the variety of life in the ecosystem or population
An organism that has a key role in maintaining the biodiversity of an ecosystem.
What is a keystone species?
Nonnative species introduced into an area, which usually upsets the balance of the ecosystem
What is an invasive species?
this cycle includes evaporation, condensation & transpiration
What is the hydrologic cycle?
This term describes a nonliving thing
What is abiotic?
The amount of energy conserved from one trophic level to the next
What is 10%?
This trophic level contains the most energy and biomass in the energy pyramid.
What is primary producers?
This process describes the formation of a community starting from bare rock
What is primary succession?
This process removes carbon from the atmosphere
What is photosynthesis?
This is said to flow through an ecosystem
What is energy?
Step in a food chain or food web
What is a trophic level?
In a food web, the lizard (a primary consumer) receives 3,000 kJ of energy. How much energy must the tertiary consumer receive?
30 kJ
The restoration of an ecological community after a disturbance, such as a wildfire, has cleared out all living things.
What is secondary succession?
this cycle is the only one without an atmospheric component
What is the phosphorous cycle?
This type of reproduction is best suited for quickly changing environments
What is sexual reproduction?
Largest number of individuals of a population that a given environment can support
What is carrying capacity?
According to this food web, this organism is an autotroph.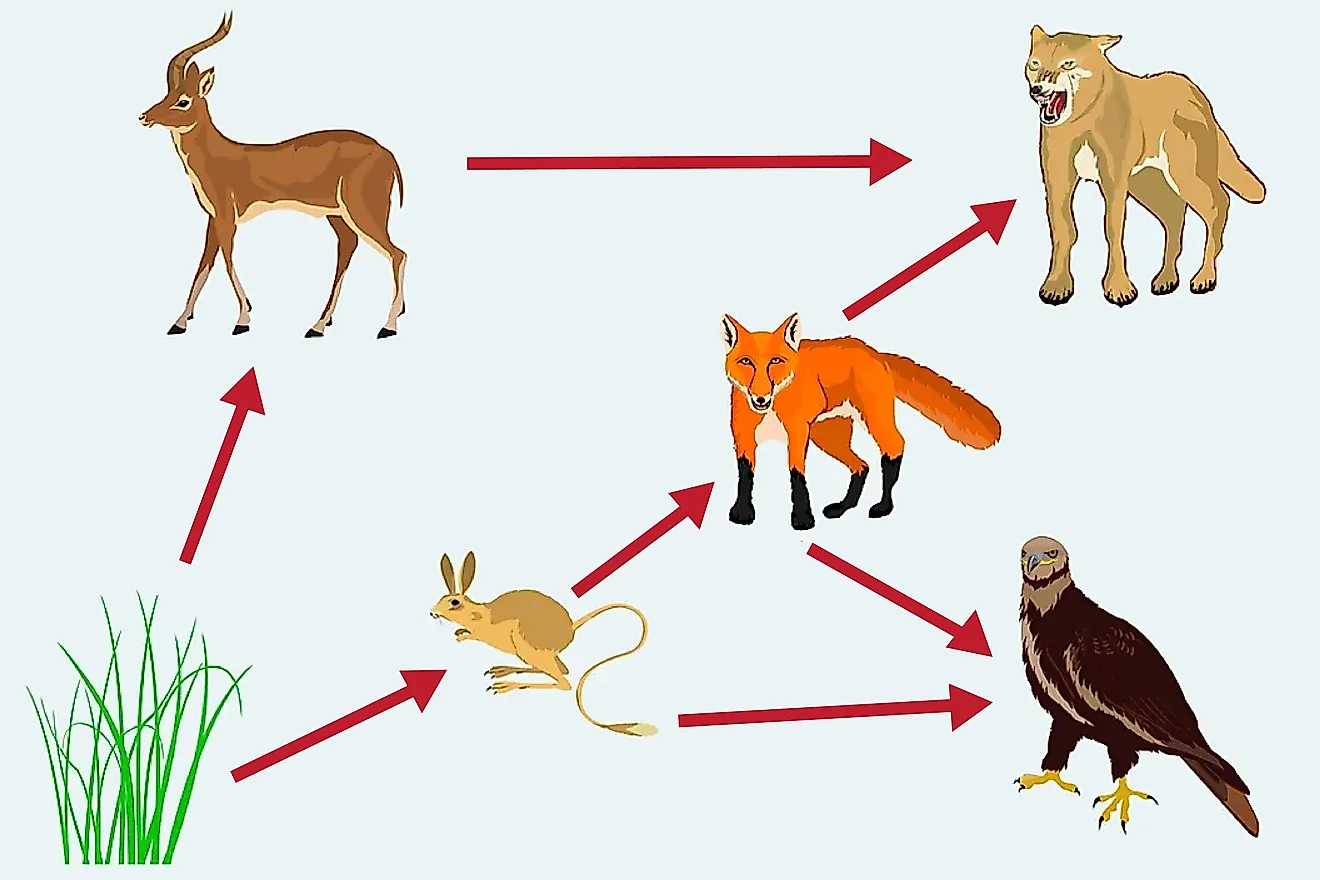
What is grass?
What is bioaccumulation (or biomagnification)?
This cycle is mostly found in the atmosphere
What is the nitrogen cycle?
These organisms are said to transfer energy, in the form of minerals & nutrients, back to producers in the soil.
What are decomposers?
A series of changes in the population sizes at different trophic levels, occurring when predators at high trophic levels are added to or removed from the system
What is trophic cascade?
According to the food web below, this organism is ONLY a secondary consumer.
What is the fox?
Process where fertilizers containing N and P have over enriched a body of water, leading to a lack of oxygen and harming those living within the water
What is eutrophication?
This process involves the conversion of nitrogen gas to the usable form, nitrate, using bacteria in soil
What is nitrogen-fixation (or nitrification)?
Examples include competition for resources & predation, both of which are factors that determine the carrying capacity.
What are density-dependent limiting factors?