What is an earthquake?
A sudden and violent shaking of the ground, sometimes causing great destruction
What is this machine?
What signs can predict an volcano eruption?
Smaller earthquakes.
What volcanoes are formed by erupting erupt slowly?
Shield volcano.
What causes earthquakes?
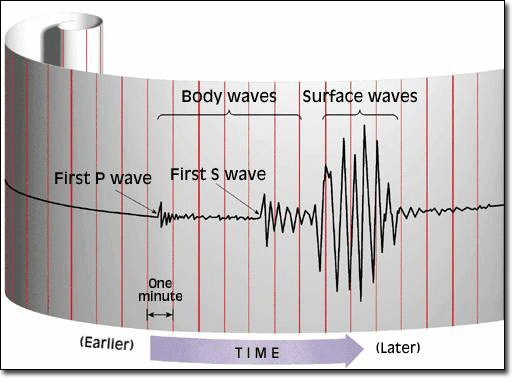
What wave arrive last in an earthquake?
L - waves.
What happens before the large event (the eruption)?
Smaller events lead up to the eruption.
What volcanoes explodes during eruptions?
Cinder volcano
Where do most earthquakes occur?
At plate boundaries.
What waves arrive second in an earthquake?
What are precursor events?
Release of gasses and changing shape of the volcano.
What volcano is a mix of the properties of a shield volcano and a cinder volcano?
Composite volcano
Which area of the world has the most earthquakes? (hint Pacific)
The Ring of Fire
What waves arrive first in an earthquake?
Primary waves.
How are graphs and charts used to predict volcano eruptions?
Scientists look at past eruptions and see the patterns.
What is tephra?
How many earthquakes happen in a year?
About 20,000 a year.
What type of measurement are earthquakes measured in? (How strong is it?)
Magnitude.
Why are rising temperatures part of predicting a volcano eruption?
The higher temperatures may be a part of the hot gasses coming from the volcano.
Where do volcanoes form?
Plate boundaries, specifically convergent.