Give a specific example of a population.
Examples may include:
A pack of dogs;
A gaggle of geese;
A flock of sheep;
A herd of horses
Define autotroph and heterotroph.
An autotroph is an organism that produces its own food (usually from sunlight).
A heterotroph is an organism that relies on other organisms for food (it must physically ingest food).
Name the dispersion pattern
Random Dispersion
The living portion of the water cycle in which water is returned to the atmosphere from plants.
What is transpiration.
A specific role that a species plays within an ecosystem, including how they affect other organisms.
What is a NICHE
This term is used to describe all of the populations within an ecosystem.
What is a community
What is the category of organisms known for breaking down dead plant and animal matter?
Decomposers
Give an example of what would happen when a population exceeds their carrying capacity.
Possible responses:
Ecosystem would degrade, less resources, more competition, etc...
Due to the burning of fossil fuels, this gas is released into the atmosphere.
carbon dioxide (CO2)
A symbiotic relationship in which one species is helped, and the other species is neither helped nor harmed.
What is commensalism.
The biosphere is defined as this.
The portion of the Earth that can sustain life.
Come up with a food chain that consists of four trophic levels.
Then, describe each level, beginning with “producer”.
Producer
Primary consumer
Secondary consumer
Tertiary Consumer
What type of growth does the graph display & what is the carrying capacity?

The type of growth is Logistic Growth
The carrying capacity is about 2000
Name one way that carbon returns to the water or air in the carbon cycle.
Possible ways carbon enters the air or water: respiration, combustion, erosion
A species that has been introduced to a new ecosystem, most likely by humans, and can cause disruption in the ecological balance.
What is an invasive species
Define Ecosystem
An ecological system consisting of the community (biotic) & physical (abiotic) factors.
Define AND describe an energy pyramid. (What percent of energy gets passed from one level to the next?)
An energy pyramid is a pyramid that reflects the amount of energy in the trophic levels.
It depicts the “10 percent law”, which states that 10% of energy from one trophic level is passed on to the next.
What is the difference between population size and population density.
Population size is the number of individuals in the population.
Population density in the number of individuals within a given area.
Name one way that carbon enters living things in the carbon cycle,
Possible ways carbon enters living things: photosynthesis, decomposition (you could even say eating).
The symbiotic relationship shared among bees and flowers.
What is Mututalism
Name and describe one process that forms ecosystems. (often happens after natural disasters)
Primary Succession - happens on rocks
(first growth)
-or-
Secondary Succession - happens on soil
What is biomass and at which trophic level would you find the most biomass
...and...
Why?!?!
Biomass is the dry weight of organic matter (living tissue) in an ecosystem.
Most of the biomass is found within the 1st trophic level (the producers), because you need a lot of them to feed higher level carnivores!
If an area suffers from deforestation, name one thing that can cause a species to go extinct?
Possible Answers
competition between consumers, lack of resources, lack of habitat, etc...
Fill in the blank
When the rabbit population increases, the wolf population ___________________.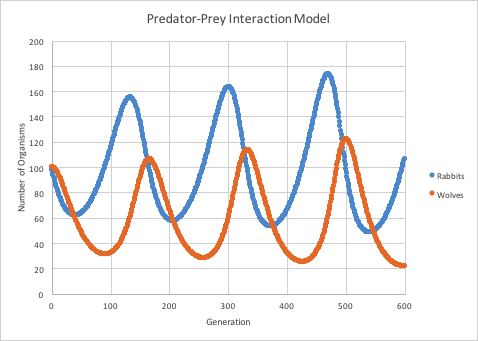
increases
What symbiotic relationship occurs when two different organisms are fighting for the same resources (space/food)?
What is competition