What is Symbiosis?
Relationships between organisms that live in the same area.
This type of Succession begins from bare rock.
Examples are: after a volcanic eruption or when a glacier retreats.
What is Primary Succession?
The trophic group that makes its own food and has the most biomass (the bottom of the energy pyramid).
What are producers? (Plants)
Animals that eat the producers and other creatures.
What are consumers?
This group is usually made up of bacteria.
What is a decomposer?
Give an example of a parasitic relationship.
Ticks, tapeworms, beetle on plants, etc.
Lichen and Moses arrive first.
What is a Primary Succession?
Creatures in higher trophic levels receive this amount of energy from the previous trophic level.
What is 10%?
Name both a Secondary and Tierary Consumer.
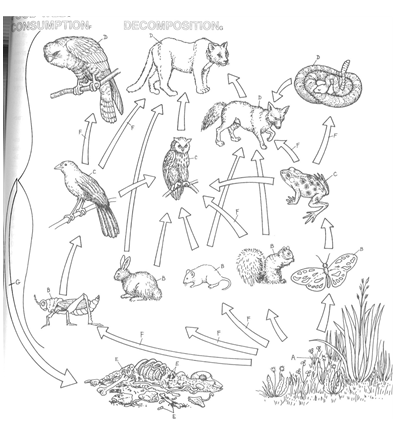
What are the Owl, Fox, and Couger
Unlike Energy in a food chain or food web Toxins do this as you move up the trophic levels.
What is increasing?
What is a mutualistic relationship?
When both organisms benefit from the relationship.
Because After a forest fire, avalanche, or hurricane existing soil and surviving seeds are already present.
Why is Secondary Succession faster than Primary Succession?
Plants.
What are Producers?
In a food web Energy is ______ as the trophic levels go up.
What is decreasing?
Given this example:
1PPM
1PPB
1PPT
The one with the highest toxin level
What is 1PPM? ( 1 part per million)
Barnacles living on the sides of whales an example.
What is commensalism
Which type of Succession results in a Climax Community?
What are Primary and Secondary Succession?
The amount, %, of energy lost to the environment in the form of heat.
What is 90%?
In this example, the Snake is:
Grass =>Lady bug => Bluejay => Snake => Hawk
What is the Tierary Consumer?
This group receives the least energy in the energy pyramid.
What is the Top predator? (Can be Tierary or Quaternary).
Ants and Aphids are one example.
What is Mutualism?
A corn field left fallow.
What is secondary succession?
This group performs Nitrogen Fixation (return nutrients to the soil).
What are decomposers?
The types of consumers.
What are omnivores, carnivores, herbivores, and decomposers?
The name for the increase in toxins in a Food Web.
What is Biomagnification?