a substance that cannot be broken down into a simpler substance
element
This property of water, allows some insects to walk on water due to surface tension. 
cohesion
A process in which an event acts as both an input and output of the same system is called a(n)
feedback loop
One of the rigid layers of the lithosphere,
tectonic plate
These organisms are essential to the nitrogen cycle, 'fixing' N2 making it useful to organisms and returning it to the atmosphere.
bacteria
the smallest unit that maintains the chemical properties of an element
atom
When in a solid state water's density is ____ than as a liquid, allowing ice to float.
Lower
Byproducts of decaying organisms mix into soil and which plants take in nutrients from the soil. Which two sphere's are interacting?

geosphere & biosphere
This gas in the atmosphere plays a vital role in keeping Earth warm through the greenhouse effect.
Carbon dioxide
Consumers play a role in cycling carbon, by releasing carbon dioxide to the environment via this process.
cellular respiration
hydrogen (H) atoms and an oxygen (O) atom bond together to make water (H2O). What term best describes H2O? Why?
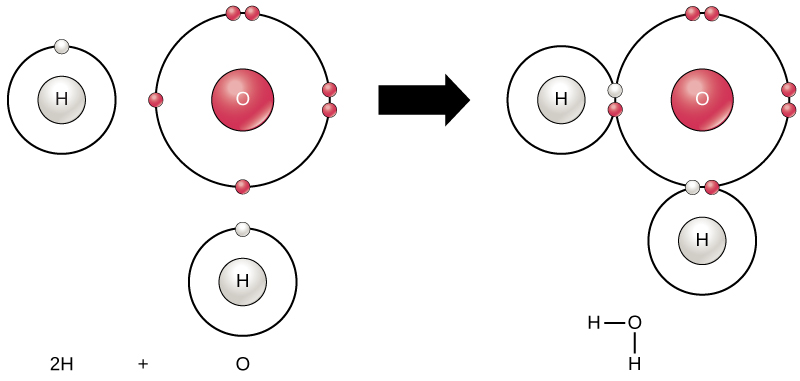
compound (two different elements chemically combined)
or
molecule - two or more atoms chemically combined WITH a covalent bond
This macromolecule is made up of nucleotides, and direct protein production.
nucleic acids
In the Arctic, melting sea ice exposes more dark ocean, which in turn absorbs more heat and causes more ice to melt...the cycle continues.
This is an example of
In the Arctic, melting sea ice exposes more dark ocean, which in turn absorbs more heat and causes more ice to melt...the cycle continues.
Positive Feedback Loop
Give a clear example of how the biosphere and the atmosphere are interconnected/ depend on each other.
EX: Organisms, such as plants depend on the atmosphere for carbon dioxide to go through photosynthesis, and release oxygen back into the atmosphere.
Which cycle is dependent on the weathering of rock, in order for nutrients to be dissolved by water and taken up by plants?
the phosphorus cycle
How do chemical bonds form?
By the sharing or exchange of electrons between atoms.
This property of water is the reason why a metal tea kettle gets hotter faster than the water inside it.
Resistance to Temperature Change
or
High Specific Heat
Give 4 clear examples of the hydrosphere.
clouds
lakes
ocean
river
glacier
water vapor
Correctly label evaporation, transpiration, precipitation, and condensation. 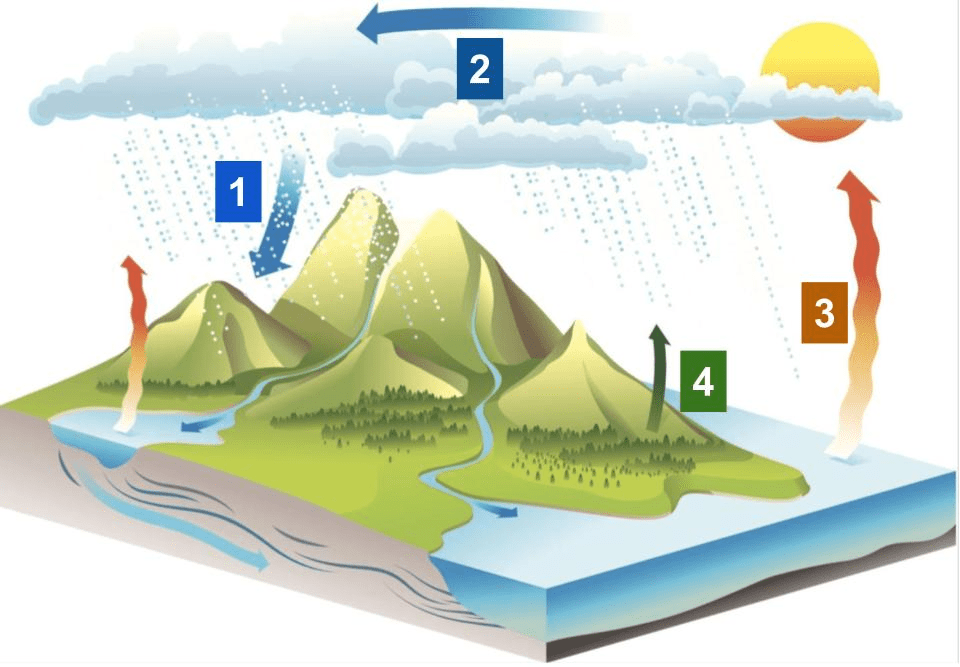
1. precipitation
2. condensation
3. evaporation
4. transpiration
Primary producers through the process of photosynthesis create this biomolecule.
carbohydrates or glucose
Use the laser pointer to identify all the parts of an atom
Polymers that consist of atoms of carbon, hydrogen & oxygen. Plants use it to store energy, and animals acquire it when they eat plants.
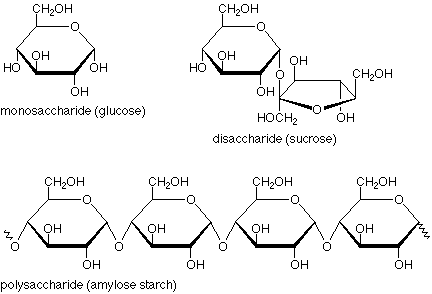
carbohydrates
give 5 clear examples of parts of the geosphere.
tectonic plate
lithosphere
mantel
core
mountain
canyon
Caption the image below using the terms tectonic plate, landforms.
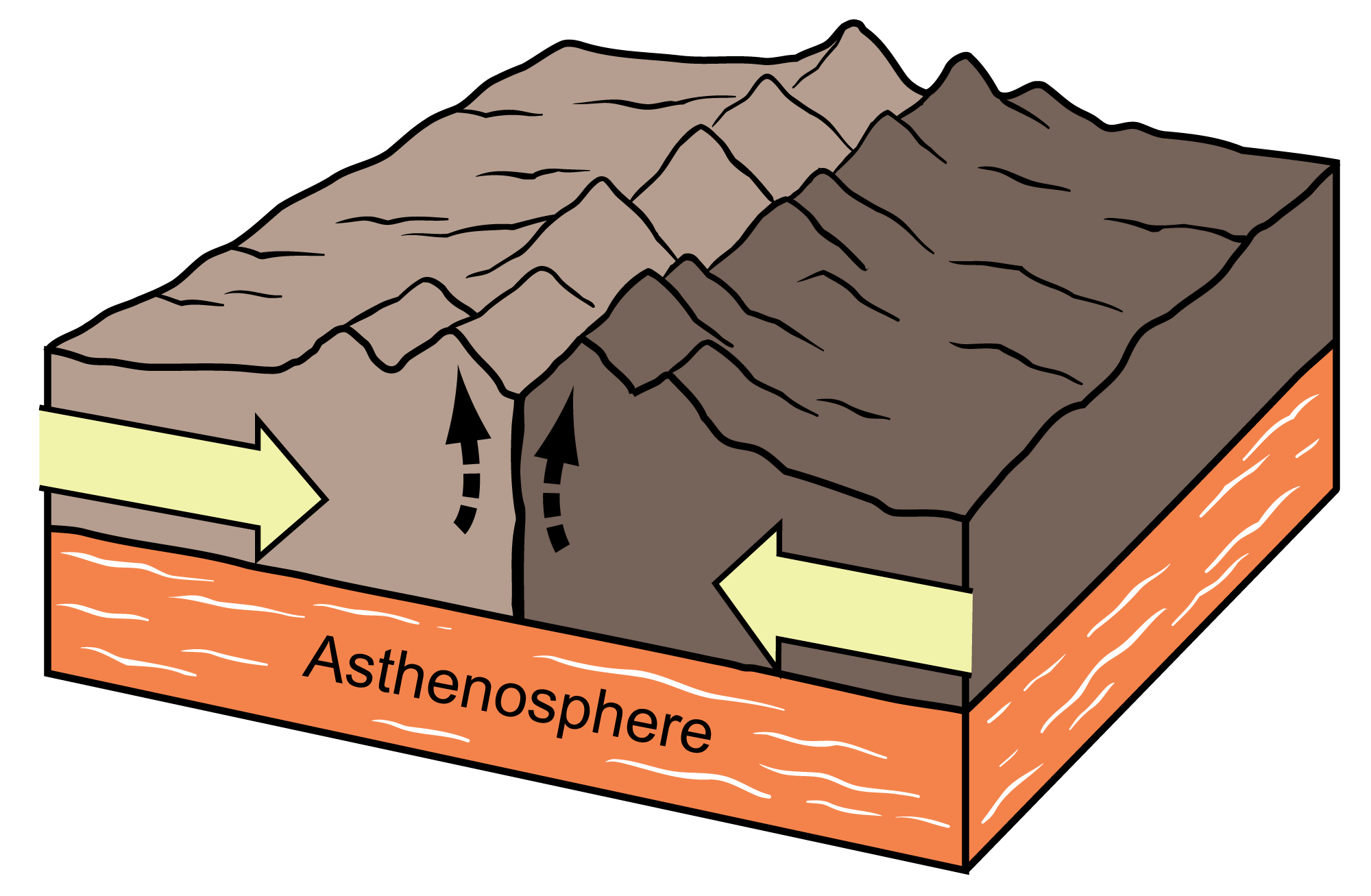
The caption should illustrate the relationship between the terms/ how they are related.
tectonic plates colliding against each other create landforms such as mountain ranges.
What is the cause and effect of eutrophication?
Cause: Excess nutrients in water from agricultural runoff, sewage, and stormwater discharge.
Effect: Oxygen depletion, leading to fish kills and the formation of dead zones.