In this type of relationship, both species involved benefit from the interaction, such as bees pollinating flowers while receiving nectar.
Mutualism
This term refers to an animal that is hunted and killed by another for food.
Prey
In this simple pond diagram, the arrows represent the flow of this, which always moves from the eaten to the eater.
energy
Because they occupy the very base of the pyramid and convert solar energy into chemical energy, plants are known by this functional name.
primary producers
This most basic level of ecological organization refers to a single living individual, such as one African Elephant.
Organism
This term describes a relationship where one organism lives on or inside a host, deriving nutrients at the host's expense.
Parasitism
In the "Green World Hypothesis," this is the reason the Earth remains green despite the presence of hungry herbivores.
higher level predators keeping herbivore populations in check
While a food chain shows a single path, this more complex diagram shows the many interconnected paths animals take to find food.
This rule of thumb states that only about this percentage of energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next.
10% rule
An ecosystem includes all the living organisms in an area as well as these non-living, physical components like sunlight and soil.
abiotic factors
Often found on cattle, these birds eat insects stirred up by the herd; since the birds get a meal and the cattle are unaffected this becomes what type of relationship
Commensalism
In a standard predator-prey line graph showing population sizes over time, why does the predator peak usually occur slightly after the prey peak?
Predators require time to convert consumed energy into reproductive success and new offspring.
In a marine food chain, the tiny phytoplankton at the very bottom are categorized by this term because they create their own food.
producer
This "predatory" species has a disproportionately large effect on its ecosystem; removing it causes the entire community structure to collapse.
keystone species
This level consists of a group of individuals of the same species living in the same area and interbreeding.
population
Neighboring plants are killed by ants, helping the Acacia tree and ants but harming the neighbor. What type of relationship exists between the tree and ants?
mutualism
In the Lotka-Volterra model, if the prey population (N) is very low, what is the most immediate predicted effect on the predator population (P)?
.png)
The predator population will decrease due to a high starvation rate.
This type of organism, often shown at the side or end of a food web, is responsible for recycling nutrients back into the soil.
decomposer
Imagine a graph showing three lines: Grass, Grasshoppers (prey), and Birds (predators). If the Birds are suddenly removed, what is the most likely 'Trophic Cascade' effect on the Grass?
The Grass population will decrease because the Grasshopper population will explode.
While a community only includes living things, this next level up includes both the biotic community and the abiotic environment.
Ecosystem
In the relationship between the Hawkmoth and the Madagascar Star Orchid, the moth's tongue is the exact length needed to reach nectar at the bottom of the flower's long spur. This is an example of which evolutionary process driven by symbiosis?
coevolution
A 'Type II' functional response graph shows that the number of prey consumed by a predator eventually levels off even as prey density continues to rise. What is the biological reason for this plateau?
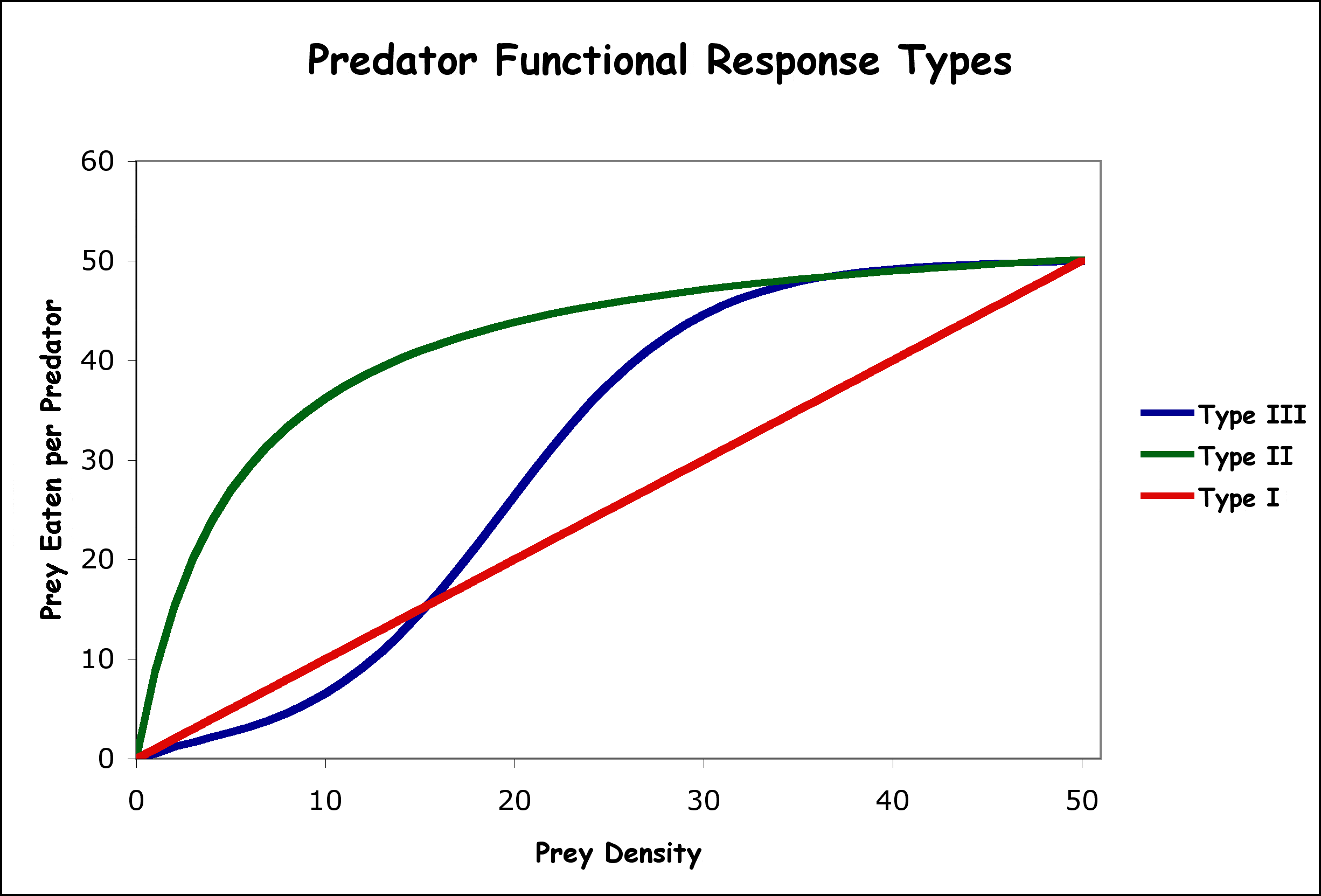
Handling time (the time it takes to kill and eat) limits the total number of prey a predator can process.
Make a food chain from this food web that makes the red tail hawk a tertiary consumer

brittlebrush-pallid winged grasshopper-collard lizard- hawk
The reintroduction of these predators to Yellowstone National Park in 1995 triggered a famous cascade that actually changed the path of the rivers.
wolves (apex predators)
This is the broadest level of all, encompassing every part of Earth where life exists, from the deepest ocean trenches to the atmosphere
Biosphere