An environment that provides the things an organism needs to live, grow, and reproduce.
Habitat
These organisms produce energy through the use of photosynthesis.
Plants or Autotrophs
A group of land ecosystems with similar climates and organisms.
What is a biome?
The definition of biodiversity is _____________________.
What is the variety of different organisms living in a certain area?
Pioneer Species
The community of organisms that live in a particular area, along with their nonliving surroundings. This includes abiotic and biotic factors.
Ecosystem
These organisms are herbivores, therefore they are called ______________ consumers.
Primary consumers
What is one of the three types of biodiversity?
Genetic Diversity. Species Diversity and Ecosystem Diversity.
During primary succession, what process takes the longest that is also the reason secondary succession is much faster?
The creation of soil
A relationship between two species in which one species benefits and the other is neither helped nor harmed.
Commensalism
These organisms are typically at the top of the food chain. They are called ________ ___________.
Apex Predators
What locations on Earth has the greatest AND least amount of species diversity?
Greatest - Tropical Rainforest
Least - Artic
Give an example of an event that would cause secondary succession to occur.
Wild fire, flood, landslide.
An organism that breaks down wastes and dead organisms.
Decomposer
This is a way to show how energy in a food web is allocated. Usually there is a large base and a pointed top.
What is an energy pyramid?
Give one benefit of Biodiversity.
Boost ecosystem productivity
Larger amount of plant species means a greater amount of crops.
Healthy ecosystems can better withstand and recover from a variety of disasters.
Greater species diversity ensures nature sustainability for all organisms.
The final stage of both primary and secondary succession results in this...
Climax Community
A series of events in which one organism eats another and obtains energy. Usually written on one line.
Food chain
Give two effects the removal of the frog from this food web would have on other organisms.
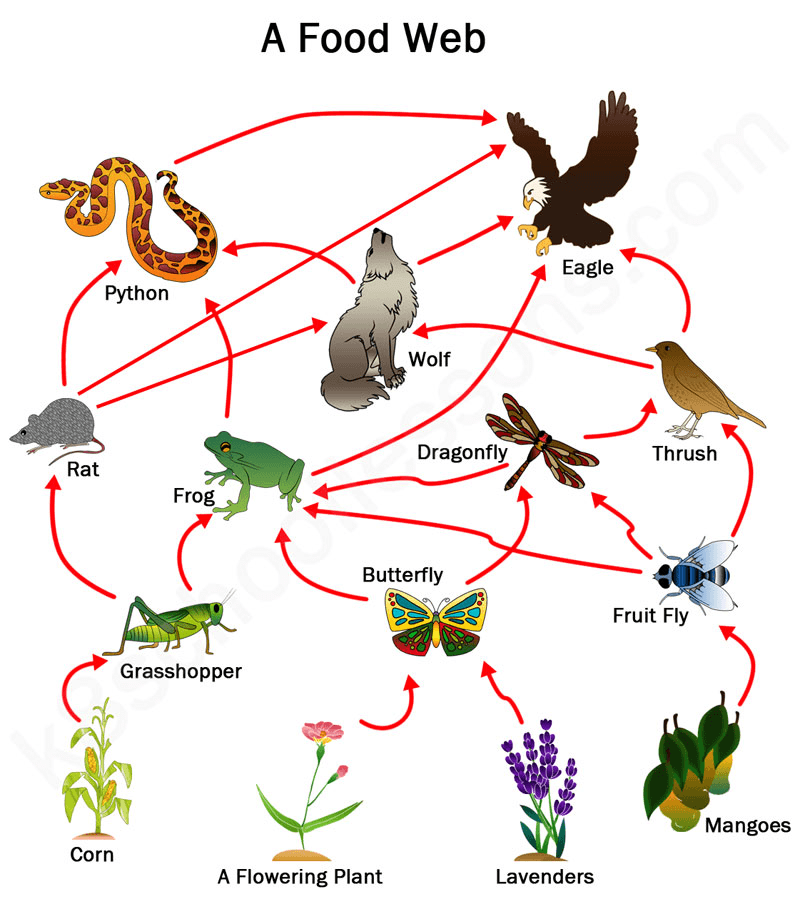
Ex. Less food for the python and eagle. Dragonfly, butterfly, fruit fly and grasshopper populations would increase.
List 3 of the 6 major biomes according to our notes.
What are the rain forest, desert, grassland, deciduous forest, Taiga (coniferous forest), Ocean, Tundra and Artic?
List 3 Services a healthy ecosystem can provide.
Protection of water resources
Soil formation and protection
Nutrient Storage and Recycling
Pollution breakdown and absorption
Contribute to climate stability
Maintenance of Ecosystems
Recovery from unpredictable events.
A group of organisms that are physically similar and can mate with each other and produce offspring that can also mate and reproduce.
What is a species?
Give an example of three different types of pioneer species.
Lichen, Moss, Fungai.