What are London dispersion forces?
Temporary attractive forces due to instantaneous dipoles in all atoms and molecules.

What is surface tension?
The energy required to increase a liquid's surface area due to cohesive forces.
What is a molecular solid?
Solid made of molecules held together by IMFs.
What does "like dissolves like" mean?
Polar solvents dissolve polar solutes; nonpolar dissolves nonpolar.
What is melting?
Solid → liquid.
What is dipole-dipole interaction?
Attractive force between the positive end of one polar molecule and the negative end of another.
What is viscosity?
A liquid’s resistance to flow, which increases with stronger IMFs.
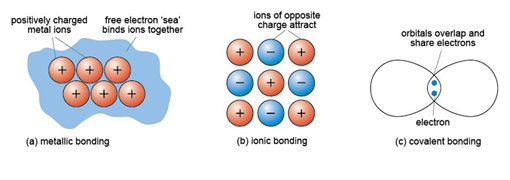
What is an ionic solid?
Solid composed of positive and negative ions held by electrostatic forces.
What makes a substance polar?
Unequal sharing of electrons + asymmetrical shape.

What phase change is boiling?
Liquid → gas.
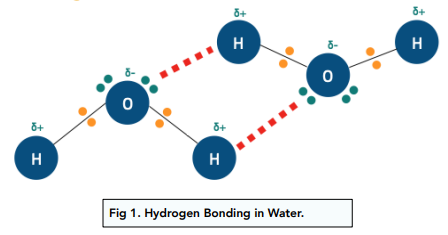
What is hydrogen bonding?
A strong dipole-dipole interaction involving H bonded to N, O, or F.
How does IMF affect boiling point?
Stronger IMFs result in a higher boiling point.
Give an example of a network covalent solid.
Diamond (carbon) or quartz (SiO₂).
Why does NaCl dissolve in water?
Ion-dipole attraction between Na⁺/Cl⁻ and polar water molecules.
What is vapor pressure?
Pressure exerted by a vapor in equilibrium with its liquid.
Which IMF exists in all molecules?
London dispersion forces.
Define capillary action.
The movement of liquid within a narrow tube due to cohesive and adhesive forces.

Compare metallic and ionic solids.
Metallic: sea of electrons; Ionic: electrostatic attraction between ions.
Explain how IMF affects solubility.
Stronger IMF between solute and solvent = better solubility.
How do IMFs affect vapor pressure?
Stronger IMF = lower vapor pressure.
Rank LDF, D-D, and H-bond by strength.
H-bond > Dipole-dipole > LDF.
Explain why water has a high boiling point.
Because of strong hydrogen
Describe the properties of network covalent solids.
Very hard, high melting point, poor conductors (usually).
Predict solubility: hexane in water.
Insoluble – hexane is nonpolar, water is polar.
Describe the process of sublimation.
Solid → gas without becoming a liquid.