What is the difference between a biotic and abiotic factor?
Abiotic = nonliving
Biotic = is or was alive
Define ecology.
The study of how living things interact with each other and their environment
Who have the most energy in the energy pyramid?
Producers
What is the difference between a food chain and a food web?
A food web is a mixture of multiple food chains.
There are three major types of symbiotic relationships, what are they?
Mutualism, Commensalism, and Parasitism
Define symbiosis.
A relationship between organisms in which at least one benefits.
Define autotroph.
An organism that can produce its own food
What is the Rule of 10?
Each trophic level only absorbs 10% of the energy from the level below.
What do the arrows in a food chain/web represent?
The flow of energy.
The picture demonstrates a symbiotic relationship. Which one is present and why?
Commensalism, the crane is using the hippo for a lookout but the hippo is not affected.
What is a limiting nutrient?
A nutrient that will limit the growth of a population.
Define niche.
The role, or way of life of a species within its environment.
If producers have 10,000 units of energy, how much energy will secondary consumers have?
10,000/10 = 1,000 units of energy (primary consumers)
1,000/10 = 100 units of energy (secondary consumers)
Name an example of a tertiary consumer.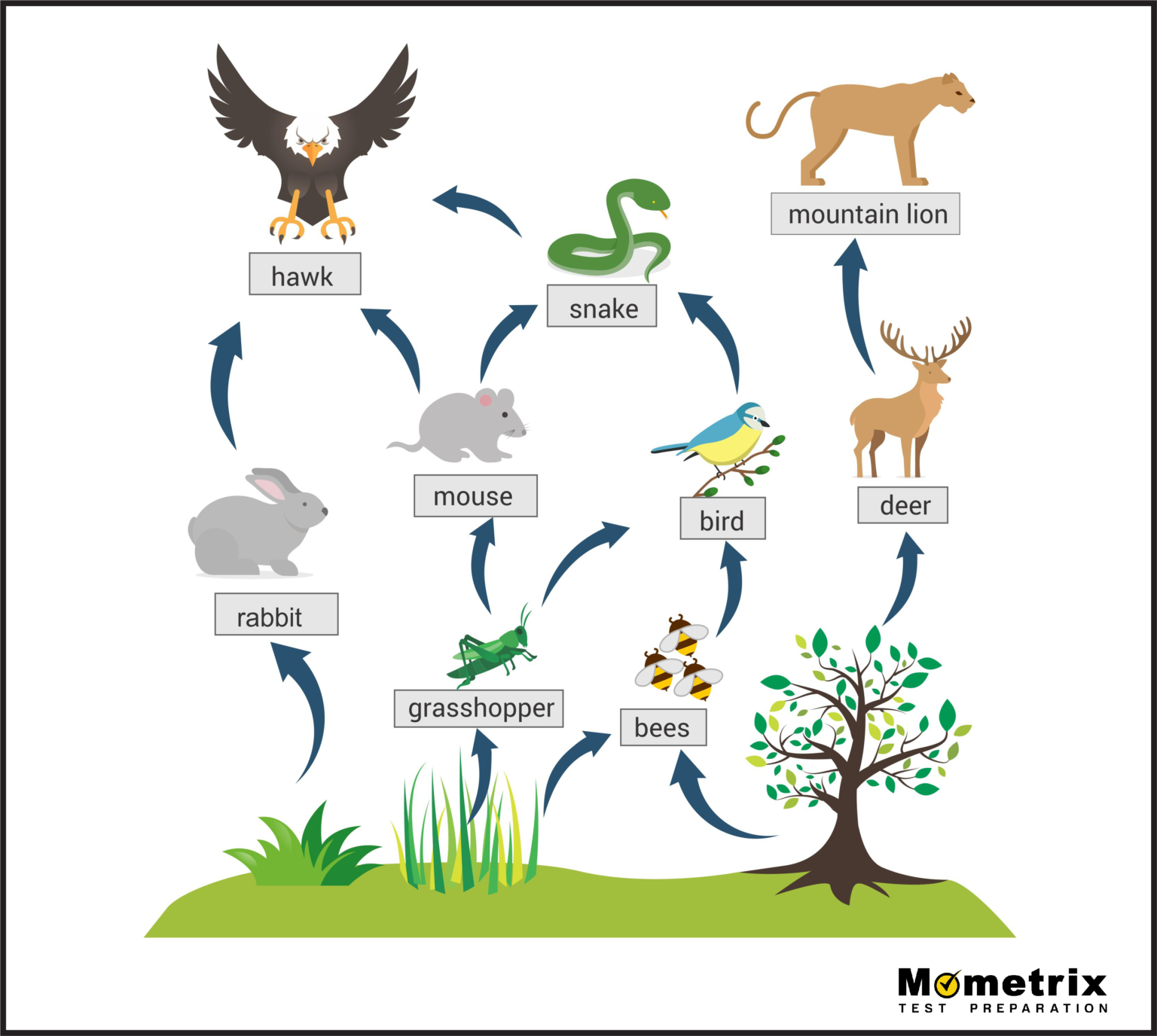
Snake or hawk.
The picture below demonstrates a symbiotic relationship. Explain how this is mutualism.
The anemone provides the clownfish with protection and shelter, while the clownfish provides the anemone nutrients in the form of waste while also scaring off potential predator fish.
What is biodiversity?
The various types of life or species in an environment.
Define commensalism.
Only one species benefits without harming or benefitting the other.
Which trophic level (number) does a tertiary consumer exist at?
4th Level
Producer -> Primary Consumer -> Secondary Consumer -> Tertiary Consumer
DAILY DOUBLE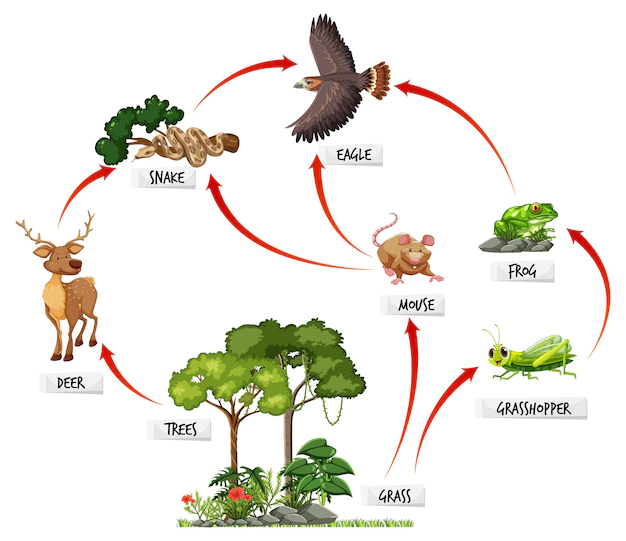 If the mouse population in this food web were to be removed, how would the grass, snake, deer, frog, and eagle populations be affected?
If the mouse population in this food web were to be removed, how would the grass, snake, deer, frog, and eagle populations be affected?
Grass = increase
Snake = decrease
Eagle = decrease
Frog = increase
Deer = increase
What relationship is presented here? What are the roles of each organism?
Predation
Cheetah = Predator
Antelope = Prey
Give an example of a niche. Explain
Hawk and owl. Owls hunt during the night, hawks hunt during the day. If two species occupy the same niche they would constantly be in competition.
Define cellular respiration.
The process of breaking down food to yield energy.
Why do the organisms at the top of the energy pyramid often need to eat several different types of organisms (EX. Bears eat salmon, deer, fruits, nuts, and honey)
Since bears are at the top of the pyramid, they can absorb a very small amount of energy. They must expand their eating options to obtain enough energy to survive.
What type of consumer is often left out of food chains and webs but connects all organisms?
Decomposers
A bee stings a fox for disturbing the hive as the fox looks for food. The bee dies after losing its stinger. Is this a symbiotic relationship and why? If so, which one?
This is not a symbiotic relationship. The fox is stung (harmed) and the bee dies (harmed). Since no organism is benefitted, this cannot be a symbiotic relationship.