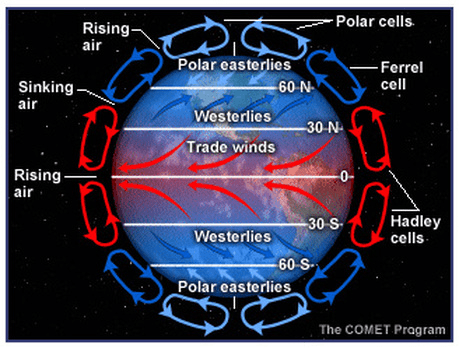
Convection currents
Gravity, water, wind, and heat can all contribute to erosion. Which of the following natural landforms are primarily formed by wind erosion?
A. deep river canyons
B. desert sand dunes
C. mudslides
D. sinkholes
B. Desert Sand Dunes
What is the law of superposition?
In a sequence of sedimentary rock layers, the oldest layer is at the bottom and the youngest layer is at the top.