Abiotic Vs. Biotic
Abiotic: Non-Living (Ex: Rock)
Biotic: Living (Ex: Algae)
Competition
-,-
Two organisms fight for the same resource, Both lose energy in exchange
Ex: Two seals fighting for food
Marine Ecosystems
The largest of earth's aquatic ecosystems, mix of fresh and saltwater environments
Endangered vs. Endemic vs. Invasive vs. Threatened
Endangered: Species at risk of extinction
Endemic: When a species is native to that specific ecosystem
Invasive: A species that somehow arrived in an ecosystem in which they are not native to.
Threatened: A species that is likely to become endangered
Biomes Defined
A group of terrestrial ecosystems with similar climate and organisms
Ecology Definition
The study of the interactions between species and their environment
Predation/Herbivory
+,-
When an organism eats another organism
Ex: Panda eating bamboo, Wolf eating rabbit
Rocky Intertidal Zone
Bonus: Mention Common species
Exists anywhere the ocean meets the land
Limpets, barnacles, hermit crabs, mussels, anemones, kelp, etc live here.
Trophic Structure (primary producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, apex predators)
Primary Producers: Species that get energy from the sun, and make food by photosynthesis (Ex: Lettuce, Onion)
Primary Consumers: Consume(eat primary producers) Herbivores (Ex: Cows, Horses)
Secondary Consumers: Consume(eat primary consumers), carnivores(Ex: House Cat, House Dog)
Apex Predator: Consume(eat secondary consumers), Tertiary consumers(Ex: Humans, Tigers)
Climate Vs. Precipitation Vs. Temperature
Climate: The long term pattern of weather in an area
Precipitation: water released from clouds in the form of rain, freezing rain, sleet, snow, or hail
Temperature: Measure of hotness or coldness measured in Fahrenheit and Celsius
*Temp + Prec determine type of animal that will grow there, which determines types of animals that survive there
CA Native Plants make up the base of the ___________ or land-based food chain
terrestrial
Parasitism
+,-
When an organism feeds off another organism and slowly consumes it or transfers disease
Ex: Ticks
Kelp Forests
Bonus: Mention Common Species
The species acts like trees in a redwood environment, but underwater, mostly found in cold water.
Sea Otters, Sea Star, Kelp, Sea Urchins, Sea Lions, Horn Shark, Many common fish
Population Vs. Community Vs. Ecosystem
Pop: A group of the same species in the same place at the same time (Ex: School of fish in a kelp forest)
Com: A group of variety of species that work together
Eco: An environment in which living things work together and live with abiotic things in the ecosystem.
All the Biomes + Ex: Species
1. Tropical Rainforests; Hummingbird
2. Savannas; Elephants
3. Subtropical deserts; Saguaro Cactus
4. Chaparral; Quails
5. Temperate grasslands; Bison
6. Temperate forests; Deer
7. Boreal forests; Grizzly Bear
8. Arctic tundra; Arctic Fox
ocean-based species make up the base of the ______ or fresh/saltwater food chain
Marine
Commensalism
When an organism benefits, but the other is not harmed or hindered
Ex: Algae on tree
Chaparral Biome
Thicket of shrubs and trees that have adapted to dry summers and moist winters, land biome.
Study this image
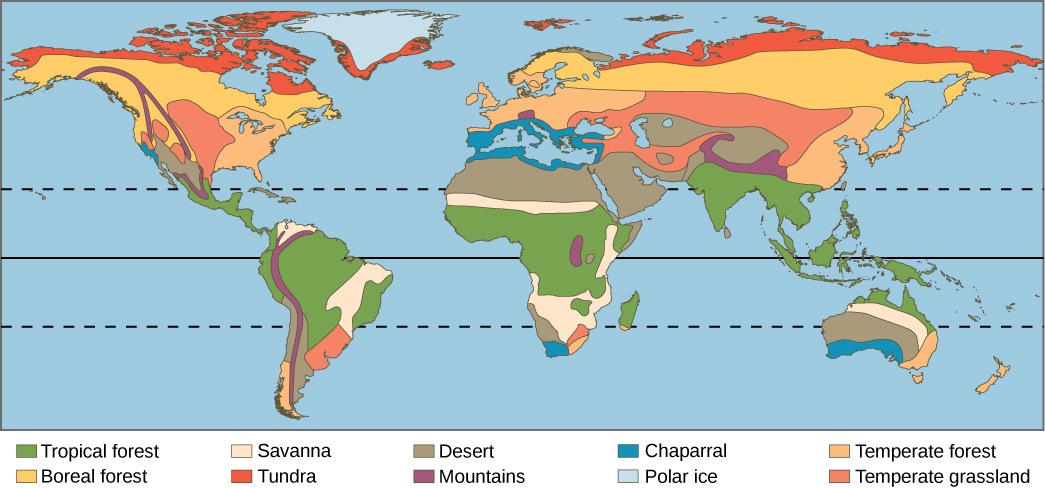
Biomes Warmest To Coolest
Forests: Tropical Rainforest, Temperate Rainforest, Deciduous Forest, Boreal forest
Non Forests: Deserts, Savannas, Chapparal, Temperate Grasslands, Tundra
Mutualism
+,+
Both organisms benefit; each provides something to help the relationship
Ex: Pollination
Symbiosis
Two organisms simply live together, can be any type of relationship
Ex: kelp and sheepshead fish
Food Chain Vs. Food Web
FC: Outlines who eats whom
FW: Includes all the food chains in the ecosystem
Temperate Vs. Tropical
Temp: Having Moderate Temperatures
Tropical: Extreme climate, warm and humid
Locations Of Biomes
Tropical Rainforests: 0 degrees latitude (Equator)
Deserts: 23 Degrees latitude north and south
All Forests: 30-60 Degrees Latitude north and south(Temperate Zone)
Tundra: Located 60+ degrees Latitude(Right Above Boreal Forest