These are indications of an old myocardial infarction via echocardiography and ECG.
What is a wall motion abnormality, thinning/scarring, increased echogenicity and Q waves on the ECG?
The type of 2D measurement used for the Left Ventricular Outflow Track
What is leading edge to leading edge?
Ejection fraction < 30%
What is severely reduced?
These two vessels (name the vessels and corresponding letter) feed.tje coronary arteries, supplying the heart with oxygenated blood.
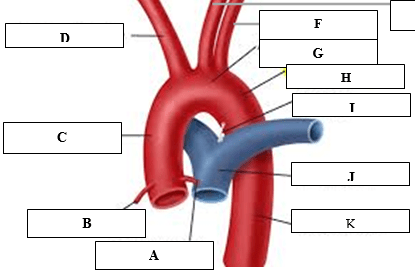
What are the coronary sinus's, letters A and B?
This line represents aortic valve closure on m-mode.
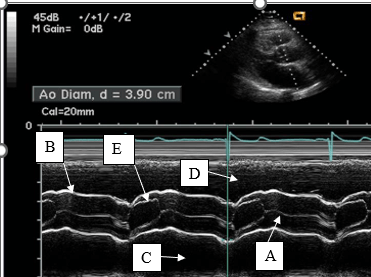
What is A?
This is the ECG timing of the left ventricular outflow track measurement.
What is early to mid-systole?
A small pericardial effusion 1-12 weeks after a myocardial infarction.
What is Dressler's syndrome?
The wall normal thickness of the posterior wall in diastole?
What is 0.6-1.1 cm?
This is one of the most important quantitative parameters of right ventricular systolic function and how it is obtained?
What is the measure of pulmonary artery pressure using the peak velocity TV regurgitant and the respiratory collapse and size of the inferior vena cava seen from the subcostal window?
This vessel supplies the anterior wall and the apex with blood. (Vessel name and corresponding letter)
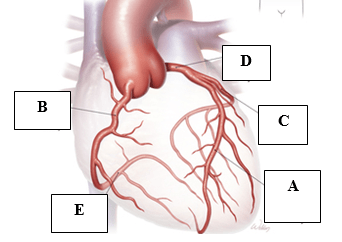
What is the left anterior descending (LAD), letter A?
Letters A and C represent these waveforms.
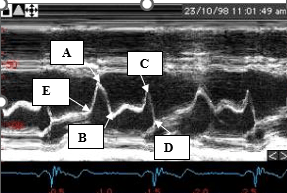
What is a- rapid or early filling and c - atrial systole or atrial kick?
The intraventricular septum and the posterior wall are measured at this time in the ECG.
What is end diastole?
The 5 steps in the sequence of events in order of myocardial ischemia and when it can be detected by echocardiography.
What is perfusion abnormalities, diastolic dysfunction, systolic dysfunction, ECG changes, angina and at the point of systolic dysfunction?
LVIDs is performed at this time
What is end-systole?
What is when the LV volume is the smallest?
The frame after AV closure?
The heart contractions in this direction at the apex and this direction at the base?
What is counterclockwise at the apex and clockwise at the base? From base to apex
This layer of the heart muscle produces the pericardial fluid, which acts as a lubricant between the inner and outer layers.
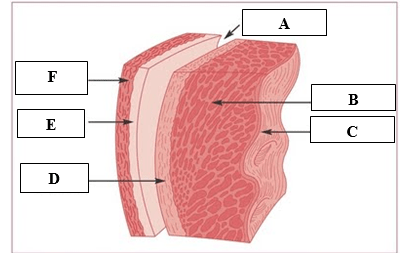
What is the visceral pericardium or the epicardium, D?
The name and description of how this measurement is performed.
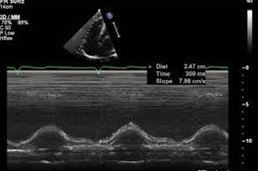
What is Tricuspid Annulus Systolic Excursion - TAPSE, m-mode (zoomed preferred) through TV annulus in a right focused view in the apical 4 chamber, measure systolic waveform excursion in a vertical line?
Normal 17 mm or greater.
This is the ECG timing of the left atrial measurement.
What is end systole?
Occlusion of this artery will cause myocardial infarction of these walls.
What is anterolateral (lateral) and inferolateral?
These are normal ranges for an aortic root measurement
What is 2.1-3.5 cm?
These are 4 qualitative assessments of the left ventricle.
What are regional and global wall motion, shape of the left ventricle, wall thickness of the left ventricle and chamber size
This is the point AND the name of the measuremnt that is measured for right sided Tissue Doppler Imaging (TDI), a measurement of the maximum velocity of the tricuspid lateral annulus during systole.
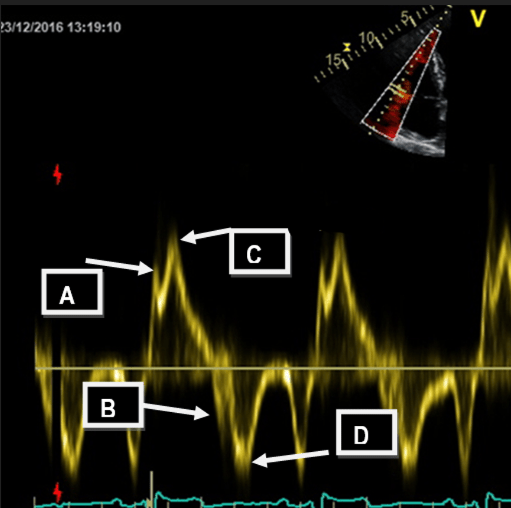
What is S' (S prime) and pont C?
Letter E represents this aortic valve cusp and it's position during systole.
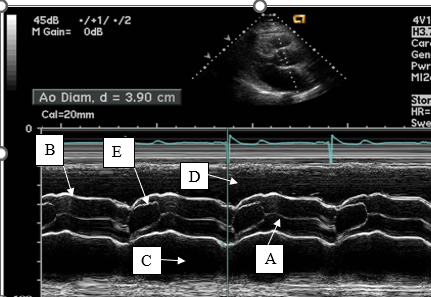
What is the right coronary cusp in the open position?
These valve actions begin and end isovolumetric relaxation.
What is aortic valve closure and mitral valve opens?
The walls represented by A and B
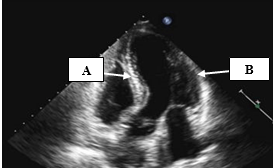
What is A - Antero septum and B- anterolateral?
This is from where and when you measure LA volume and it's normal value
What is AP2 and AP4, end-systole and 34 ml/m2?
This septal motion pattern in PSAX, a qualitative assessment of right ventricular systolic function, is indicative of a pressure volume overload pattern.
What is systolic and diastolic septal flattening?
The ejection period is represented by these to points on the Wigger's Diagram.
DAILY DOUBLE : What two valves are opening and closing at these same points?
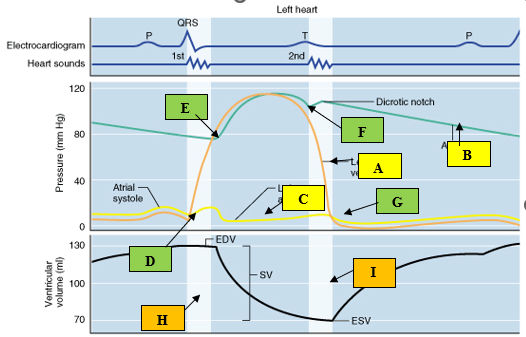
What is E - F?
DD: What are the Aortic and Pulmonic valves?
The name for this indirect sign of aortic valve regurgitation on M-mode.
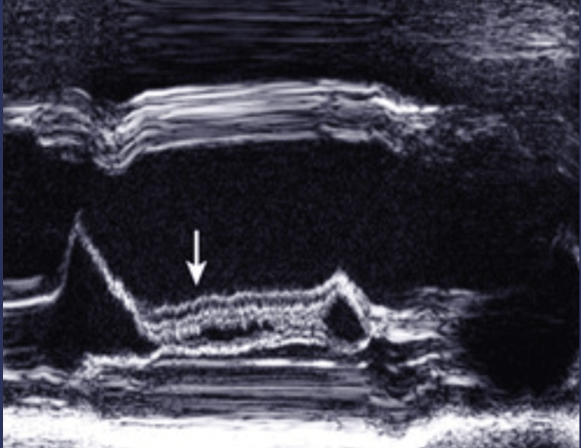
What is anterior mitral valve leaflet diastolic fluttering?
The valve action that begins and ends isovolumetric contraction.
What is mitral valve closure and aortic valve opening?